Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > USB Pinout: A Comprehensive Guide
Universal Serial Bus (USB) was initially designed in 1996 for the standardization of peripherals connected with computers. Common peripherals are keyboards, mice, cameras, and printers. Over time, USB has evolved and now become the pillar of modern connectivity. USB has become essential for connecting our daily life applications including printers, and power supplies. Smartphones, digital cameras, and the list goes on.
USB Pinout is the arrangement of pins inside the USB connector. These pins are responsible for data transfer and power production. There are different types of USB connectors such as USB type-A, USB type-B, Micro USB, and Mini USB. The pin configuration of the USB connector determines the type of USB connector. Therefore, the understanding of USB connector pins is essential.

The most commonly used USB connectors are type-A and type-B. Type-A connector consists of two data pins (D+ and D-) and two power pins (VCC and GND). The D+ pin is responsible for data transmission and D- pin is responsible for carrying the data. The other two pins VCC and GND are used for providing +5V and common ground to electrical circuits respectively. Type-A USB connectors are mostly used for computers and chargers.
Type-B USB connector, on the other hand, has four pins. The assignment of four pins is one power (VCC), two data (D+, D-), and one for ground (GND). Type-B USB connectors are commonly used in printers, scanners, and cameras.
Other types of USB connectors such as micro-USB and mini-USB also have two power, two data, and one ground pin. These USB connectors are designed for compact devices such as cameras, tablets, smartphones, and MP3 players. Pinout of different types of USB connectors has different features including data transfer rate and power. Therefore, a detailed understanding of USB pinout is important for anyone passionate about gaining the knowledge needed for troubleshooting and communication.
This article will enable you to understand the USB pinouts, USB types, USB pinout diagrams, USB data transfer, USB power delivery, USB cable types, and their functionalities.
 About PCBasic
About PCBasic
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
Universal Serial Bus commonly known as USB is nothing but an interface designed to simplify the connection between computers and peripherals such as keyboards, mice, scanners, printers, digital cameras, and mobile phones.
USB was initially designed by American companies, namely Intel, IBM, and Microsoft Corporation, in the mid-1990s. The idea behind this was to provide a standard method for connecting various peripheral devices with computers. Since then, USB has evolved and replaced many specialized connectors with a standard USB interface.
USB serves as the bridge between the host and peripheral device, which has two functions, i.e., data transmission and providing electricity to peripheral devices. A standard USB consists of four pins: two for data transfer and two for power supply. Data transfer pins are used for sending and receiving data and power supply pins are used for +5V supply and GND. Each of the wires is designated with a unique color.
|
Pin No. |
Wire Color |
Signal |
Description |
|
1 |
Red |
VCC |
+5V |
|
2 |
White |
D- |
Data- |
|
3 |
Green |
D+ |
Data+ |
|
4 |
Black |
GND |
Ground |
Standard USB Pinout
USB connectors come in many different types such as Type-A USB, Type-B USB, Micro-USB, and Mini-USB. We will cover all these in the coming sections of the article.
