Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > A Comprehensive Guide to PCBA: Its Meaning, Types, Process and Suppliers
A PCB assembly (also known as PCBA) is a productive part of modern electronics where an electronic component is placed on the printed circuit board (PCB) with each component performing its distinct function toward completion of a circuit. This week we will cover how guide layout, types of guide PCBA manufacturing, its definition, production procedure, and important suppliers.
As well as these steps, we also recommend the Chinese suppliers which deal with PCBA and help with the right components and effective procurements of the devices. This information is useful for all people interested, novices or experts in the electronics hobby.
PCBA is an acronym for Printed Circuit Board Assembly. It is the assembly of electronic components onto a printed circuit board (PCB) and also refers to the output of such assembly or the system produced by the assembly. In the following we will analyze PCBA from two perspectives – the process and the product.
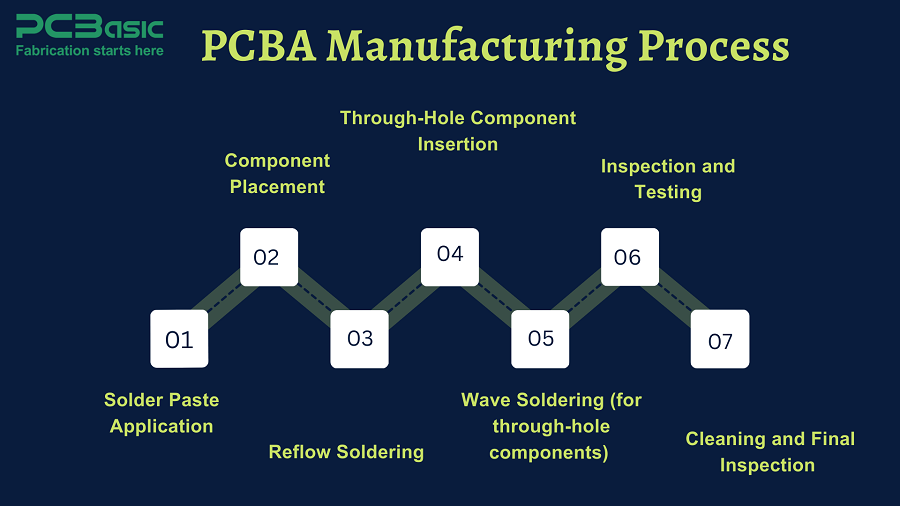
PCBA is a process that involves the assembly of an electronic circuit by mounting electronic components like resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits onto a bare PCB. The process comprises sequential operations which include several key processes, such as:
● Solder Paste Application
When applying solder paste, a fine layer of the mix is spread onto the solder pad for the PCB utilizing a stencil.
● Component Placement
Automated machines guarantee precision and speed in the mounting of surface mounted (SMT) and PCB components.
● Reflow Soldering
For SMT components, solder paste is melted using heat for devices’ safe connections.
● Through-Hole Component Insertion (if required)
Through-hole components are placed in the prepared slots of the PCBs. This is carried out either manually or with automatic insertion tools.
● Wave Soldering (for through-hole components)
In order to solidify through-hole components, the board is positioned above a solder wave that is heated to ensure these components are securely fixed.
● Inspection and Testing
Comprehensive quality control utilizes visual inspection, x-ray and functional testing to find defects and confirm the assembled PCBA meets the performance and reliability requirements.
● Cleaning and Final Inspection
All flowing and dirty materials are cleaned followed by a quality check to ensure the surface of the board is fully intact.
The verification of the circuit board at the PCBA stage guarantees that the board is functioning and ready to be used in an electronic appliance. This is an essential procedure in the assembly of electronics and must be performed with precision, control and oversight of quality, and compliance to standards of the industry.
Once the assembly is done and all required checks are done, PCBA serves as an electronic mounting structure ready to be integrated into various devices like computers, medical equipment, automobiles, electronics, and industrial machinery. A PCBA is currently fully assembled and has all the components soldered onto the board ready to be integrated into a larger systems or product plus other functionality features.
To put it succinctly, PCBA is both an assembly process of turning a Bare PCB into a complete circuit, as well as the end products that may be directly integrated in electronic devices.
