Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > Overview of a GPU PCB
The GPU PCB or Graphics Card PCB, play a vital role in modern computing and high-performance graphics processing. It is not just a substrate that carries components, but a complex platform that determines power efficiency, thermal performance, and overall graphics computing power.
In this blog post, we explore a few questions about GPU PCBs:
Structure of a GPU PCB
Components on the GPU PCB
Difference Between a GPU PCB and a Graphics Card
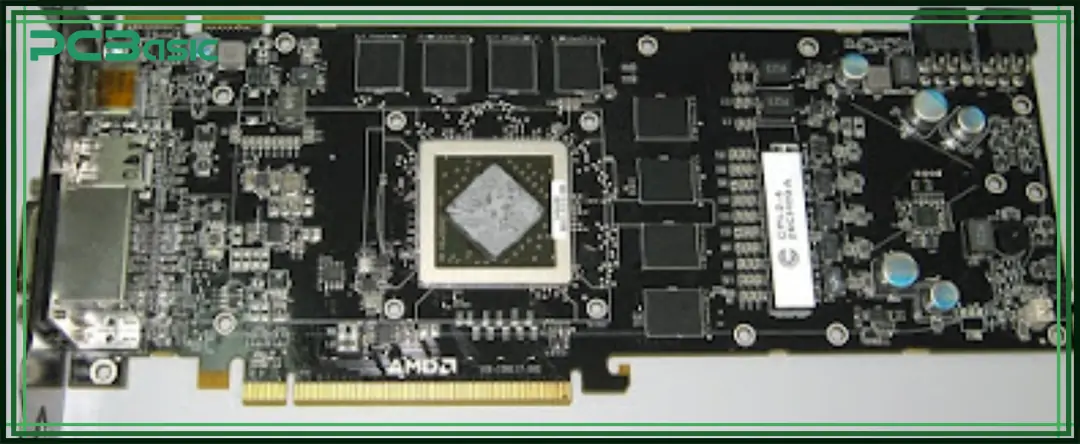

A GPU PCB, whose full name is Graphics Processing Unit Printed Circuit Board, refers to the internal PCB of the graphics card. It's commonly referred to as the graphics card PCB or GPU PCB.
It acts like a foundation that holds and connects all the electronic components on the graphics card.
You can think of it as a bridge between the brain and the skeleton of the GPU. All the important components - such as the GPU core, memory, power modules, fan connectors, and video ports - are mounted on this board.
 About PCBasic
About PCBasic
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
If we want to understand how a graphics card works, we must first understand the circuit board it uses - that is, the GPU PCB. The board is filled with various key components that work together to allow the graphics card to process images at high speeds and stably. The following is a brief introduction to the main parts of the graphics card PCB:
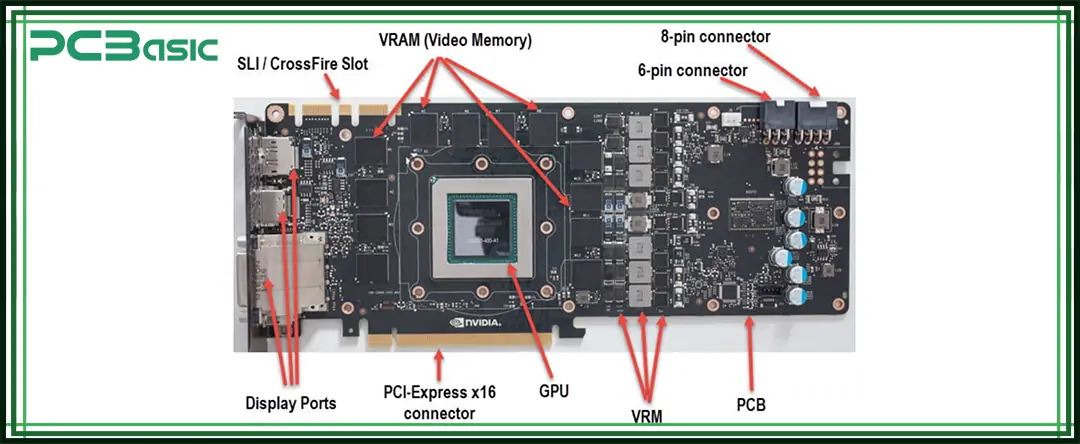
• GPU Chip: The brain of the graphics card
It is the core part of the entire graphics card, which is specifically responsible for image processing, such as game screen, high-definition video and picture processing. It runs at very high speeds and generates a lot of heat, so it needs a good cooling system to stay cool.