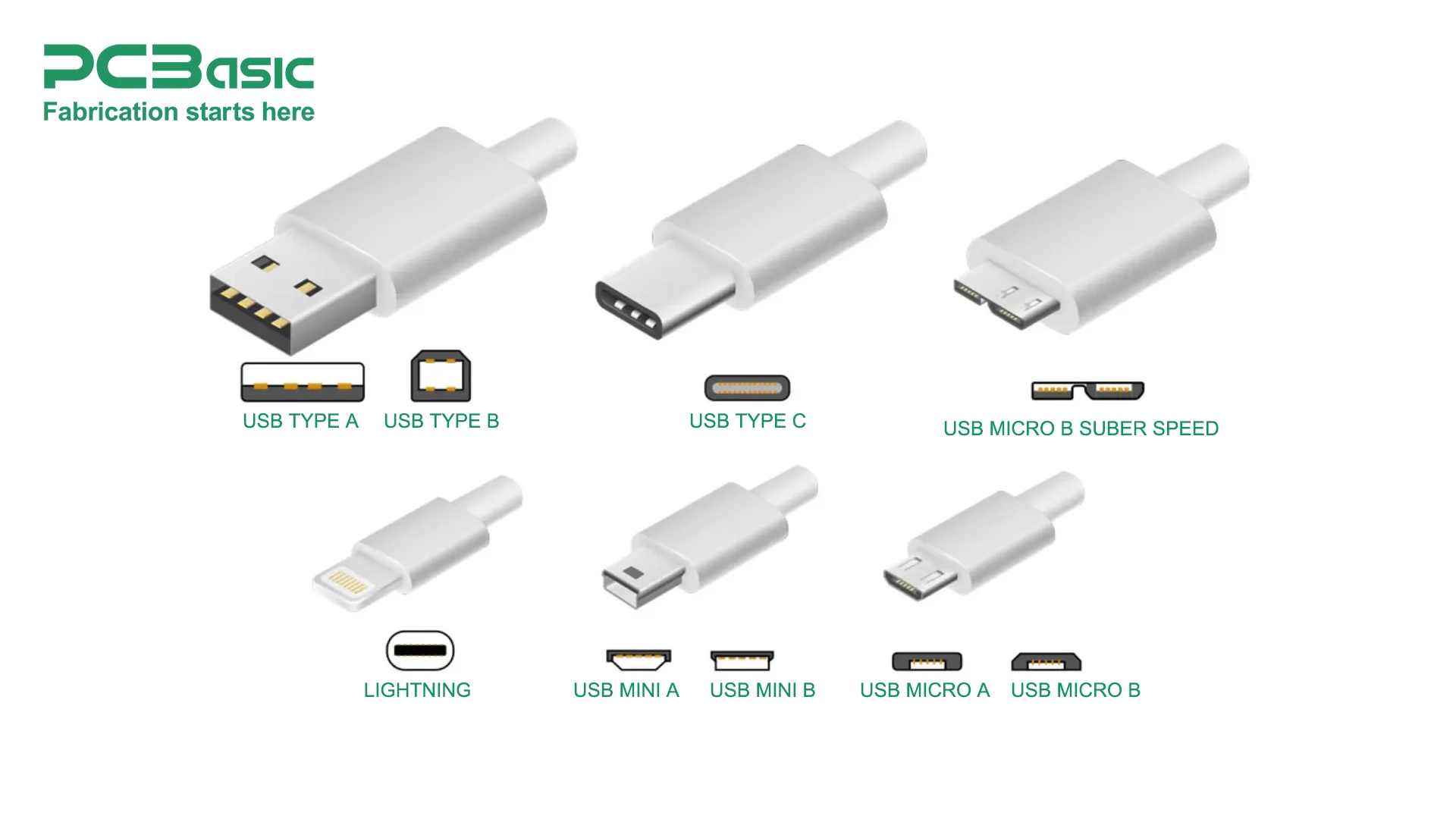

When delivering power or transferring data, each pin within a USB connector plays an important role. Ensuring a correct connection for a USB connector is paramount for seamless communication between devices such as smartphones, digital cameras, or other modern gadgets. This section provides an overview of every USB type pinout to offer a clear understanding for technical professionals.
USB technology has a variety of types and configurations to meet the specific needs of the device. The most common USB types are USB Type-A, USB Type-B, Micro USB, Mini USB, and USB Type-C.
1. USB Type A: Type A is the standard rectangular connector commonly found on computers, flash drives, and chargers. There are two versions of Type A connectors i.e. Male (Plug) and Female (Socket). Female (socket) is found on the host controller whereas Male (plug) is found on peripheral devices such as keyboards, mice, and other devices.
Type A USB pinout consists of four pins, two for data transfer and two for power supply. However, a newer version of Type-A USB consists of nine pins. Type A USB connectors are widely used in personal computers, mobile phone chargers, gaming devices, smart TVs, and music systems.
2. USB Type B: These connectors are square-shaped and mostly found on scanners and printers. Type B ports are upstream connectors that are only found in peripheral devices. Just like the Type A USB connector, the Type B connector also has four pins (VCC, D+, D- and GND). The USB 3.0 and newer versions consist of nine pins with an additional five pins for a faster data transfer rate.
3. Micro USB: As modern devices are becoming smarter and smarter, traditional USB Type A and USB Type B connectors are no longer suitable. Therefore, Micro USB Type connectors were born. Unlike Type A and Type B USB connectors, Micro USB connectors are smart, compact, and smaller.
USB pinout of Micro USB is different than Type A and Type B USB connectors. Micro USB consists of five pins which are Power supply pins (VBUS (+5V), GND), Data transfer pins (D+, D-), and identification pins (ID). Micro-USB is widely used in smart devices such as mobile phones, gadgets, tablets, audio systems, wireless headphones, and other portable devices.
4. Mini USB: Mini USB was initially designed for digital cameras and older smartphones. Mini USBs are larger than Micro USBs and smaller than Type A/Type B. The pins configuration of the Mini USB and Micro USB are the same i.e. Power supply pins (VBUS (+5V), GND), Data transfer pins (D+, D-), and one pin for identification (ID).
5. USB Type C: The USB Type C is a reversible connector, which means that it can serve as a connector for both the host and the devices. Type C USB connectors have gradually replaced the Type A/Type B connectors. Among all types of connectors, the Type C USB connector has the fastest data transfer rate (up to 10Gbps). Type C USB has 24 pins configuration, which will be discussed in the later section.
In USB, each pin in the connector plays an essential role. Whether it is about delivering the power, transferring the data, or identifying devices, it is all about establishing the correct connection. Therefore, understanding the pinout of each USB type is of paramount importance. This section provides in-depth details of each USB type pinout configuration.
Standard Type A USB connector has four pins each with a unique color which are shown in the figure below. Type A USB allows only downstream connection because their purpose is to connect to hosts.