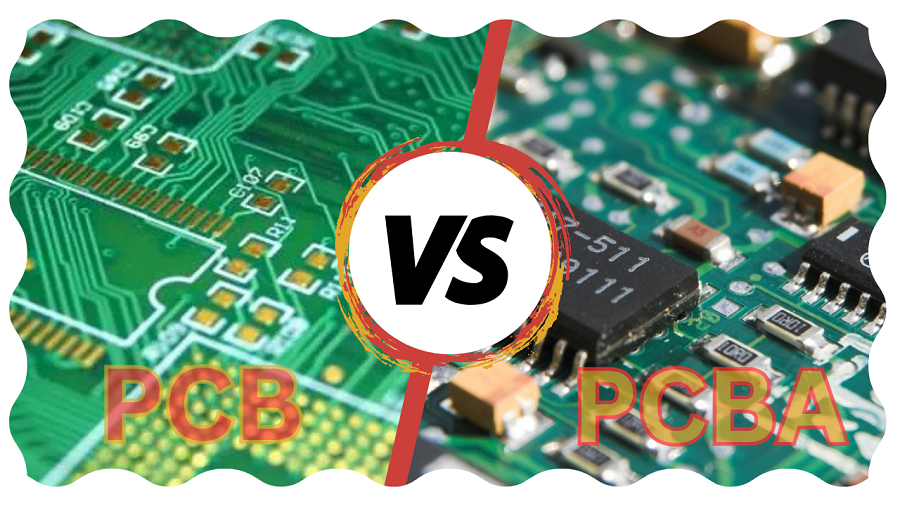
A printed circuit board (PCB) is a naked board with conductive routes that act as the basis for electronic circuits, while a printed circuit assembly (PCBA) is a fully mounted board that adds electronic components. PCBs are non-functional in themselves, while PCBA is ready for use in electronic devices. The table below reveals the significant difference between PCB and PCBA:
|
Aspect |
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) |
PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) |
|
Definition |
A bare board with copper traces but no electronic components. |
A fully assembled board with all necessary electronic components soldered. |
|
Components |
Only the board with conductive pathways, pads, and substrate material. |
Includes resistors, capacitors, ICs, connectors, and other electronic components. |
|
Manufacturing Stage |
An intermediate product used in electronics manufacturing. |
The final assembled version ready for integration into electronic devices. |
|
Functionality |
Non-functional on its own; serves as a foundation for circuits. |
Fully functional and capable of powering electronic devices. |
|
Production Process |
PCB fabrication involves etching, layering, and drilling. |
PCBA includes component placement, soldering, and quality testing. |
The printed circuit card mounting (PCBA) can be classified based on layers, materials, production methods and applications, and performs specific features in each electronics. From unilateral to multipurpose PCBA and Flex to stiff designs, the alternative depends on the complexity and requirements of the device. In addition, different mounting techniques such as SMT, continuous holes, and mixed PCBA performance and durability are affected.
There are many types of PCB mounting that meet the level of different requirements, budgets and complexity.
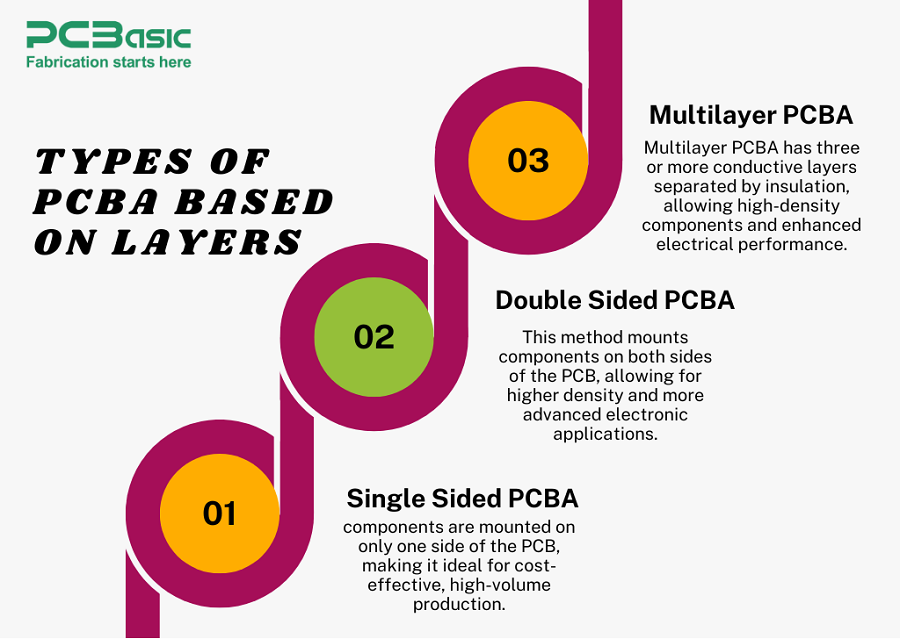
1. Single-Sided PCB Assembly:
In this type, components are placed only on one side of the PCB. Due to its simplicity, one-sided mounting is low cost, ideal for high quality production.
