Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > Mouse PCBs: A Comprehensive Guide
The mouse PCB is known popularly as the foundation of every computing mouse! It houses the basic components that enable clicks, tracking, and wireless connection. When customizing a PCB, knowing the essentials of mouse circuit boards is vital. This guide will help you understand everything about circuit board design, types, and considerations.
A primary application is seen around the gaming community, where players use high-performance mice with PCBs built to ensure smooth and precise function.
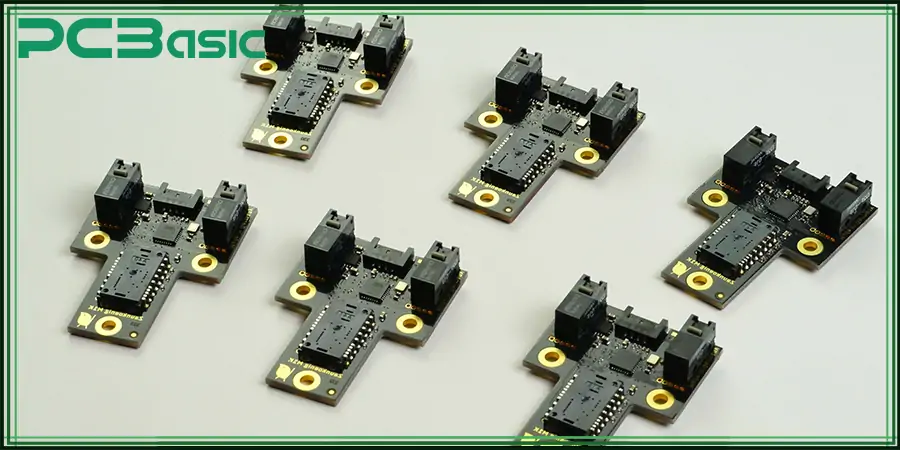
By now, you’re probably wondering what a PCB is. A PCB is an electronic structure that holds the parts of a computer mouse. Think of this as the foundation on which the mouse is built. It usually contains all the vital elements needed to accept and process user input and translate hand gestures into digital movement or signals in your computer.
For clarity, the mouse depends on the PCB to communicate with the computer concerning basic functions like tracking, clicking, and motion. Most computer mouse PCBs are created with top-tier engineering to ensure they stand the test of time.
The functionality of a mouse PCB depends on the key components that contribute to the overall performance. The components of a computer mouse PCB include:
1. Wireless Module
This component utilizes a wireless function that enables Radio Frequency processing (RF) and Bluetooth connectivity. It fosters easy communication and navigation on the computer without the help of multiple wires.
2. Battery Unit
Wireless mouse PCBs feature a power unit for extended standby and use time.
3. Microcontroller
This acts as a sensor to track the movement, translating it to a digital signal in the computer. The microcontroller also provides precision for every click, acting as the processing unit where all commands are executed.
4. Optical/Laser Sensor
The optical sensor is the part of the mouse PCB that is responsible for making tactile feedback possible. The optical sensor makes use of LED light to ensure every movement is tracked and there is responsiveness during gameplay or casual use.
5. Switches/Buttons
This component is responsible for right and left clicks, scrolling, and added input that can be programmed. Flagship mice, for example, use lasting Omron switches to ensure durability in gaming mouse PCBs.
6. Mouse Bites
Mouse bites in PCB are tiny perforations in the circuit. These perforations make the separation of panels easy and neatly organized.
7. LED Lighting
RGB and LED lighting are components of mouse PCBs that enhance the aesthetic appeal for users who love customization, especially gamers.
8. Scroll Wheel Encoder
Another important component of the mouse PCB is the scroll wheel encoder. This is responsible for converting scroll movements into electronic input.
Do you know what PCB your mouse is currently using? If you do, good luck. If you don’t, you’re about to find out. In this section, we will compare the various types of printed circuit boards and what makes them unique.
A wired mouse-printed circuit board is usually linked to the computer through a PS/2 or USB connection. This is because of the low latency that occurs while minimizing the delay in decoding input from the user. A major benefit of this printed circuit board is that it doesn’t require a replaceable or rechargeable battery, as the computer provides the power.
A wireless computer mouse PCB on the flip side comes with an RF or Bluetooth module in place of the USB or PS/2 interface. In this case, there is a cable-free interaction from the mouse to the computer. The advantage of the wireless printed circuit board is the provision for a greater range of motion and portability. Designers will have to consider battery life and latency when creating one.
When it comes to the office mouse circuit board, priority is placed on efficiency and reliability. They do not have as many buttons as the regular version, feature lower dots per inch (dpi), and have basic microcontrollers. These attributes contribute to the affordability of office mouse PCBs and how energy-efficient they are.
In contrast, the gaming mouse houses a circuit board built for the best possible performance. It has a higher DPI sensor, a few custom buttons, and onboard memory for better usage. These boards have a fast polling rate that takes care of lag and delivers quick responses while playing games.
Standard rigid mouse circuit boards are generally used because of their high quality and durability. They provide stable support for easy use and manufacturability.
Rigid-flex mouse PCB, on the other hand, comes with a more complex layout and ergonomic appearance. They are used in top-tier gaming environments where saving space is a top priority. The flexibility of rigid-flex circuit boards makes them flexible and easy for internal components to be integrated, improving the overall performance.
To get the best performance, the layout of the computer mouse PCB must be crafted in a way that positively influences the overall efficiency. By carefully positioning the signal traces and vital components of the mouse, designers can mitigate signal interference and other factors that are necessary for a smooth experience. As someone looking to design a custom mouse circuit board, here are the key factors to take into consideration:
● Placement of the Sensor
Whether you are using a laser or optical sensor, placing it wrongly will negatively impact the performance of the mouse. The sensor must be aligned at the bottom of the board to ensure movements are properly traced and communicated to the computer.