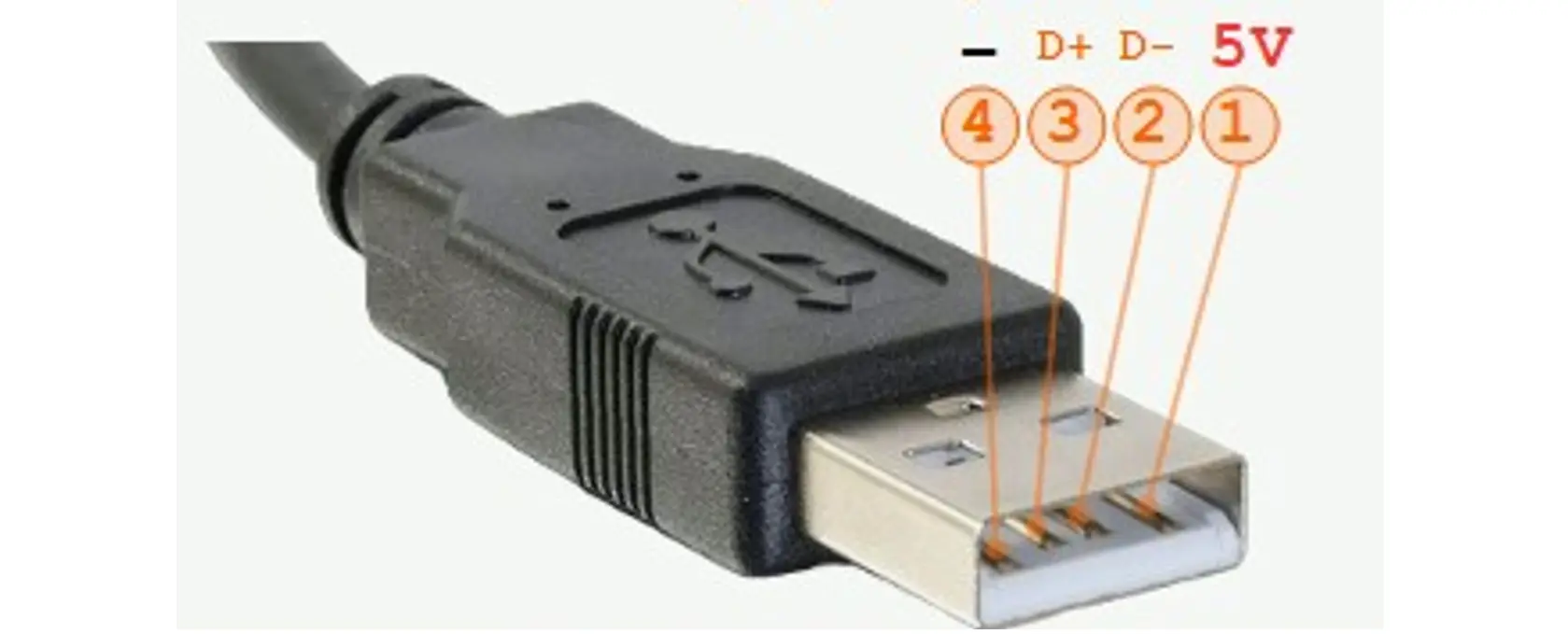
Each pin in the connector has a special function and it is essential to understand them correctly.
a. VCC: This pin supplies +5V power to the connected peripherals. The power supply source is crucial for charging devices such as keyboards, mice, and other mobile portable devices. The typical provided current through this pin is 500mA.
b. D-: Negative data signal pin (D-) works with the positive data signal D+. It plays a critical role in transferring data from a USB flash drive to a computer. Both D- and D+ pins work on the differential pair approach to reduce electromagnetic interference while transferring data.
c. D+: Together with Pin (D-), the positive data signal line (D+) enables the bidirectional data transfer between the host and devices.
d. GND: In any electrical system, a stable ground connection is essential to prevent any electrical noise from interfering with data signals.

Note: The newer version of the Type A USB connector has nine pins for a faster data transfer rate.
Standard USB Type B connectors also have four pins, each with a unique color. Type B USB connectors are upstream connectors that are mostly found on scanners and printers. To achieve a faster data transfer rate, the USB Type B also has an additional five pins.
The advantage of a Type B connector over a Type A connector is that it cancels out the chances of creating a connection between two hosts.
a. SSTX-/+: Out of five pins, one differential pair of SSTX+ and SSTX- are used to achieve super speed transmission.
b. SSRX -/+: One differential pair of SSRX- and SSRX+ are used to achieve super speed reception.
c. GND Drain: The GND drain serves as the extra isolated ground pin for two differential pairs used to achieve super speed.