2. Double-Sided PCB Assembly:
This includes increasing components on both sides of the PCB. The two-sided unit is more complex than unilateral mounting and is suitable for high density and more advanced electronic devices.
3. Multilayer PCBA
Multilayer PCBA consists of three or more leading layers, separated by insulating materials, which enables high density component positions and improves electrical performance.
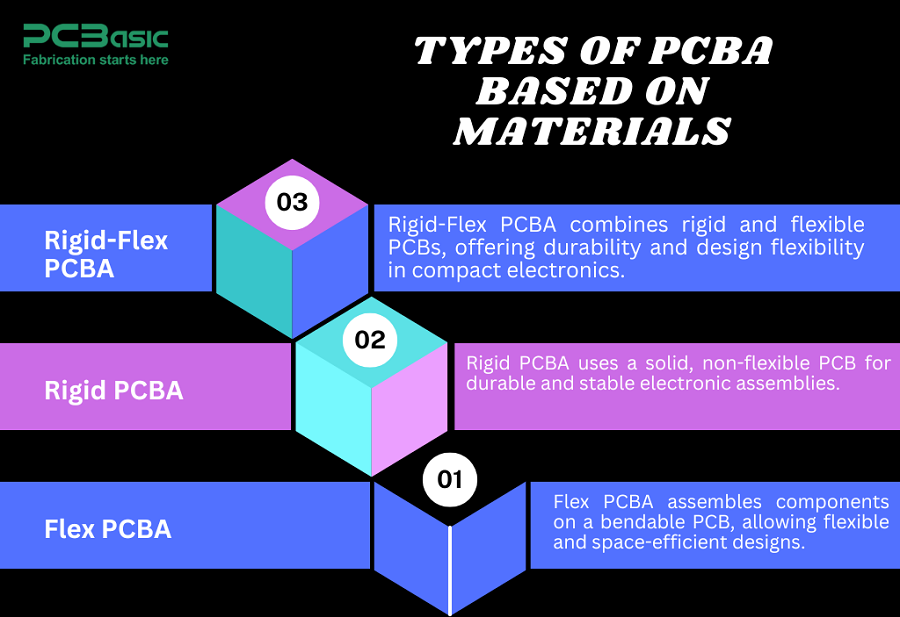
1. Flex PCBA
Flex PCBA is made of flexible substrates such as polyamide, so it can bend without breaking. It is light and used in wear, medical equipment, and folding electronics.
2. Rigid PCBA
Rigid PCBA has a solid FR4 substrate, offering durability and stability. It is common in computers, automotive systems, and industrial electronics.
3. Rigid-Flex PCBA
Rigid-Flex PCBA combines rigid and flexible sections, enabling compact designs without connectors. It is used in aerospace, military, medical, and advanced consumer electronics.
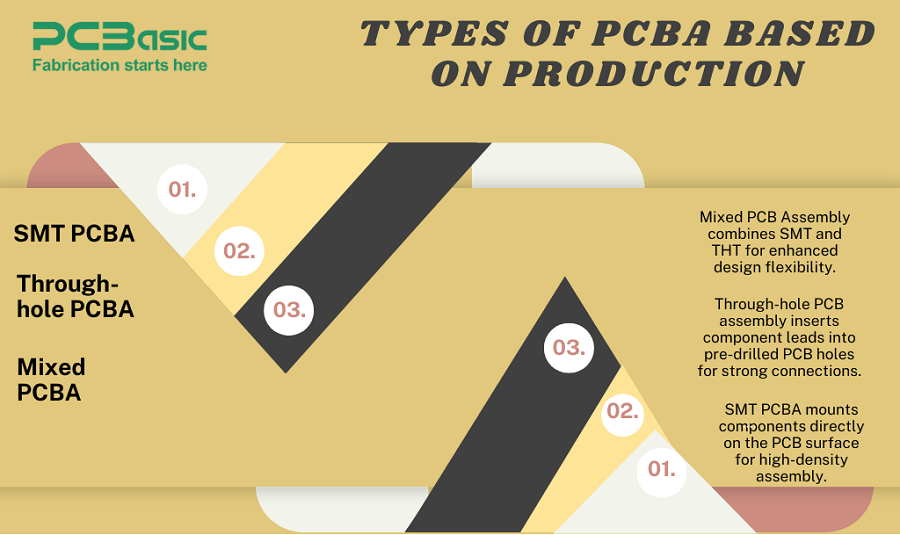
1. SMT PCBA
SMT is today’s most used mounting technology. This includes the growing components directly on the surface of the PCB eliminating the requirement for the hole. SMT has many advantages including, but not limited to low size, weight and complication, high density of components, and better performance at high frequencies.
