Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > What are PCB HS Codes?
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are the main element of any electronic product. Since these electronic devices are traded globally, they need a unique identifier for easier export and importation processes. This is why PCB HS codes are so important.
Harmonized Systems (HS) codes are the systems customs authorities use to classify traded goods globally. When importing or exporting PCBs, you must declare their correct HS codes to comply with regulations and customs tariffs.
Read on as we explain the PCB HS code, its importance, and how it is classified.
A PCB HS code, or Harmonized Tariff Schedule code, is an 8-digit numeric code assigned to printed circuit boards and other electronic components for customs purposes. The HS system is maintained by the World Customs Organization (WCO) and used globally by over 200 countries and economies to classify traded goods.
The first 6 digits of the HS code indicate the item's category and subcategory, such as semiconductors or circuit modules. The last two digits provide a more detailed product description.
Using the correct 8-digit HS code is vital for importers and exporters, as it determines applicable import duties and tariffs and forms a key part of customs declarations. In addition to tariff rates, PCB HS codes are important for trade statistics and requirements for rules of origin compliance.

Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
Understanding the breakdown of an HS code for a PCB board is crucial for classifying your PCB products accurately. HS codes are 8-digit classifications organized in a specific structure by the World Customs Organization.
Let's examine each part of the HS code:
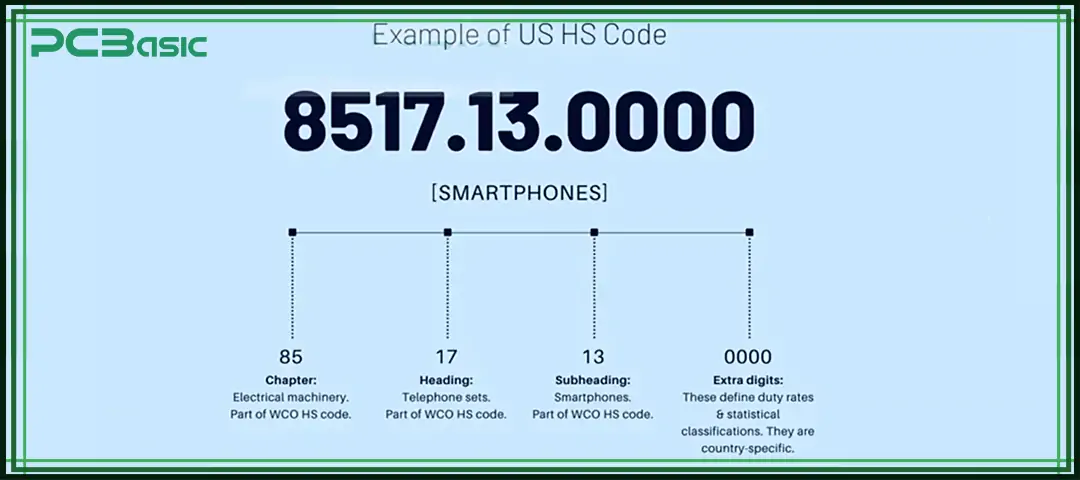
The first two digits of an HS code specify the chapter. All PCB products fall under Chapter 85 which covers electrical machinery and equipment.
The next two digits represent the headings within each chapter. Headings differentiate between broad product categories. Printed circuit boards are classified within either heading 8534 for bare boards or 8517 for assembled boards.
After the headings come the two-digit subheadings, these provide greater specificity about the product type. For example, 8534 further breaks down into subheadings for single-sided, double-sided, multilayer, etc. bare boards.
The remaining four digits are used to define attributes in finer detail. This can include layer count, board material, component inclusion and other technical specifications. More digits equate to a more precise classification.
So in summary, the full 8 –8-digit HS code conveys layered product information from general to very specific.
Taking the code 8534.00.90 as an example:
● 85 denotes chapter 85 (electrical machinery)
● 34 indicates heading 8534 for bare printed circuit boards
● 00 is the subheading for boards without distinguishing attributes
● 90 specifies this bare board is a multilayer.
Three main HS codes apply to different types of printed circuit boards. Understanding their definitions is critical for identifying the appropriate code to use.
This code covers finished populated and unpopulated printed circuit boards, including single—or multi-layer boards made of glass fiber-epoxy resin, ceramic, etc. This classification includes both rigid and flexible printed circuits, which are applied extensively in various electronic applications.
This code includes circuit packs with mounted ICs and other electronic components. Examples are communications circuit modules for routers, switches, PBXs and network gateways.
This residual category includes lead frames for semiconductor devices, chip carriers, and other circuit substrates not specified elsewhere. It typically applies to unpopulated or semi-populated boards in component or wafer form that are not ready for incorporation into finished goods.
The classification covers various electronic hardware used in manufacturing and assembling electronic devices.
There are several important reasons why PCB manufacturers need to understand printed circuit board HS code.
● Streamline duty rates: Duty rates vary significantly depending on the code. Using the wrong code could result in substantial extra import duties and fees.
● Ensure customs efficiency: Customs authorities require the HS code on all import/export declarations to process shipments efficiently and collect necessary duties and taxes. Incorrect codes cause delays.
● Inform trade analysis: HS codes are used globally for import/export statistics. Inaccurate trade data affects market analysis and domestic production planning for governments.
● Comply with trade agreements: Rules of origin under free trade agreements dictate the originating country based on HS codes. Non-compliance could lead to loss of preferential tariff treatment under FTAs.
● Address regulatory needs: HS codes may indicate regulatory requirements for international shipments affecting health, safety, security or the environment.
● Support supply chain partners: Supply chain partners need HS codes for freight forwarding, shipping documents, letters of credit and other trade compliance processes.
● Avoid unwanted costs and risks: Using HS classification resources ahead of time helps avoid unwanted costs, delays or legal risks associated with international PCB shipments due to misunderstanding or misuse of PCB HS codes.
You can search the databases below to easily identify the right HS codes for your PCB products.
World Customs Organization HS Classification Database:
https://www.wcoomd.org/en/topics/nomenclature/instrument-and-tools/hs-nomenclature-2017-edition.aspx
US Customs and Border Protection HTS Search: https://hts.usitc.gov/
Indian Customs HS Code Finder: https://www.cybex.in/hs-code-finder.aspx
UK Trade Tariff Tool: https://www.gov.uk/trade-tariff
EU Export Helpdesk for Exporters: https://trade.ec.europa.eu/access-to-markets/en/home
Chinese Customs HS Code Search (Chinese site): https://www.hsbianma.com/
HKTDCHS Code Search: https://www.censtatd.gov.hk/en/index_hs_code.html
Australia DFAT Free Trade Agreement Portal: https://ftaportal.dfat.gov.au/
Japan HS Code: https://www.customs.go.jp/tariff/index.htm
Canadian Customs Tariff Code: https://www.cbsa-asfc.gc.ca/trade-commerce/tariff-tarif/menu-eng.html
The increasing amount of international trade has led to the need for system classification for export and import purposes. HS codes play an important role in streamlining global trade, especially for the identification of PCB products.
Using these HS codes makes it easier for customs authorities to identify PCB shipments, enabling accurate declarations and payment of customs duties.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