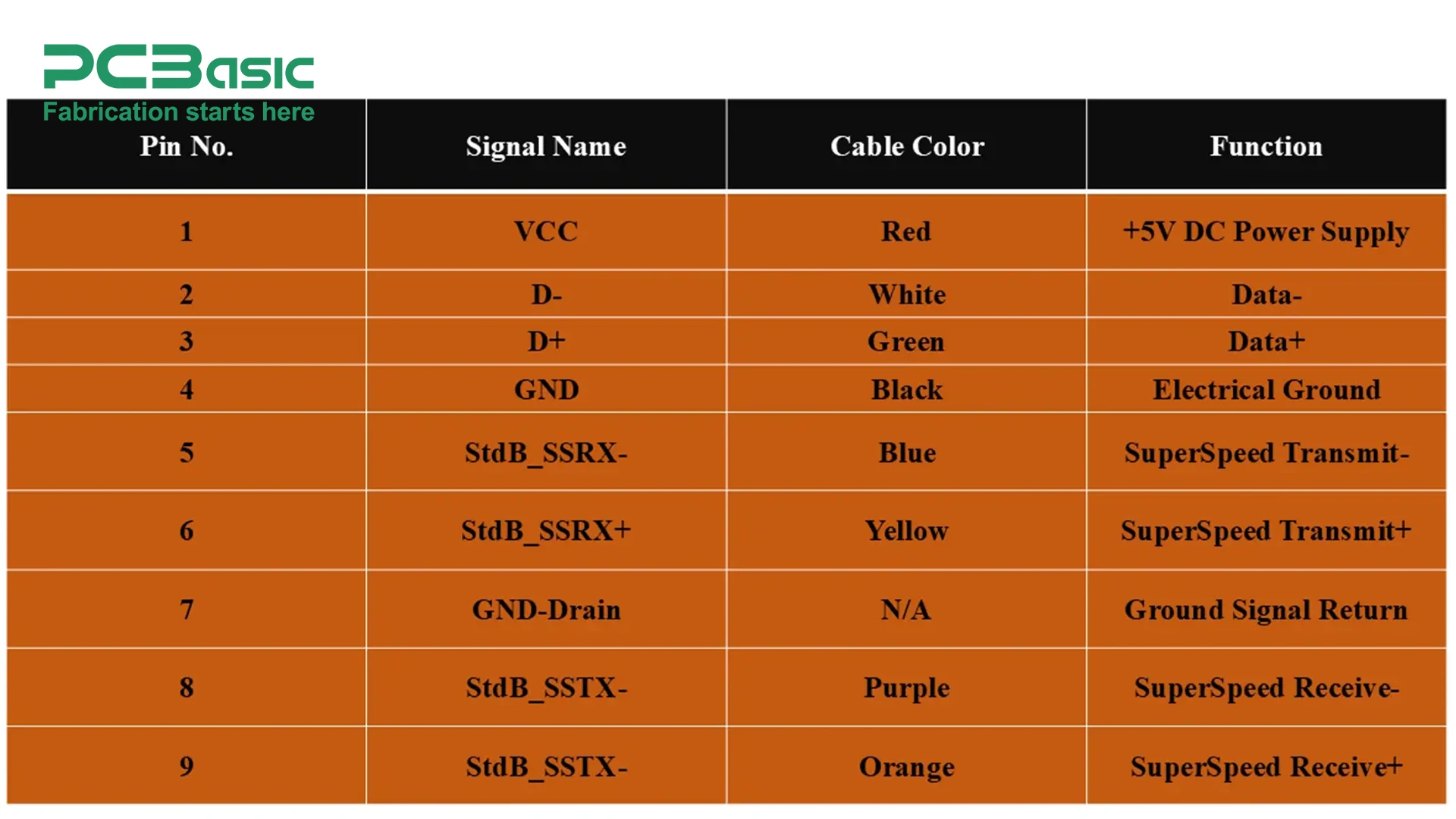
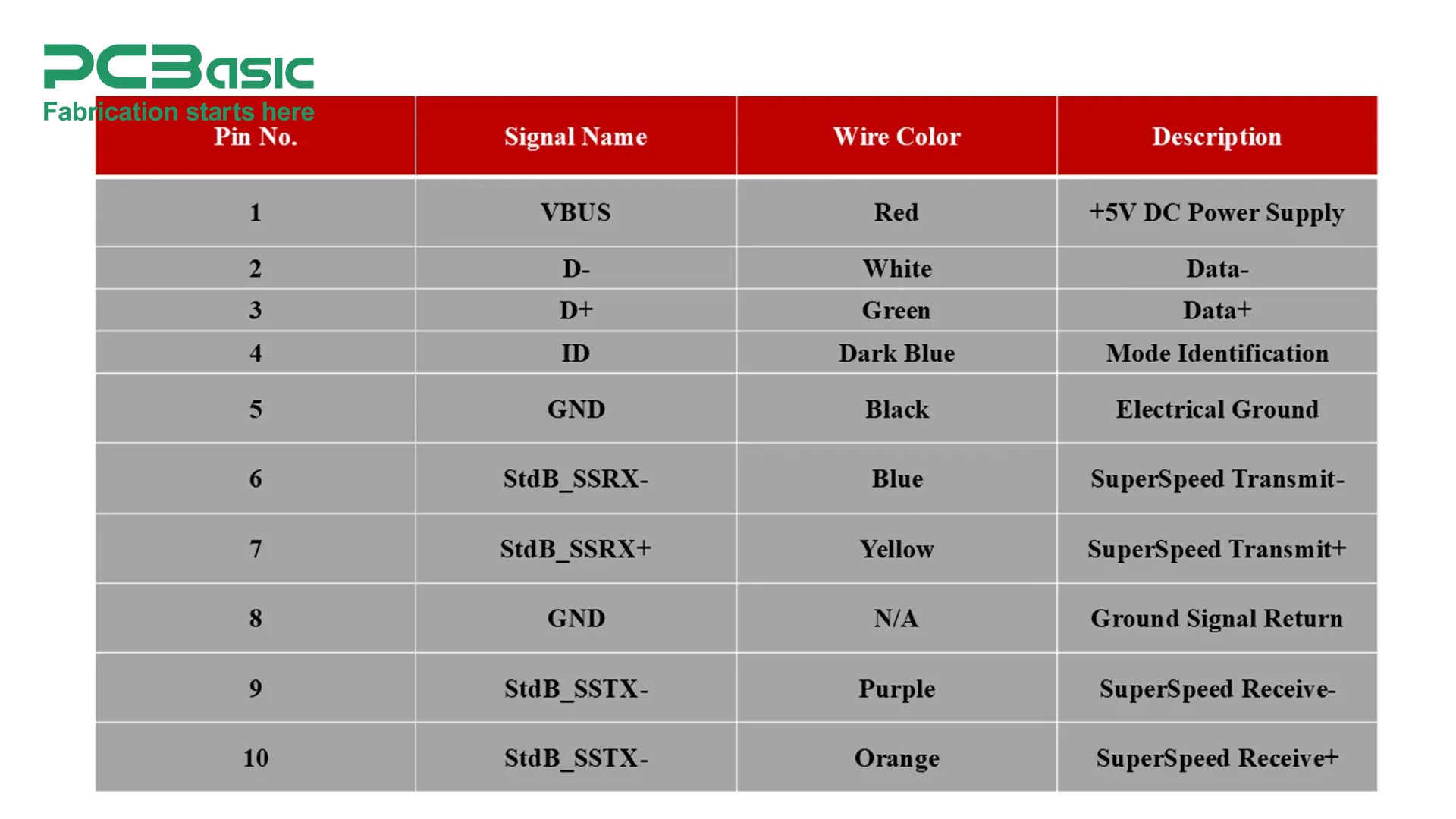
Micro USB was designed for smaller devices such as smartphones, portable routers, digital cameras, earphones, and other portable electronics. Before the advent of Type C USB, Micro USB connectors played an important role in standardizing charging and data exchanges.
Micro USB is smaller than mini-USB, and rs have slowly replaced theType A/Type B connector. The pinout of a Micro USB is different from the Type A/Type B. Unlike Type A and Type B USB connectors, a Micro USB connector has five pins, which are VBUS, D-, D+, ID, and GND. Typical current rating of Micro USB in USB 2.0 versions is 500mA and 2.5 Watts. Whereas, in later USB 3.0 versions, it can deliver up to 900mA and 4.5 Watts of power.
a. VBUS: Pin 1 (VBUS) is the power supply pin that provides constant +5V to the peripheral devices.
b. D-: D- (Pin 2) is nothing but a negative differential pair signal with a D+ pin for bidirectional communication. The differential pair ensures smooth data transfer by reducing electromagnetic interference and cross-talk between signals.
c. D+: Pin 3 works with D- to send and receive data signals.
d. ID: Pin 4 known as the identification pin allows devices to determine their roles i.e. host or peripheral device. It also determines which device acts as a power source host or peripheral once connected.
e. GND: Pin 5 serves as the electrical ground to ensure the stability of the electrical circuit.
Mini USBs are larger than Micro USB and are widely used in electronic devices such as digital cameras, MP3 players, early smartphones, and portable devices. Mini USB has also five pins for data transfer, power supply, and device identification.
a. VBUS: Pin 1 serves as the power supply source of +5V DC.
b. D-: Pin 2 works with the D+ as a differential pair for smooth data transfer between the host and peripheral device.
