Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > What are SMT Components - A Comprehensive Guide to SMT System
The electro components of SMT production focus on electronic Surface Mount Technology (SMT) elements and embrace a description of all system components within this approach. SMT components operate as an integrated system with production lines to create high-quality PCB processing methods. The research investigation focuses on electronic SMT components that are crucial elements for current circuit board assembly methods.
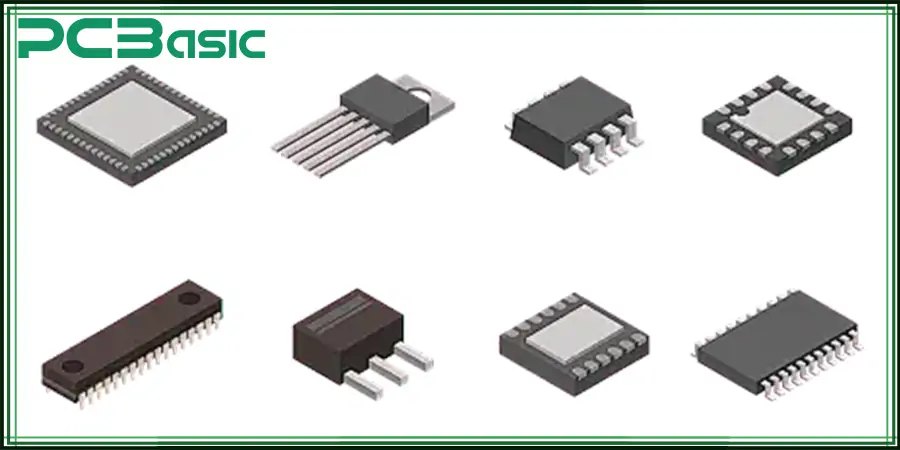
Are you looking for high-quality SMT components and assembly solutions? Explore PCBasic’s wide range of SMT products designed for precision and reliability.
What is smt meaning? The PCB assembling method named Surface Mount Technology (SMT) allows for electronic component attachment. The installation pattern of PCB components differs from through-hole technology because SMT components require direct surface placement instead of drilled holes.
The mounting method enables more compact device designs along with increased density of components and enhanced system performance.
An SMT system consists of:
1. SMT Components: PCBs use SMT Components as their electronic elements for placement.
2. SMT Production Line: The SMT Production Line contains all machines utilized for handling SMT components' placing and soldering functions along with effective inspection measures.
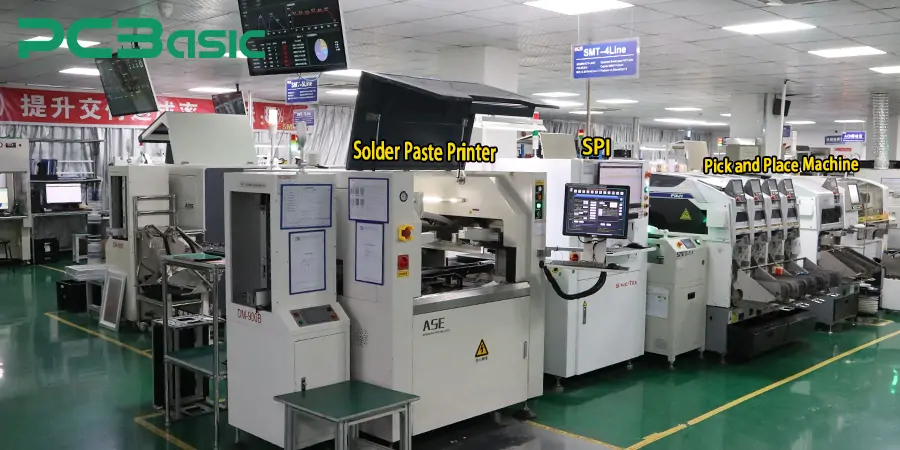

3. SMT Process: The surface mount soldering process includes ordered steps that guide electronic parts assembly.
These elements form a crucial part of the SMT assembly process because they enable better efficiency as well as product quality to deliver dependable electronics products.
SMT components represent the electronic parts which function as part of the SMT manufacturing procedure. The components function differently from conventional through-hole elements because their design omits the leads that go through PCB holes. The small solder able terminations of these components directly attach to the PCB surface.