2. Through-hole PCB Assembly
This method of assembly uses holes in a PCB to insert components and then stitches them in reverse direction. Through collection offers strong mechanical connections and good electrical conduction, which is perfectly designed for heavy components or equipment subjected to mechanical forces.
3. Mixed PCB Assembly
This style incorporates both through hole and SMT techniques to meet the design specification of the electronic unit. Mixed assembly is used when both methods are required to meet a specific performance and design scope.
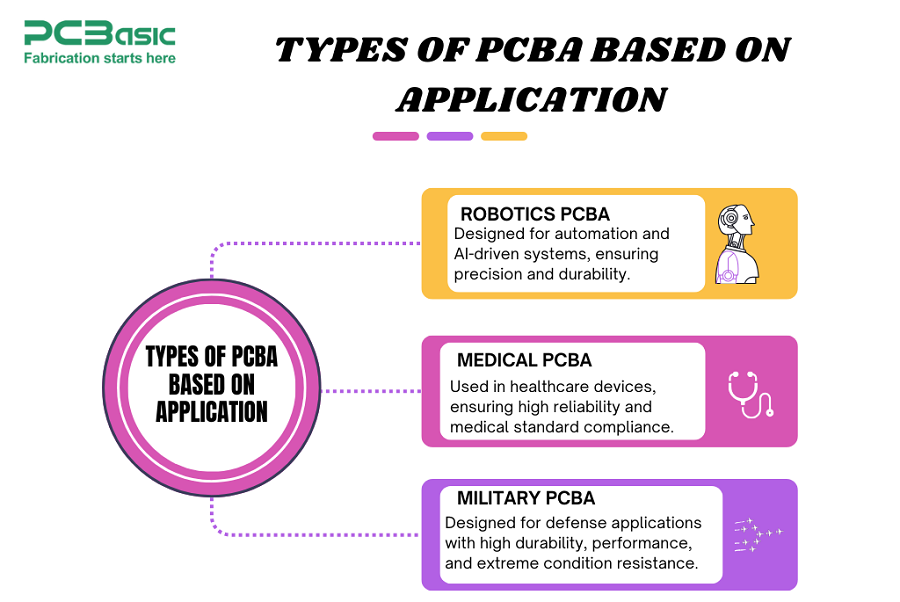
1. Robotics PCBA
Created for the automation and AI systems which has great precision and ensures stability.
2. Medical PCBA
Applied in healthcare models where there is a greater need for accuracy and compliances to medical devices.
3. Military PCBA
Focused around defense systems so the design is rude, has high performance, and can endure harsh environmental conditions.
The table below provides a detailed classification of PCBA types.