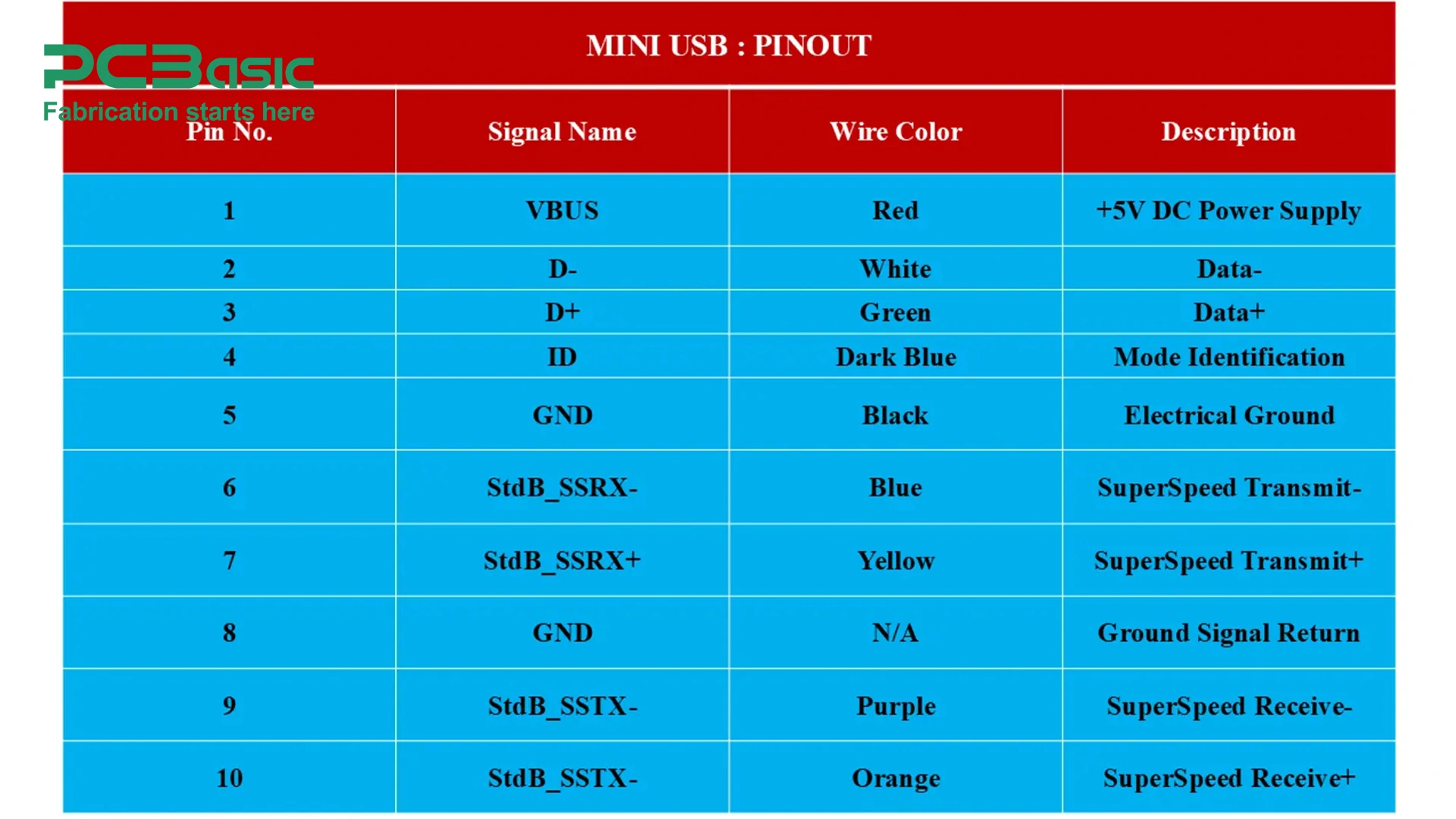
c. D+: Pin 3 works with D- for data transmission and reception.
d. ID: Pin 4 is the mode identification pin which determines whether the device is the host or peripheral device. The other mode is to determine whether the host is operating as a power source or peripheral device once connected.
|
GND |
SSTX+ |
SSTX- |
VBUS |
CC |
D+ |
D- |
VBUS |
SSRX- |
SSRX+ |
GND |
SBU1 |
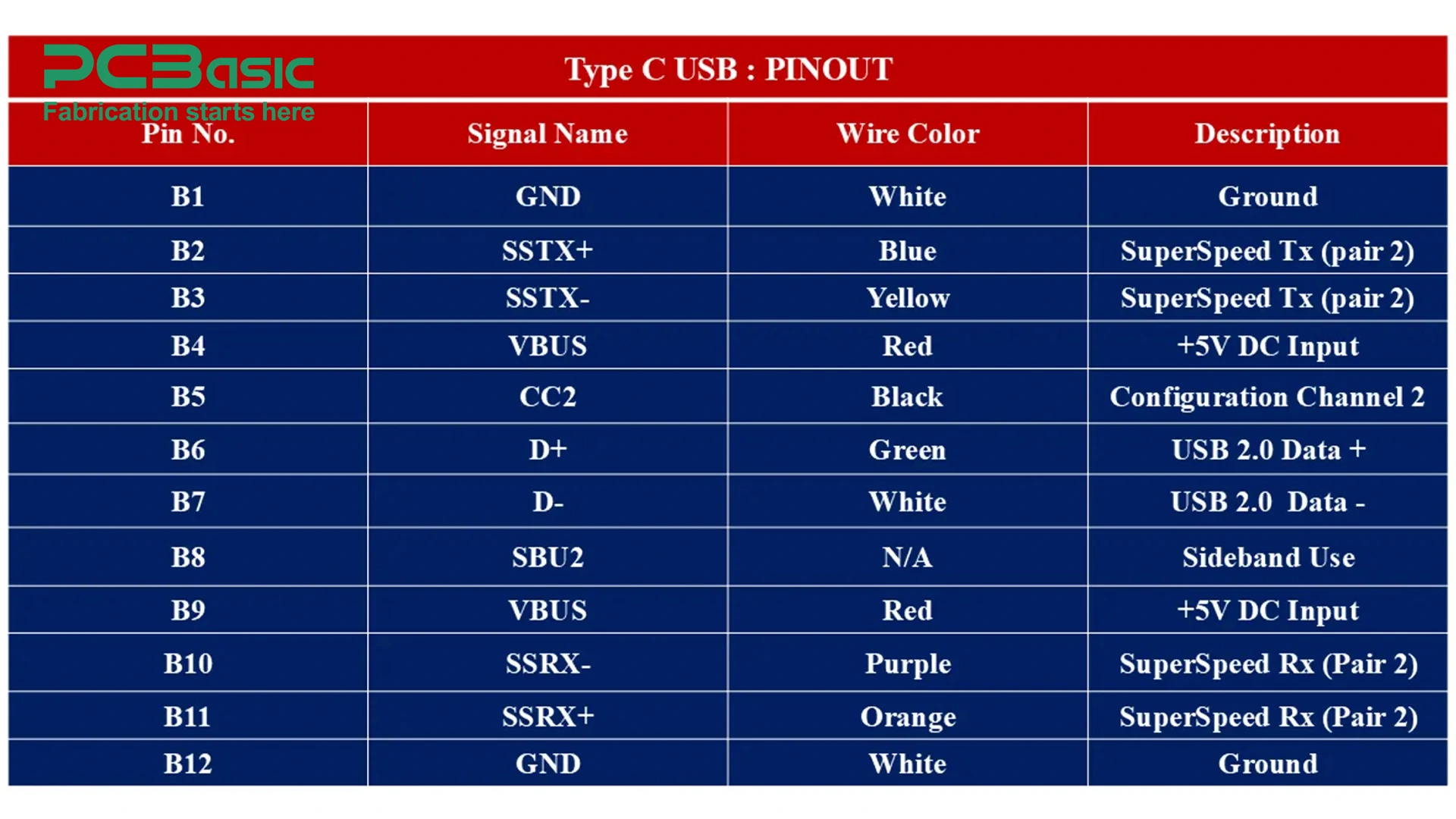
|
GND |
SSTX+ |
SSTX- |
VBUS |
CC |
D+ |
D- |
VBUS |
SSRX- |
SSRX+ |
GND |
SBU2 |
Standard Type C USB Pinout Configuration