The categories of SMT components include passive components together with active components as well as connectors and LEDs. The different components have essential functions during PCB construction and electronic device operation.
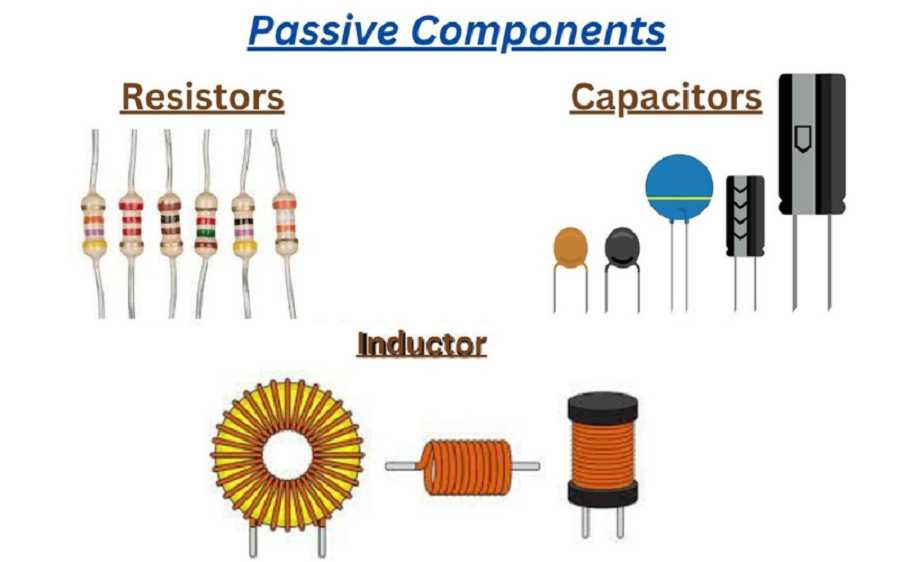
Electronic circuits needed passive components for signal transmission regulation as well as energy storage and filtering functions. These standalone components need no external power supply thus they work independently. The basic elements are key components for electrical circuit building because they stabilize the system while ensuring correct power management.
Resistors:
Resistors serve to regulate electrical current movement through devices where ohms (Ω) functions as their measurement type. The electronic circuit industry depends on capacitors to split voltages, adjust signaling voltage levels and keep electrical currents inside safe boundaries. Among the available components of this type there are fixed resistors and variable resistors or potentiometers as well as surface mount resistors.
Capacitors:
Electrical energy storage happens within capacitors that also enable voltage stabilization while filtering out noise in electronic circuits. Different components of power supply circuits as well as audio systems require the technology because it enables signal processing structures. Symmetrically between the capacitor groups stand ceramic devices with electrolytic and tantalum as well as film capacitors dedicated to execute specific tasks.
Inductors:
Electrical current running through an inductor generates storage of energy inside a magnetic field. Digital systems utilize inductors to achieve power regulation objectives and noise disturbance fighting functions and filter performance. Power supplies and radio-frequency circuits together with transformers make up the essential applications where these devices are commonly used.
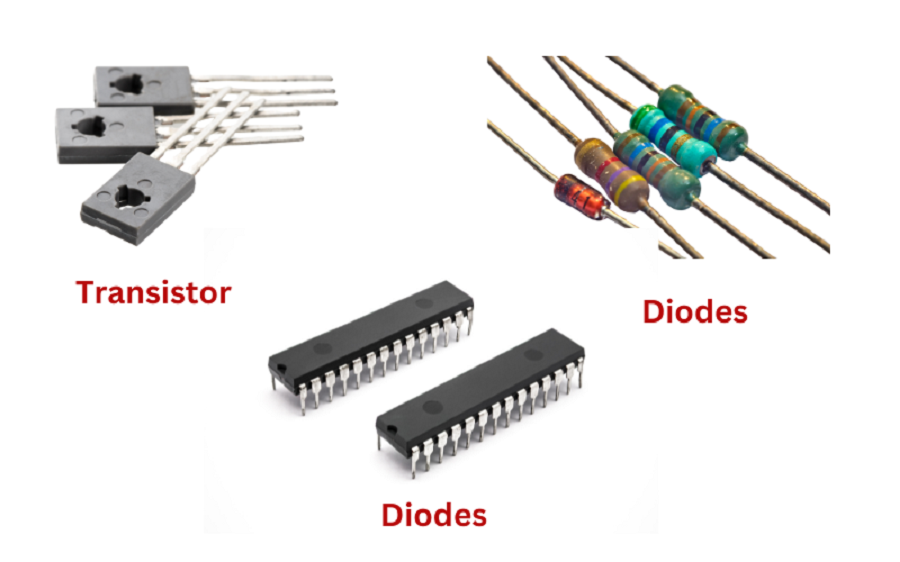
Active components must obtain external power sources because they establish the flow control of electricity through circuits. Active devices maintain vital functions because they enable both signal amplification and signal switching operations alongside processing signals.