|
Category |
Type |
Description |
|
From Layers |
Single-Sided |
A PCB with components and circuits on only one side. |
|
|
Double-Sided |
A PCB with conductive layers and components on both sides. |
|
|
Multilayer |
A PCB with three or more conductive layers, used for complex circuits. |
|
From Materials |
Flex |
A flexible PCB that can bend, ideal for compact devices. |
|
|
Rigid |
A solid, inflexible PCB used in most standard applications. |
|
|
Rigid-Flex |
A combination of rigid and flexible sections for advanced designs. |
|
From Production |
SMT PCBA |
Uses Surface Mount Technology (SMT) for component placement. |
|
|
Through-Hole PCBA |
Components are inserted into drilled holes and soldered for strong connections. |
|
|
Mixed PCBA |
A combination of SMT and through-hole assembly techniques. |
|
From Application |
Robotics PCBA |
Designed for automation, AI, and robotic systems. |
|
|
Medical PCBA |
Used in medical devices, ensuring precision and reliability. |
|
|
Military PCBA |
Built to withstand extreme conditions for defense applications. |
The PCB device for printed circuit board (PCB) is defined as the cultivation of electronic components on a printed circuit board to get a functional circuit. Several stages in this process will ensure that the reliability and functionality of electronic devices are completed. Let's check important procedures:
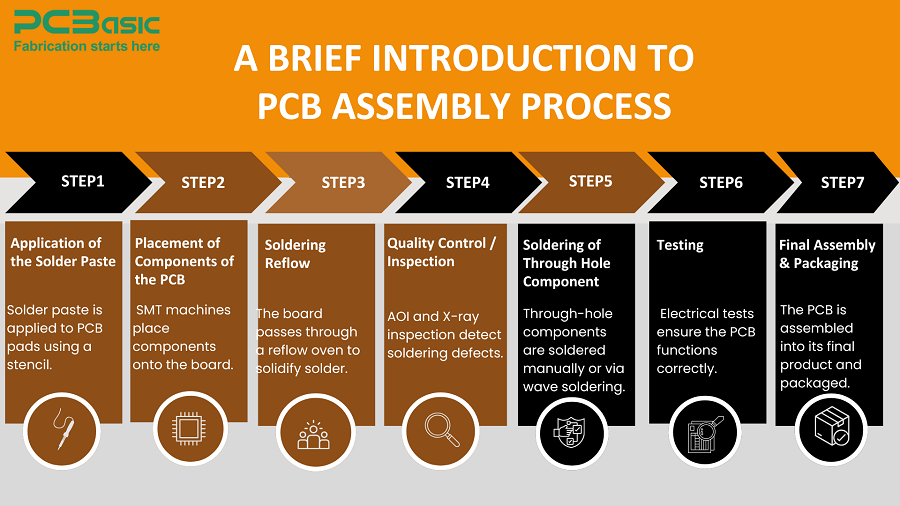
1. Application of the Solder Paste
A stencil is used to apply solder paste to the predefined places on the PCB, where components will be put into position. This paste contains solder particles with flux that are meant to bond effectively.
2. Placement of Components of the PCB
Boards of resistors, capacitors, and ICs are attached to the solder-pasted boards by Surface Mount Technology (SMT) machines. This operation is automated for maximum efficiency.
3. Soldering Reflow
In this step, the PCB is put in a reflow oven. Because the soldering paste's melting temperature is lower than the soldering temperature, the components are melted into place at the PCB. The solder profile of the oven is designed in a way that the components are not damaged while reaching the required temperature.
4. Quality Control / Inspection
Post soldering, the board is used to check for any alignment, soldering mistakes, or missing parts, Automatic Optical Inspection (AOI), and X-ray inspection for more complicated boards are used.
5. Soldering of Through Hole Components (When required)
Through-hole components can be soldered using hand soldering, and wave soldering, wherein solder in a molten state is poured on the leads of the components.
6. Testing
During the testing stage, the employee identifies and corrects possible electrical issues with ICT and Functional Testing to ensure the board works properly before the last assembly stage.
7. Final Assembly & Packaging
After testing, the device is put within its final housing and packed for shipment or put into a greater device system. PCB assembly is a crucial step in electronics manufacturing, ensuring that components are correctly placed, soldered, and tested for quality and performance.
With a reputation for dependable and affordable mounting solutions, PCBasic is a prominent supplier of printed Circuit board assembly (PCBA). The company’s expertise revolves around offering large scale production prototypes. Their services include Surface Mount Technology (SMT), Through Hole (THA), and mixed technology PCBA.
PCBasic customers are from different high-end industries such as electronics, medical instruments, automobiles, and industrial automation provided high quality service with advanced quality assurance and fast response. His proficiency in custom PCB design, component sourcing, and comprehensive PCB test development has made him the best choice for many customers seeking cost effective and efficient PCBA Services.
The printed circuit board assembly (PCBA) is very important in the electronics field. It essentially turns printed circuit boards (PCBs) into a working unit. The concept of PCBA is important for both experts and hobbyists to understand the connectors that exist between stages and forms of PCB and PCBA. Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Through Hole Technology Assemble (THA) bear different benefits for different applications.
The guide distinguishes diversity of PCBA in relations to layers, materials, production techniques and their uses, as well as emphasizing the correct choice for a particular electronic device. Achieving the necessary standards of quality for electronics, medical devices, and automotive systems is a complex multi-step process known as assembly.
Speed and quality being paramount, it has never been easier to purchase reliable services from PCBA suppliers like PCBasic. With the right understanding of PCBA and electronic construction, designing a working prototype or preparing for mass production is child's play. This guide aims to tackle the hurdles presented by contemporary technology and streamline the process of PCBA.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
