Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > Ball Grid Array Soldering | BGA Assembly and Repair
As electronic devices become smaller and more powerful, traditional packaging methods are gradually being replaced by more compact and efficient solutions. The BGA (Ball Grid Array) technology has become the core of high-density circuit design, while it also brings unique challenges, especially during the BGA soldering process.
Whether you are using BGA chips or handling BGA assembly, understanding ball grid array soldering is a crucial step in helping you manufacture high-quality PCBs.
Ball Grid Array (BGA) is a packaging method specifically designed for mounting integrated circuits. It is different from the traditional packaging with thin pins around the edges. At the bottom of the BGA chip, there are rows of very small solder balls used to connect with the circuit board. This design allows for more connection points, has better heat conduction effects and more stable electrical signal transmission.
If you want to know "What is BGA?" In simple terms, it is a compact and efficient chip packaging method widely used in high-performance electronic devices like CPUs and GPUs.
Compared with other packaging methods, BGA chips have many obvious advantages, which also makes them a commonly used packaging option in PCB manufacturing nowadays:
• Higher pin density:
BGA packaging can arrange more connection points in a very small space and is suitable for making small-sized and multi-functional circuit boards.
• Better thermal performance:
The solder balls underneath the BGA chip come into direct contact with the circuit board, which can help the heat inside the chip dissipate more quickly and prevent overheating.
• Superior electrical performance:
Because of the shorter connection distance, the signal travels faster, and there is less interference and noise. It is particularly suitable for chips that operate at high speed.
• Greater mechanical reliability:
Compared with the previous thin pins, BGA solder joints are more solid and less likely to break due to temperature changes or external forces.
It is precisely because of these advantages that ball grid array soldering is becoming increasingly important in various high-performance and high-density electronic products, such as mobile phones, computers, servers, and so on.
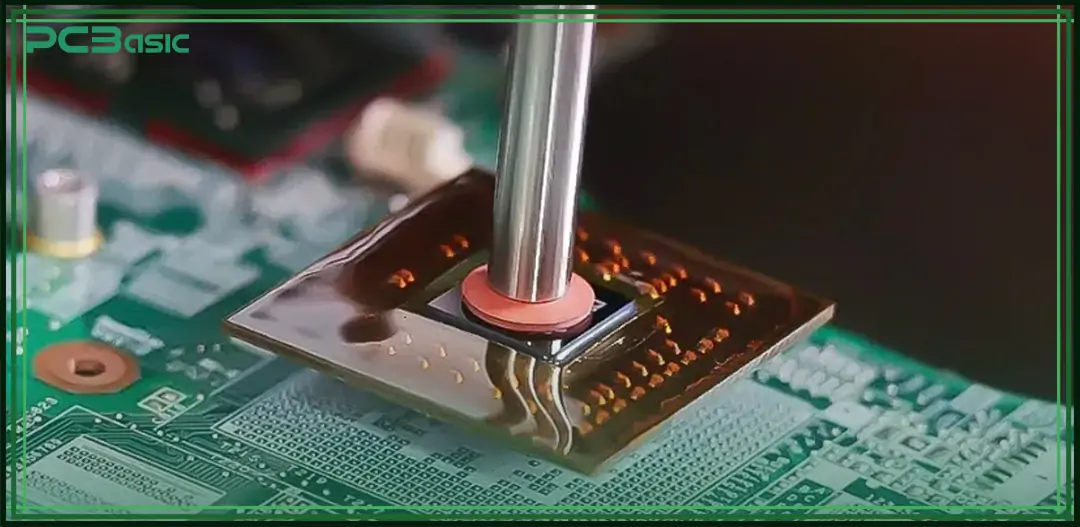
Correct BGA soldering can make the connection between BGA chips and circuit boards more secure and stable. The entire ball grid array soldering process is roughly divided into the following several steps:
• PCB Preparation
First, clean the solder pads on the circuit board thoroughly, and then apply a layer of flux to ensure that the subsequent solder can be firmly adhered.
• Stencil Printing
Apply solder paste to the PCB pads with an SMT stencil. This solder paste is used to assist in soldering, just like "glue".