Transistors:
Electronic switches and amplifiers are two functionalities transistors perform. Microprocessors as well as amplifiers and switching circuits use these component types for their operational functions. The basic transistor categories consist of Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs) together with Field-Effect Transistors (FETs).
Diodes:
The device allows forward current flux but blocks any reverse direction current flow. These devices serve dual purposes as rectifiers and function as voltage regulators and processing signals in both situations. There exist three main diode types including rectifier diodes together with Zener diodes as well as light-emitting diodes (LEDs).
Integrated Circuits (ICs):
The integration of electronical components such as transistors resistors and capacitors into one package makes use of integrated circuits. The combination of microcontrollers and processors and memory chips reduces electronic device size while optimizing performance output.
The establishment of electrical connections between PCBs or between PCBs and external devices happens through connectors. The three versions of connectors include board-to-board connector’s wire-to-board connectors along with flexible ribbon connectors. The quality of electronic signal transfer depends on high-quality connectors which also prevent electrical system breakdowns.
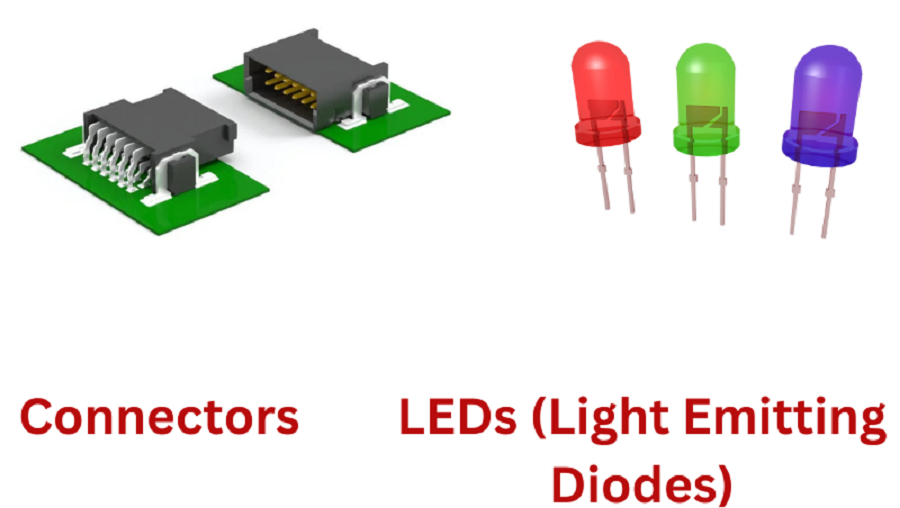
Transparent light emissions that stem from electricity processing occur in semiconductor devices named LEDs. Light Emissive Diodes (LEDs) work in conjunction with visual indicators and display systems and lighting controls for applications. The combination of energy-efficient operation and long runtime and adjustable color output makes these devices suitable for various electronic systems.
The automated SMT production line adopts sophisticated machines which properly place and solder electronic components. Efficiency and error rates decrease when an SMT line achieves proper optimization.
The Surface Mount Technology (SMT) production process depends on computer-controlled machines which guarantee precise results during PCB assembly operations. The SMT production machine chain executes solder paste application and SMT component placement and connection soldering and end-product inspection. The SMT line contains machines that build electronics with reduced human mistakes while boosting operational speed. The following article provides an exhaustive guide regarding fundamental SMT equipment utilized for modern-day PCB manufacturing operations.
