Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > Overview of Printed Circuit Board Assembly
Printed circuit board assembly (PCBA) is a core step in modern electronics manufacturing. By integrating various circuit board components onto the printed circuit board, we can create a fully functional electronic device.
By knowing the PCBA meaning, process of PCBA and how to select a PCB assembly manufacturer you can always improve the performance and reliability of your product. This blog will cover the fundamentals of PCB manufacturing and assembly and will also introduce PCBasic as a PCB assembly service that guarantees quality.
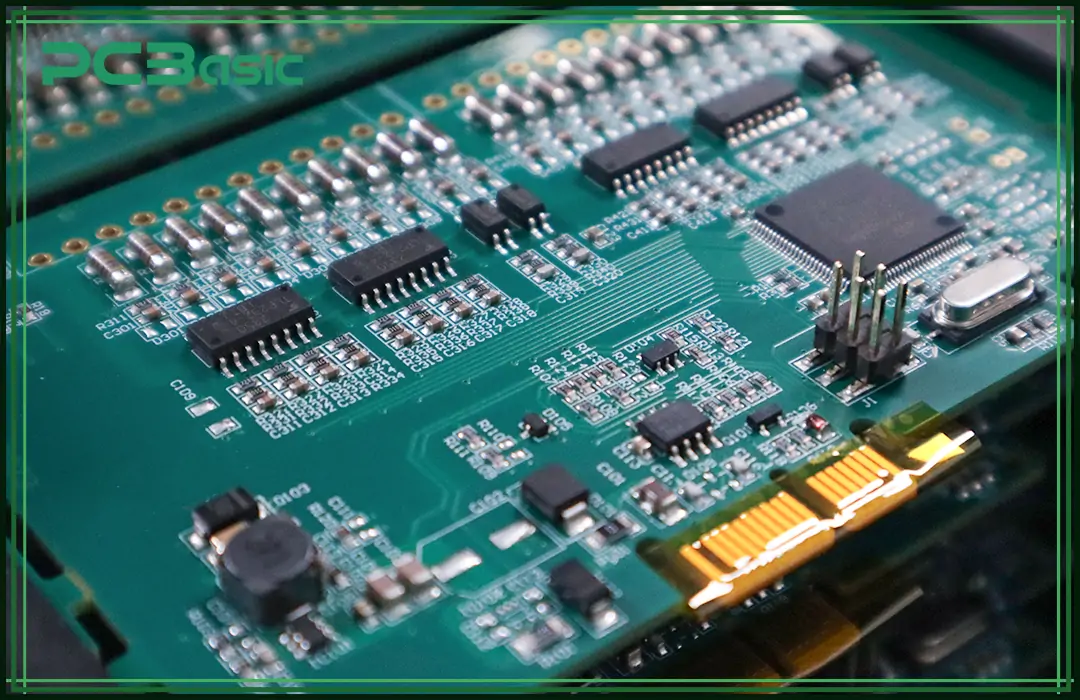
Printed circuit board assembly (PCBA) is a complex, precise process that is full of details. It is intended to solder and attach all the different circuit board components onto a bare PCB (Printed Circuit Board) to obtain complete electronic device functionality. The PCB that completes the process of printed circuit board assembly has various circuit board components like resistors and capacitors compared with the bare printed circuit board, which only serves as a circuit carrier. These components are then formed by assembling the PCB and creating the real electronic functionality inside the PCB.
The PCBA meaning is not only to solder components to the circuit board, but more importantly to ensure the precise placement and reliable connection of each component. Therefore, PCBA is not only assembly, but also a combination of engineering design, precision manufacturing and rigorous testing technology.
Choosing an experienced PCB assembler is crucial. Professional PCB assembly manufacturers, such as PCBasic and WUS Printed Circuit, have advanced production equipment and strict quality control processes. They can not only ensure that each electronic component is soldered to the PCB in a precise position but also ensure its stable performance and reliability through a series of tests.
In short, the PCBA meaning is to transform a bare PCB that originally only has the function of circuit connection into a complete and operational electronic component through a scientific and rigorous assembly process, laying the foundation for the normal operation of various electronic devices.