• VRAM (Video RAM): The temporary memory of the GPU
VRAM acts as the GPU’s “temporary storage,” It is used to store image data, such as texture and picture information. The larger and faster the VRAM, the better the graphics card can handle high-resolution images or large-scale games.
• Voltage Regulators (VRMs): The power middleman
The VRM adjusts the voltage from the power supply to levels that the GPU and VRAM can safely use. A well-designed VRM helps the graphics card stay stable under heavy workloads and prevents power-related issues.
• Power Connectors: Supplying energy to the GPU
High-performance graphics cards consume a lot of power, and the motherboard alone can’t supply enough. That’s why additional power connectors (like 6-pin or 8-pin plugs) are needed to connect the GPU to the power supply and ensure it gets enough energy.
• Capacitors and Inductors: The stabilizers and filters
Capacitors temporarily store electricity and help smooth out voltage changes, while inductors filter out electrical noise. Together, they reduce electromagnetic interference and make power delivery more stable.
• PCIe Interface: The link between GPU and motherboard
This is the connector that plugs the graphics card into the motherboard. It allows the GPU to receive data from the CPU and memory. Most modern GPUs use the high-speed PCIe x16 interface.
• Cooling Interfaces: Parking spots for cooling devices
Since GPUs generate a lot of heat, the PCB has designated spots for installing cooling systems like fans, heat sinks, or liquid cooling. A well-designed cooling setup keeps the GPU running efficiently over long periods.
In short, a well-designed GPU circuit board needs to be precise in layout, carefully soldered, and reliable in power and heat management. Only then can the graphics card perform at its best while staying safe and stable.
A GPU PCB is usually not only one layer, but is composed of multiple layers of circuit boards stacked on top of each other. This multilayer structure is like a layered cake. Each layer has its own function, cooperating with each other, so that the graphics card can run stably and efficiently.
Depending on the performance and complexity of the graphics card, the number of GPU PCB layers is generally between 6 and 12 layers, and some high-end graphics cards are even more. The following is an explanation of the role of each major layer:
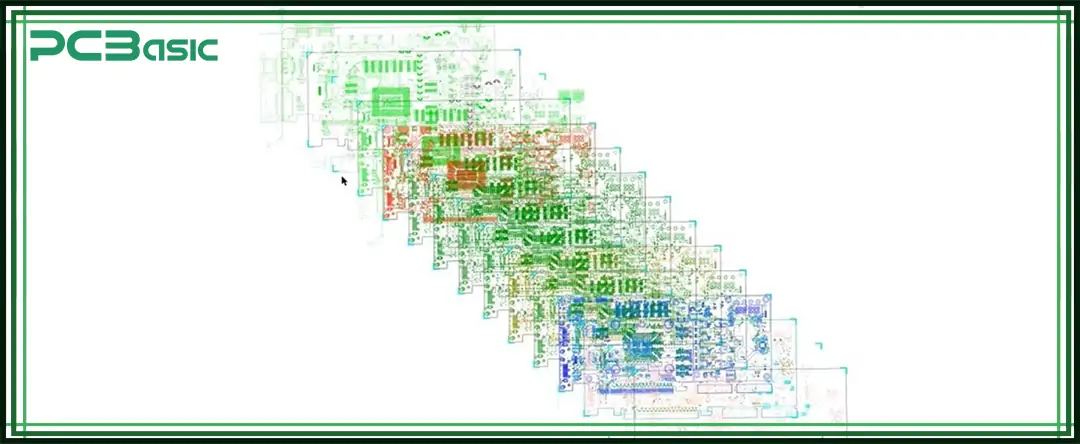
● Top Layer
This is the top layer, which is used to install the GPU chip, memory modules (VRAM), capacitors, inductors, and other key components. It's the side we can actually see.