The solder paste printer stands as the initial equipment used in SMT assembly line processes. The machine creates thin solder layer deposits on PCB pads by using either stencils or screens for printing.
Accurate paste application in this step becomes vital because irregularities in paste spread may result in connections between soldered points together with improper joint attachment and component position problems. Present-day solder paste printers operate with automated inspection and alignment capabilities which guarantee high precision levels.

The SMT component placement function holds complete jurisdiction over the operation of the pick and place machine. The machine chooses parts from reels and tubes as well as trays before accurately positioning them according to board programming coordinates.
These machines operate swiftly and finish fast placement operations of numerous thousand components within one hour through exact precision. Nowadays advanced versions of these systems conduct visual inspections to verify component alignment and position before the placement operation.
Through the reflow smt soldering machine the PCB receives heat that causes solder paste to melt while linking board components to the PCB. The temperature regulation profile in the reflow process allows the solder material to melt and achieve proper flow before it solidifies. The machine employs several heating programs which let the PCB experience slow temperature transitions while maintaining component integrity.
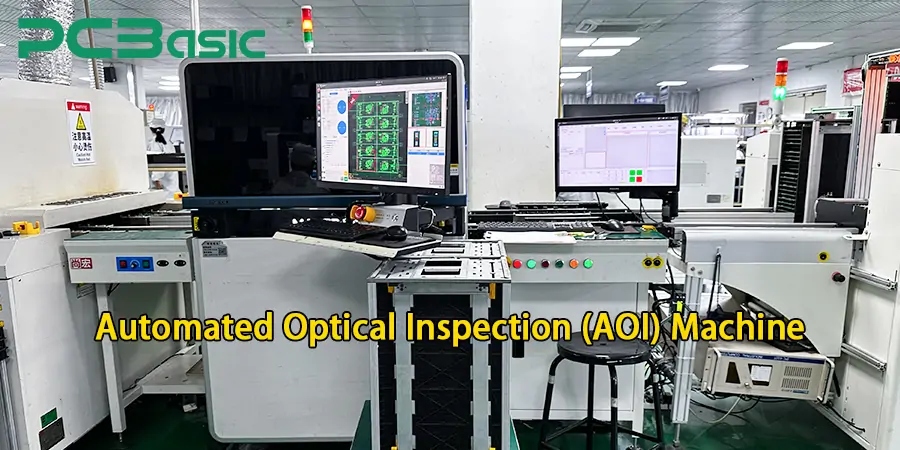
The AOI machine operates after soldering to perform automated component analysis and searches for placement errors and solder bridge faults and component absence problems. High-definition cameras perform a reference check on the PCB by comparing it with an acceptability standard. The system warns operators about potential issues so they can check or rectify the problems.
Sometime before starting mass production a first article tester examines the assembled PCB to assure design conformity alongside high quality standards. The examination process reveals problems at an early stage to protect massive production from expensive manufacturing mistakes.
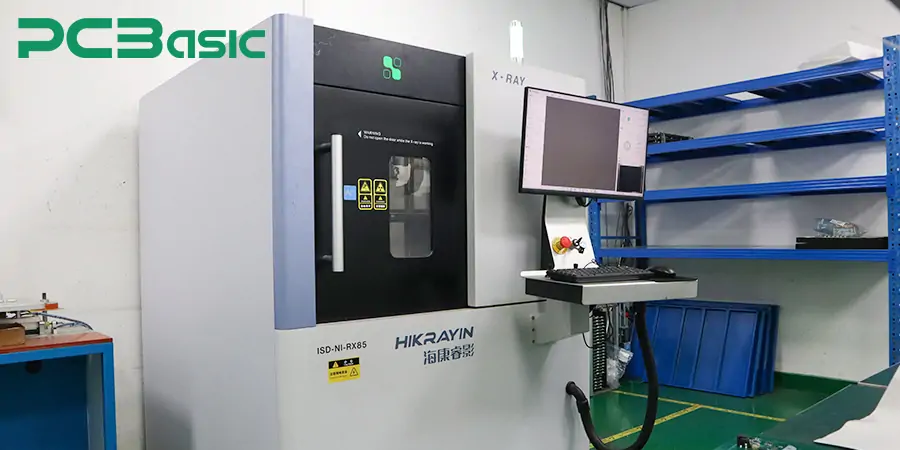
X-ray inspection plays an essential role in detecting hidden solder defects since it focuses on components including Ball Grid Arrays (BGAs) and other leadless packages. The lack of detectable defects beneath these components forces the use of X-ray machines for quality assurance inspections because traditional optical methods prove insufficient.