a. VBUS (4 pins): Four pins are assigned to VBUS, which serves as the power supply for the connected device. These pins can deliver up to 20 volts and 5 amps.
b. GND (4 pins): Ensures ground connection and stability.
c. CC (2 pins): Two pins are assigned to detect the orientation of the plug. These pins are responsible for detecting the roles between devices such as power delivery or data transfer.
d. D+ and D- (2 pins): Like other USB types, these pins support basic data transfer between devices.
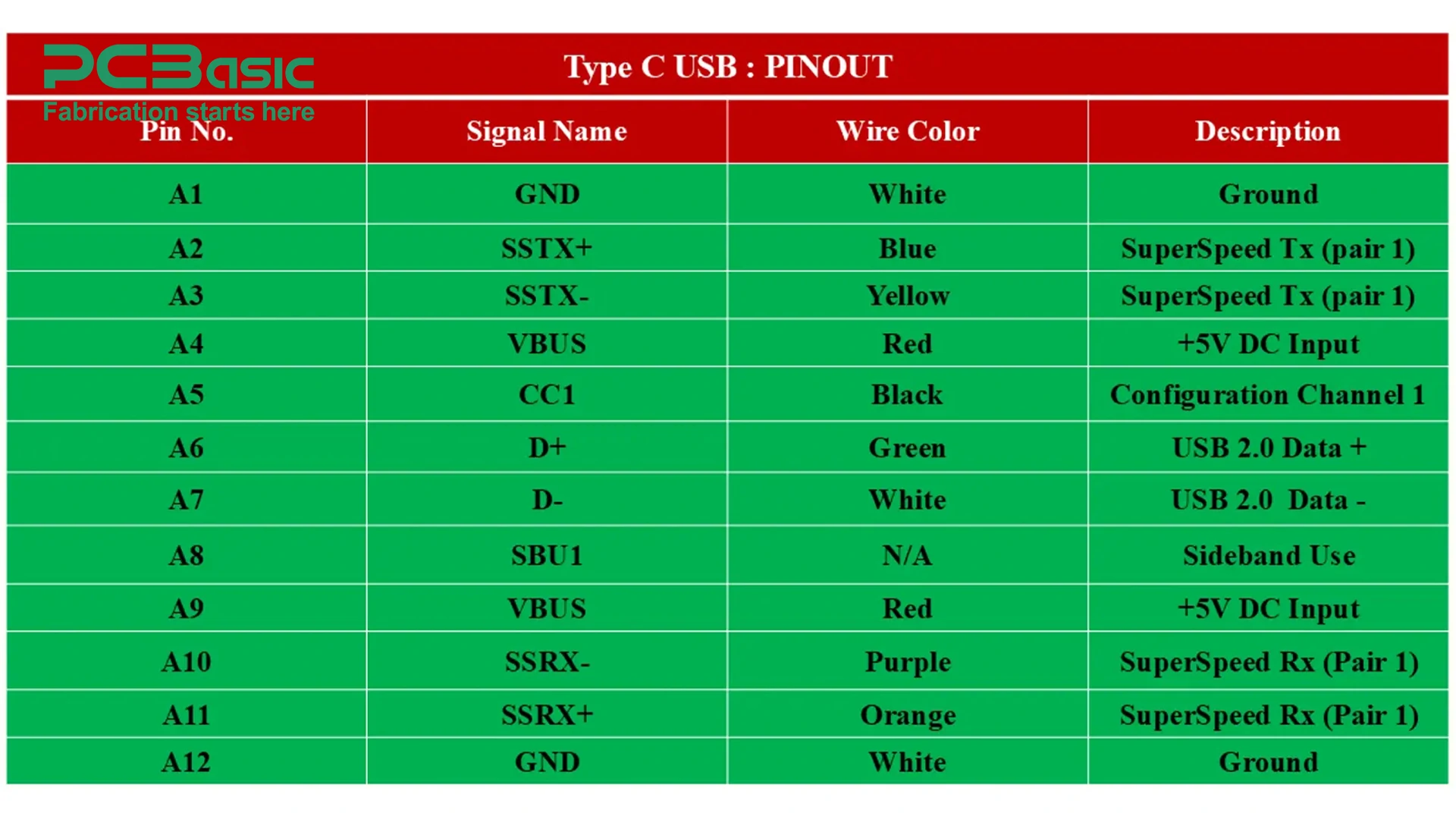
e. SuperSpeed Differential Pairs (8 pins): Differential pairs of SuperSpeed signals enable data transfer speeds up to 10 Gbps.