• BGA Placement
Accurately place the BGA chip onto the solder paste through a pick-and-place machine, aligning each solder ball with the pads on the circuit board. The position must be very precise.
• Reflow Soldering
Send the circuit board with the BGA chip attached to the reflow soldering oven. It will be heated to a certain temperature, allowing the solder paste and solder balls to melt together and firmly solder the chip onto the board.
• Cooling
After soldering, it should be cooled slowly to harden and fix the solder points, so as to avoid problems caused by temperature changes.
The entire process is not only highly efficient but also ensures that the solder quality of each board is very stable, making it suitable for mass production.
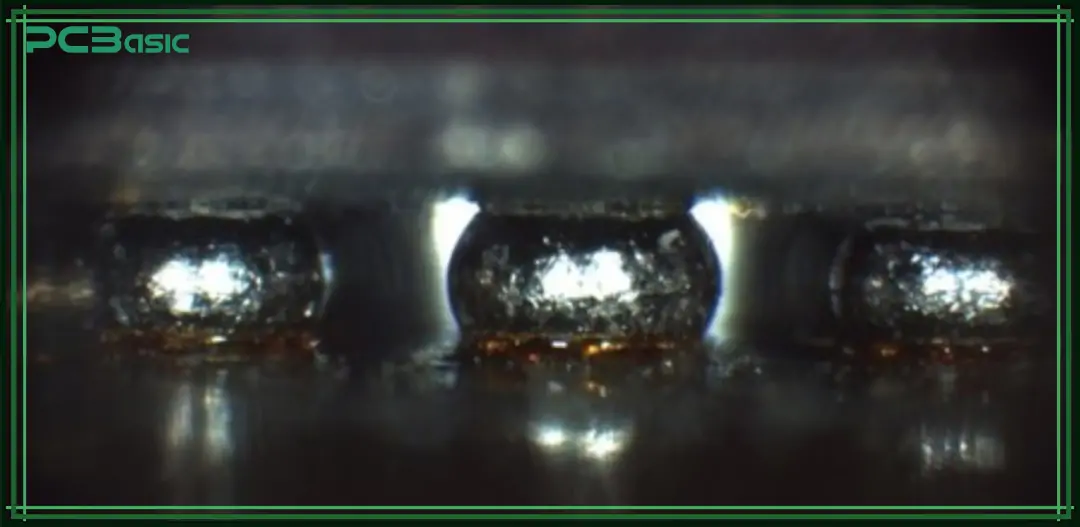

Despite its many advantages, BGA soldering still faces some technical challenges:
• Voids: Air bubbles or gaps inside the solder joints can weaken the connection.
• Cold joints: The solder doesn’t fully melt or bond properly, making the joint unreliable.
• Bridging: Solder balls accidentally connect to each other, causing short circuits.
• Open circuits: Some solder balls don’t connect to the PCB, leading to poor or missing electrical contact.
• PCB warpage: High temperatures during soldering can cause the circuit board to bend, resulting in bad connections.
Because the solder joints are hidden underneath the BGA components, these defects can be hard to detect and fix without proper inspection tools.
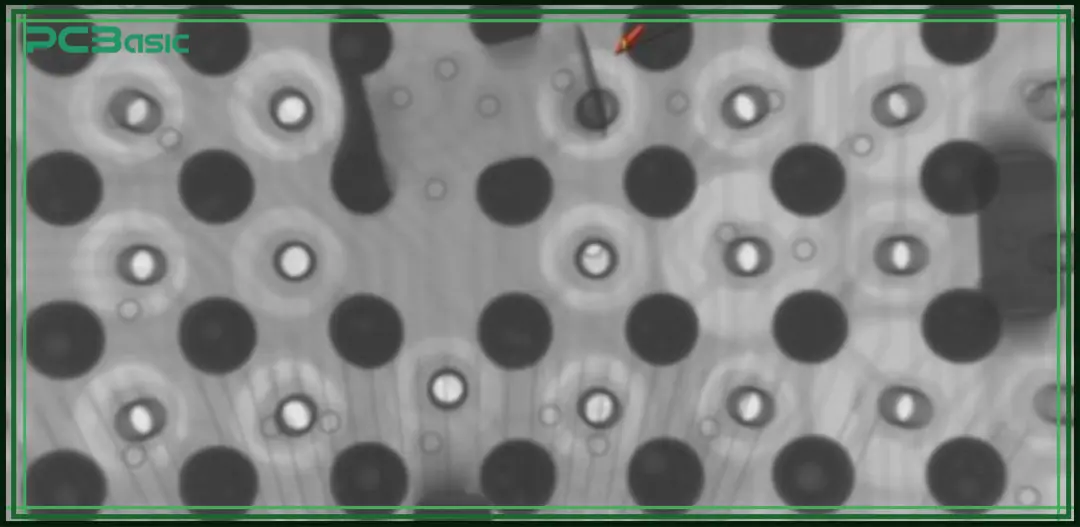
Since BGA soldering joints are hidden beneath the chip, specialized inspection methods are required:
• X-Ray Imaging: Reveals solder ball alignment and defects.