The PCBs are marked by the laser coding machine which embeds identification codes and serial numbers as well as barcodes for complete tracking purposes. The tracking facility enables manufacturers to monitor their product batches which permit quality control activities and helps stop counterfeit components from entering the supply chain.
A flying probe tester functions as an adaptable test apparatus which verifies circuit continuity and discovers short faults and solder defects by conducting point-by-point board probes. The flying probe tester functions as an ideal solution for prototype testing along with low-volume production because it can accommodate different PCB designs without needing custom-made testing fixtures.

The SMT equipment used together to assemble electronic parts with high efficiency to support modern electronics manufacturing functions.
An automated SMT PCB assembly process places and soldering SMT components correctly on printed circuit boards with precision accuracy. The pathway starts with PCB design then proceeds through stages such as final testing and repair which lead to the production of excellent electronic assemblies.
A designer needs specialized software Altium Designer Eagle or KiCad to design the PCB before assembly begins. Component positioning and soldering pads along with circuit connections exist within the layout.
The last design undergoes conversion to Gerber files to generate production information for creating stencils and machine programming. Correct PCB planning directs the manufacturing process toward smooth operation while lowering defect numbers and producing superior results in the SMT procedure.
The procurement assembly process begins by using solder paste consisting of small solder particles together with flux material. The simultaneous operation of a solder paste printer or simultaneous squeegee application directs the stainless steel stencil to distribute solder paste on printed circuit boards.
The solder paste distributes accurately due to its application through the stencil. Solder paste application quality plays a vital role because both extra and insufficient amounts lead to solder connection breakdowns and solder bridges and poor solder connection quality.
The SMT components automatically receive placement from the pick and place machine located on the PCB after solder paste determination. The machine removes components either from reels or trays or feeders to exactly position them on pads with solder paste. These advanced versions of machines use vision alignment systems to perform precise checks on component placement and orientation for maintaining high placement accuracy.

The PCB enters a soldering oven containing sectioned heating zones soon after component placement. The solder paste transforms into liquid during this process to join components to their specified pads on the PCB thus creating strong electrical connections.
Controlled heating-cooling protocols applied to boards lead to minimum component tensile strain during the reflow process. Through appropriate reflow soldering techniques manufacturers achieve dependable and excellent solder joints.
After soldering finishes Robotics-based Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) continues its operation with X-ray inspection machines to detect product defects. AOI systems rely on high-definition cameras with optical features to verify component alignment and solder bridges and technological component absence yet X-ray instruments should be used exclusively to test solder unions within Ball Grid Arrays (BGAs) and Leadless Packages.

Functional tests of the built PCB ensure correct system operation. The combination of In-Circuit Testing (ICT) and Flying Probe Testing enables inspection of open circuits along with shorts and components’ correct placement. Testing failure allows a PCB to enter troubleshooting but only after complete fault identification and rectification meets deployment requirements.
The detection of defects requires PCB repair practices which combine desoldering with rework procedures. The removal of broken components through desoldering tools enables surface mount soldering to restore functional parts back to the circuit board. Highly skilled SMT operators conduct these repairs to maintain product dependability.
The SMT assembly method streamlines PCB manufacturing which delivers precision along with high quality at exceptional efficiency thus becoming the common technique for electronics manufacturing today.
The production of miniature circuit boards with high performance and affordable costs depends on SMT components for modern electronics manufacturers. The structure of an SMT system combines manufacturing elements between components and a production line with assembly procedures to produce efficient electronic parts.
Manufacturers achieve top-grade electronic products with low defects through their use of advanced SMT machines and inspection methods. Knowledge of SMT components and assembling processes remains essential for all stages of PCB operations and circuit board repair technicians.
PCBasic provides all necessary solutions for SMT components, PCB repair tools as well as expert SMT manufacturing services. The entire selection of SMT solutions is available on our website for review.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