f. SBU1 and SBU2 (2 pins): Both pins support alternate modes such as HDMI output.
Data transfer is a critical task to exchange data between different devices such as flash drives, computers, and external hard drives. USB technology has evolved over the years to meet the demands of high-speed data transfer. Different USB types have different data transfer rates.

Earlier versions of the USB types, such as Type A and Type B, have less speed than the later USB types, such as Micro USB and Type C USB. USB pinout plays a crucial role in data transmission, as discussed in the above section. The pins which enable smooth data transmission are the D+ and D- pins. Differential pairs of super-speed pins enable high-speed data transmission.

USB pinout diagrams are an effective way to understand the pin configuration of each USB type. USB pinout diagram will also enable technical professionals to ensure correct wiring. Whether it’s a Type A, Micro USB, or Mini USB, these wiring diagrams will play a critical role in establishing a correct connection.
|
USB 2.0 |
VCC |
D- |
D+ |
GND |
USB Type A Pinout Diagram
|
USB 3.0 |
GND |
SSTX+ |
SSTX- |
VBUS |
D- |
D+ |
VBUS |
SSRX- |
SSRX+ |
USB Type A Pinout Diagram with Super Speed Pins
|
USB 2.0 |
VCC |
D- |
D+ |
GND |
USB Type B Pinout Diagram
|
USB 3.0 |
GND |
SSTX+ |
SSTX- |
VBUS |
D- |
D+ |
VBUS |
SSRX- |
SSRX+ |
USB Type B Pinout Diagram with Super Speed Pins
|
USB 2.0 |
VCC |
D- |
D+ |
ID |
GND |
Micro USB Pinout Diagram
|
USB 2.0 |
VCC |
D- |
D+ |
ID |
GND |
Mini USB Pinout Diagram
|
GND |
SSTX+ |
SSTX- |
VBUS |
CC |
D+ |
D- |
VBUS |
SSRX- |
SSRX+ |
GND |
SBU1 |
|
GND |
SSTX+ |
SSTX- |
VBUS |
CC |
D+ |
D- |
VBUS |
SSRX- |
SSRX+ |
GND |
SBU2 |
USB Type C Pinout Diagram
USB cables are designed to meet the specific connectivity needs for data transfer and power delivery. This section will cover the most common USB cable types and their wiring diagrams. The key differences between USB cables such as Micro USB vs Mini USB and USB plug types are discussed in this section.
a. USB Type A to Type B Cables: Standard USB cables are used to connect devices like computers, scanners, and printers. Applications include file transfer and charging of devices. USB Type A to Type B wiring diagram features four wires (VCC, D-, D+, and GND).
b. Mini USB Cables: Most portable devices use Type A mini-USB cables such as digital cameras, electronic gadgets, and MP3 players. Mini USB cables were compact in design but were replaced by Micro-USB cables due to the advancement in technology.
c. Micro USB Cables: Most modern gadgets such as power banks, smartphones, tablets, and digital cameras use Micro USB cables due to their compact design. The wiring diagram of a Micro USB cable includes five (VBUS, D-, D+, ID, GND). Micro USB vs Mini USB pin configurations are the same, but they differ in size. Both have one additional pin for mode identification.
In conclusion, understanding USB pinout will not just give you the knowledge but enrich your technical expertise. As a professional Electronic Engineer, understanding USB pinout will enable accurate data transfer and power delivery among different electronic devices. Familiarity with different USB Types enables you to choose the right option for your devices. Understanding pinout diagrams, USB types, wiring diagrams, USB cable types, and pin configuration will not only enhance your technical knowledge but also help you in your professional career.
-

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