● Button Layout
You want to ensure that the circuit board aligns with the outer shell of the mouse. This makes it easier to engage with and convenient to use.
● Signal Integrity
As a wireless mouse designer, you should consider building PCBs to transmit and receive strong and weak signals. By properly routing high-speed signals, you can improve the mouse's performance and reduce interference.
● Durability and Reliability
All components of the board should be soldered securely, and traces should be reinforced to take on heavy or repeated clicks and movements.
● Power Efficiency
When designing a wireless mouse circuit board, power management is important to ensure there is extended battery life. This can also be achieved by using low-power microcontrollers.
● PCB panelization Mouse Bites
Mouse bites in PCB play a crucial role in the design of a mouse circuit board. They make it possible to take the board apart, especially during mass production. This approach reduces waste and makes sure that there are smoother edges on the panels.
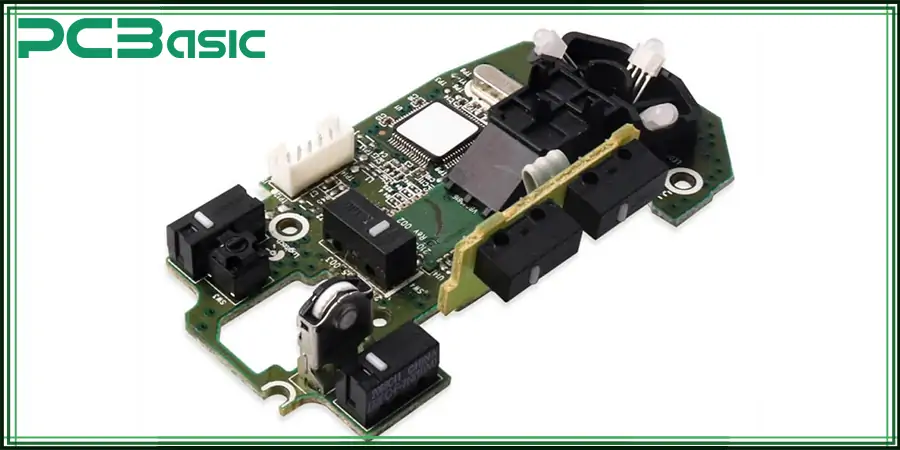
Now that all careful considerations have been noted, it is time to go through the actual manufacturing process of a typical mouse circuit board. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the process involved in manufacturing a printed circuit board:
Trained engineers design a blueprint for the board using industry-standard PCB software. This is to ensure that the layout is ideal for smooth functioning.
Copper is etched in layers to form a circuit. Traces and vias are used as connecting components in this circuit system.
The components are attached to the board using through-hole or Surface-Mount Technology (SMT).
Each unit of the mouse circuit board is subjected to rigorous testing to ensure it is durable, responsive, and has good signal integrity.
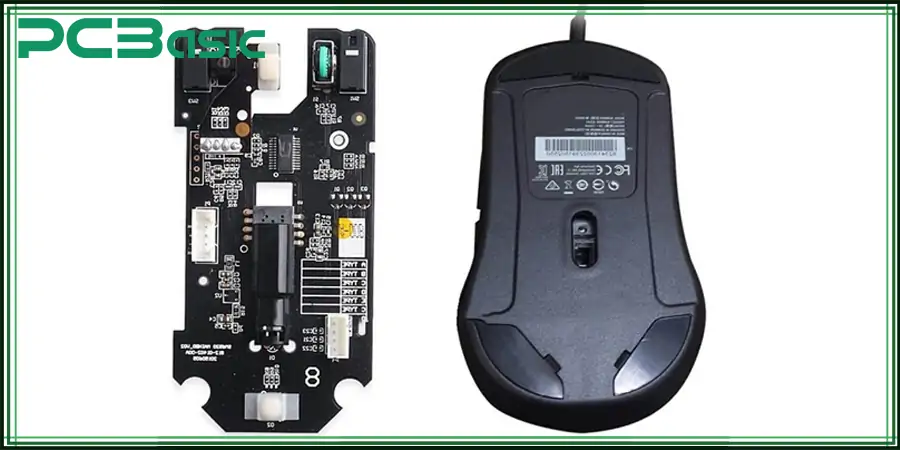

Mouse circuit boards are essential in different applications, such as:
● Personal and Office Use
Standard PCBs are used in day-to-day office work as well as in home environments. These variants are mostly designed for casual users who only want the basic mouse functions to execute simple tasks.
● Ergonomic & Specialty Mice
Professionals who are designers, animators, or experts in CAD modeling will always require an ergonomic mouse with rigid-flex printed circuit boards for comfort over prolonged usage.
● Industrial & Medical Devices
Some industries make use of special mouse circuit boards for accurate motion tracking and control. In the medical field, for example, special PCBs are incorporated into the navigation system of surgical tools to get a precise tracking of the movement.
● Gaming Peripherals
Gaming mouse PCBs support a high DPI sensor, enhanced processing units, and custom buttons to enable precise movement and swift response during competitive gaming. They are also applied in high-precision machines like robotic controls.
The printed circuit board is the heart of any computer mouse as it determines the quality of connectivity, function, and performance. Whether you are designing a gaming mouse PCB, an office variant, or a wireless mouse PCB, knowing the components and manufacturing process that go underway is crucial. As more innovative technologies are introduced, circuit board designs will continue to improve user experience and ensure speed, accuracy, and more custom options for various applications.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