In the PCB assembly process, in order to install various electronic components onto the board faster and more stable, PCB assembly manufacturers usually use several common techniques. The following are three main PCB assembly techniques, each with its own characteristics, suitable for different types of boards and electronic components.
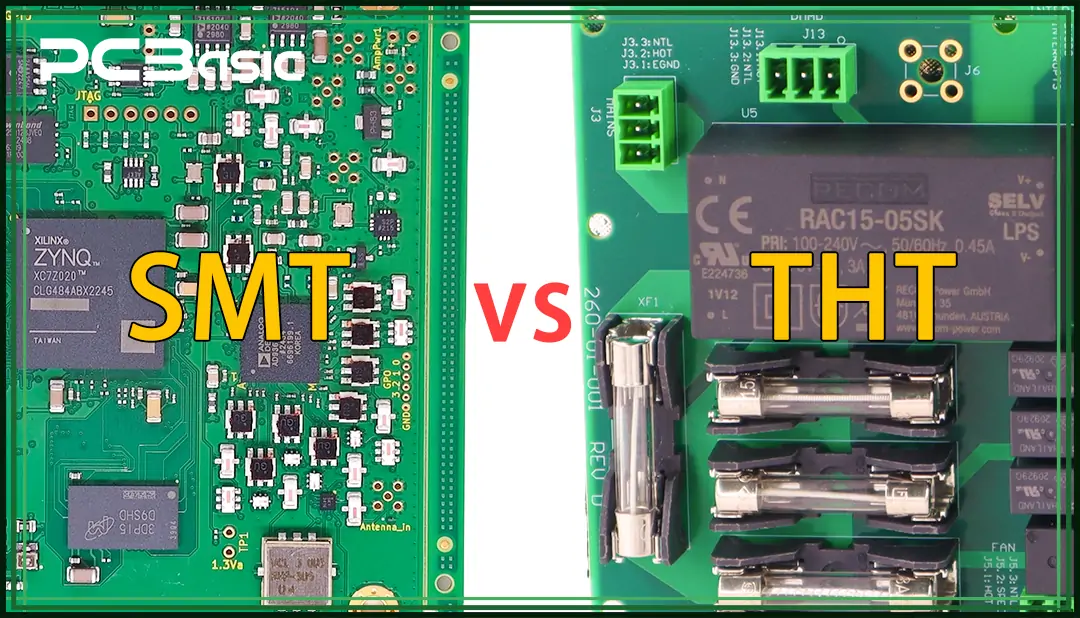
Surface mount technology (SMT) is a highly automated technology that has become one of the most commonly used PCB assembly methods. Its core principle is to mount small, compact electronic components directly onto the surface of the circuit board.
In the SMT process, solder paste is first applied on the board where the components need to be placed (similar to cream on bread to help hold the components in place). The chip then automatically and accurately places each electronic component in the correct position according to the coordinates of the design drawing. Once this is done, the board is "reflow soldering" - the solder paste is melted at a high temperature, and the components are firmly glued to the PCB.
Advantages of SMT:
• Fast Production: SMT machines can quickly mount a large number of components, making it ideal for mass production.
• High Precision: Modern pick-and-place machines offer incredible accuracy, ensuring components are perfectly aligned.
• Compact Design: SMT allows for smaller, more densely packed circuits, which is crucial for devices like smartphones and laptops.
Through-hole technology (THT) is a more traditional PCB assembly method. It is especially suitable for circuit board components that are larger in volume and require stronger connections.
In the THT process, each circuit board component comes with a pin (similar to a thin wire). These pins will pass through small holes in the PCB and emerge from the other side. Next, a soldering worker or automation machine will solder the pins on the back of the circuit board to ensure that they are firmly attached to the board.
Advantages of THT
• Stronger connection: Because pins of components go directly through the board and is soldered firmly from the back, the connection strength is higher. This connection is particularly suitable for equipment that is subjected to greater pressure or vibration, such as industrial equipment, automotive circuits, etc.