• Automated Optical Inspection (AOI): Checks for surface-level issues.
• Electrical Testing: Validates connectivity in BGA packages.
These methods ensure the quality of the entire BGA assembly.
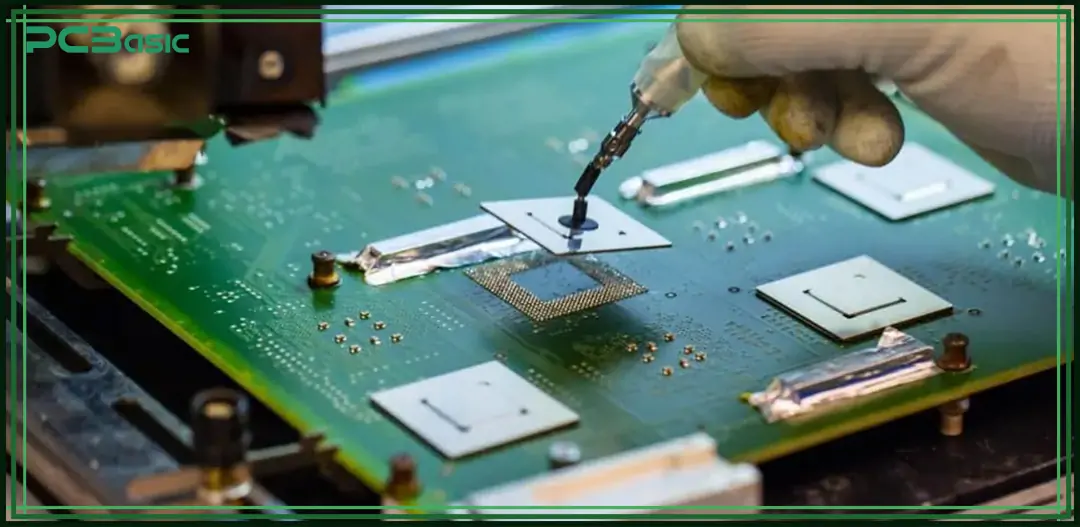
When a BGA chip has issues, it’s usually not necessary to scrap the entire circuit board. Instead, it can often be fixed through a rework process. However, since the solder joints of a BGA are hidden underneath the chip, the repair is more difficult and requires professional tools and skills. Here are the common steps for BGA rework:
• Removing the faulty chip (Desoldering)
Use a hot air gun or rework station to carefully remove the problematic BGA chip from the board.
• Cleaning the pads
Clean off any leftover solder and dirt from the pads under the chip to prepare for the next step.
• Reballing the chip
Attach new solder balls to the removed chip so it can be soldered again onto the PCB.
• Repositioning and re-soldering
Place the re-balled chip back in its original position, align it carefully, and use controlled heating to melt the solder balls and reconnect the chip.
Although this process is a bit tricky and requires precise handling, it’s much more cost-effective than throwing away the whole board.
Mastering BGA soldering is essential for working with modern BGA packages. From understanding what is BGA to troubleshooting BGA assembly issues, proper techniques ensure high-quality, reliable electronics.
Whether you're assembling or repairing BGA components, precision and the right tools make all the difference in ball grid array soldering.
By optimizing your BGA soldering process, you can leverage the full potential of ball grid array technology in your PCB designs.
If you need any BGA soldering, contact PCBasic.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