● Power Layer
This layer is mainly used to distribute power, supplying voltage to various places on the board that need power, such as the GPU core, VRAM, cooling fans, and more. It can ensure voltage stability and prevent voltage fluctuations from affecting the operation of the graphics card.
● Ground Layer
As the name suggests, this layer is connected to the ground. It does two things:
1. Reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) so that signal transmission is cleaner.
2. Improve signal integrity to prevent high-speed signal errors.
This layer is very important and is the basis of high-speed circuit design.
● Signal Layer
This layer is responsible for transferring data, such as data exchange between the GPU and VRAM, or data transfer between the GPU and the motherboard through the PCIe interface. Because the data transmission speed is very fast, the wiring should be especially careful, and it should avoid interference and delays.
● Internal Routing Layers
These layers are mainly used to optimize the routing layout. The components on the graphics card are dense, and the surface wiring is not enough. Therefore, it is necessary to arrange the power lines, signal traces, and other connections through the internal layer to ensure that each signal can smoothly "go" to the location.
Designing a GPU PCB is a very complex work, involving managing power, heat dissipation, structural strength and many other aspects. Designers need to pay special attention to the following key points in the design process:
1. Power Distribution
High-performance graphics cards require a lot of power support, and the design must ensure that the circuit board can withstand high current, otherwise it is prone to voltage instability or overheating, affecting performance and even causing board burning.
2. Signal Integrity
The data transmission speed between the GPU, VRAM and motherboard is very fast. If the wiring design is not reasonable, there will be signal interference, data loss and other problems. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately control the circuit impedance and wiring mode, so that the data transmission is fast and stable.
3. Thermal Management
The graphics card emits a lot of heat when it is running. If the heat is not dissipated, the graphics card will soon slow down or even crash. Therefore, the PCB needs features like thermal vias, large copper areas, and reserved spots for fans or liquid cooling to help remove heat effectively.
4. Component Placement
Components such as power supply modules should be placed as close as possible to the GPU chip, which can reduce power loss and electromagnetic interference. VRAM is usually lined up around the GPU to shorten the distance between data so as to improve efficiency.
5. Mechanical Stability
The graphics card is generally equipped with a heavy radiator. If the PCB itself is not strong enough, it is easy to bend and damage because of long-term stress. Especially when used in high-end gaming computers or workstations, the strength requirements for the board are higher.
GPU PCBs are often confused with graphics cards. They are two different level concepts, although they are closely related, but not equivalent.
Quick Comparison Table:
|
Item |
GPU PCB |
Graphics Card |
|
What it is |
The circuit board where the GPU chip is mounted |
A complete graphics card that can be installed into a computer |
|
Includes |
GPU chip, power circuits, signal traces, etc. |
GPU PCB + heatsink + VRAM + output ports + casing |
|
Usable on its own? |
No – it’s just the board |
Yes – plug and play |
|
Use case |
For chip-level design and manufacturing |
For end-user installation and use |
|
Example |
A bare board in the factory with components mounted |
The RTX 4060 graphics card you buy and install in your PC |
GPU PCBs are the foundational components of modern graphics cards, supporting performance output for high-end gaming, AI computing, and 3D rendering. From complex multilayer designs to critical signal, power and thermal management systems, GPU PCBs have become much more than a support board—they are the heart of visual computing.
Understanding the structure and functionality of Graphics card PCBs helps us understand why GPU PCBs are so powerful. If you're a hardware designer, gamer, or tech enthusiast, diving into the technical details of GPU PCBs will make you more aware of the charm of modern graphics technology.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