• Suitable for larger components: THT is more suitable for larger, heavier components, such as capacitors, transformers or connectors, which require stronger physical support.
Although the operation speed of THT is slower than SMT, its fastness and stability make it irreplaceable in some circuits with high connection strength requirements. So it is also a very important technology.
The PCBA manufacturing process consists of multiple interlocking precise steps. Each of them determines whether an assembled printed circuit board can be run stably.
Solder paste printing is the first step in the PCB assembly process. Through a precision steel mesh, the solder paste is accurately printed to the specified pad position on the PCB. These locations are the areas where the circuit board components are placed.
After the solder paste application is completed, PCBs enter the automatic pick-and-place stage. In this step, the pick-and-place machine identifies the areas on the PCB where solder paste has been applied and then quickly and accurately mounts various circuit board components onto the board. This process mainly uses surface mount technology (SMT), which is suitable for the vast majority of modern electronic products and is one of the core steps in printed circuit board assembly manufacturing.
After the component is attached, the PCB will go into the reflow oven. The solder paste, which was temporarily solidified, is melted by heating at a high temperature. As the temperature gradually lowers, the melted solder paste firmly solids the components to the PCB. After completing this step, the circuit board has an initial electrical connection. This stage plays both a fixed and conductive role in the PCB assembly process.

To ensure quality, every board undergoes Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) or other testing to check for issues such as component misalignment, missing components, cold solder joints, and so on. For complex components like BGAs, which cannot be inspected visually, X-ray inspection is used for further verification. This step is critical for maintaining the reliability of PCB assembly services.
Not all circuit board components are suitable for SMT. For components that require high mechanical strength or handle high power, Through-Hole Technology (THT) is still used. In this step, operators or machines insert components into pre-drilled holes on the PCB in preparation for soldering. This method is commonly found in prototype PCB assembly or in industrial control applications.
After THT components are inserted, they need to be soldered. This is where wave soldering or selective soldering comes into play. In wave soldering, the entire board passes over a wave of molten solder. Selective soldering, on the other hand, is better suited for boards that combine SMT and THT components. This stage is extremely important in mixed-technology PCB assembly services to ensure that all THT components are securely connected.
Once all components are soldered, each finished PCBA undergoes functional testing. This includes electrical performance tests, switch operation tests, communication checks, and more—ensuring that every board meets its design specifications. This step determines whether the printed circuit board assembly is truly successful and is essential for customer satisfaction.
After testing, the circuit boards are cleaned to remove any residual flux, dust, or contaminants. The cleaned PCBs are then dried, treated for anti-static protection, and neatly packaged for shipment. Whether it’s large-scale PCB manufacturing and assembly or small-batch prototype PCB assembly, this final step is critical and should never be overlooked.
PCBasic combines professional expertise, smart manufacturing, and strict quality control to deliver reliable PCB assembly services.
• Experienced Team: 10+ years in PCB design and project management, with R&D collaboration with PhD teams from top universities.
• Flexible Production: Shenzhen factory for small batches, Huizhou factory for large-scale orders—both self-owned and fully equipped.
• Integrated Resources: In-house stencil & fixture production and 1-hour stencil delivery for fast response.
• Smart Supply Chain: Intelligent components warehouse, guaranteed original parts, and instant BOM import with online quoting.
• Certified Quality: ISO13485, IATF 16949, ISO9001, ISO14001, UL certified, IPC member, and over 20 patents in quality management.
• Advanced Inspection: Equipped with flying probe testers, AOI, X-ray, and functional testing systems to ensure product quality.
With PCBasic, you get precision, speed, and a trusted partner in every order.
The printed circuit board assembly is an indispensable core part of modern electronic products. With a deep understanding of the PCB assembly process, the technology used, and choosing professional PCB assembly manufacturer, you can ensure that your products are stable and reliable.
Whether you need small batch prototype PCB assembly or complete PCB manufacturing and assembly, choosing an experienced PCB assembler such as PCBasic will be a key step in the success of your product. Let a professional team assemble your electronic components for efficient, high-quality delivery.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
