Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > Circuit Symbols: The Language of Electronics
This article describes the importance of circuit symbols electronics for better design with perfection to understand electrical systems without flaws.
Circuit symbols are a valuable component in adding to the formation of circuit diagrams. They are used as a universal language to make the description of electrical systems easier and less complicated. These symbols make the most complicated diagrams presented understandable because they have a standardized manner of depicting components that include resistors, capacitors, and transistors. Without them, diagramming and interpretation, especially for complex layouts such as PCBs, would just not be possible at all.
Electronics may seem quite simplistic on paper in theory, but as the designs get much more complex, it will be quite hard to create and comprehend the layout with non-standard symbols. Circuit symbols make it easy for technicians and engineers to determine how things fit together while making it easier to build, troubleshoot, and explain how a circuit works.
Especially in modern electronics, circuit diagrams are critical for representing how a system works. Referring to an organized diagram with symbols can assure engineers that they not only explain but also understand the principles behind the functioning of the circuit. Such clarity is necessary for designing, collaborating, and debugging on advanced projects.
To put it simply, circuit symbols are not a luxury but a necessity. Circuit symbols are a basis for taking abstract ideas into actual working systems and, with proper knowledge, allow smooth operation and easy maintenance of electronic devices, particularly in a team environment. Therefore, with a good knowledge of circuit symbols, endless opportunities in the electronics field open up for an engineer.
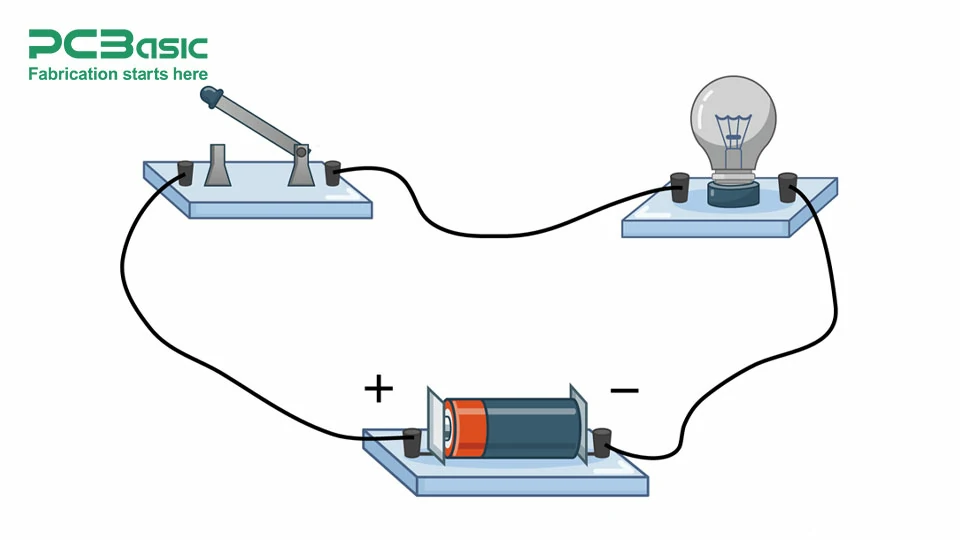
Here are some circuit diagrams featuring various circuit symbols, illustrating their crucial role in making circuits easier to understand and interpret. Diagram 1 is a simple closed circuit involving 4 basic components resistor, capacitor, lamp, and battery. Diagram 2 is a bit complex compared to Diagram 1 involving a diode LED and switch as well.
The circuit symbols are the building blocks of circuit diagrams, showing a unified way of representing electrical components. It makes the representation and designing of circuits by engineers and technicians very easy irrespective of their complexities. It is now basic for professionals in electrical and electronics to know these circuit symbols.
|
Component |
Symbol |
Description |
|
Resistor |
|
It Limits the flow of current in a circuit.
|
|
Capacitor |
|
It Stores electrical energy in an electric field. |
|
Inductor |
|
Stores energy in a magnetic field when current flows through it.
|
|
Diode |
|
Allows current to flow in one direction only.
|
|
LED |
|
Emits light when current flows through it.
|
|
Transistor (NPN) |
|
Type of transistor that acts as a switch or amplifier in circuits.
|
|
Transistor (PNP) |
|
Another type of transistor works similarly to the NPN transistor.
|
|
Battery |
|
Supplies power to the circuit.
|
|
Switch |
|
Opens or closes a circuit to control the flow of current. |
|
Fuse |
|
Protects a circuit by breaking the connection if the current exceeds a safe level. |
|
Transformer |
|
Transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. It steps up or steps down the electrical energy.
|
|
Zener Diode |
|
Allows current to flow in reverse direction when voltage exceeds breakdown value. |
|
Lamp |
|
Converts electrical energy into light and heat; commonly used for lighting or as an indicator.
|
In addition to component symbols, circuit diagrams also include symbols that represent various circuit conditions. These symbols indicate the state of the circuit, such as whether it is open, closed, shorted, or grounded. Understanding these conditions is essential for interpreting the behavior and functionality of a circuit during operation. Below is a chart of common circuit condition symbols and their descriptions:
|
Condition |
Symbol |
Description |
|
Open Circuit |
|
A break in the circuit where current cannot flow.
|
|
Closed Circuit |
|
A complete circuit where current flows uninterrupted.
|
|
Ground |
|
A reference point in the circuit with zero voltage is often used for safety and stability.
|
|
Power Supply |
|
Represents the source of electrical energy for the circuit.
|
|
Open Switch |
|
A switch in the "off" position breaks the circuit.
|
|
Closed Switch |
|
A switch in the "on" position completes the circuit.
|
|
Connected Wires |
|
Shows that two wires are connected.
|
|
Crossed Wires (Not Connected) |
|
Indicates that two wires cross but are not connected.
|
Logic gates are the fundamental entities or building blocks in a digital circuit. These perform logical operations on one or more incoming signals to drive a single output and enable the circuit to work. Each gate has its unique symbol and function while designing and analyzing a digital system like computers, microcontrollers, and digital communication devices. These symbols make it easy to represent complicated operations and simplify the design process.
Below is a chart of logic gates and their symbols:
|
Logic Gate |
Symbol |
Description |
|
AND Gate |
|
Outputs HIGH (1) only if all inputs are HIGH.
|
|
OR Gate |
|
Outputs HIGH (1) if at least one input is HIGH. |
|
NOT Gate |
|
Inverts the input; outputs HIGH (1) if the input is LOW (0), and vice versa.
|
|
NAND Gate |
|
Outputs LOW (0) only if all inputs are HIGH; inverse of AND gate.
|
|
NOR Gate |
|
Outputs HIGH (1) only if all inputs are LOW; inverse of OR gate.
|
|
XOR Gate |
|
Outputs HIGH (1) if inputs are different; outputs LOW (0) if inputs are the same.
|
|
XNOR Gate |
|
Outputs HIGH (1) if inputs are the same; outputs LOW (0) if inputs are different.
|
These are not just random drawings denoted in electrical circuits. Every one of these circuit symbols shows the functionality or situation of the circuit or electrical component. Each symbol is designed in such a manner as to depict the characteristic of behavior or function of the component in electrical systems.
Simplicity and Functionality
Circuit symbols are clear and kept as simplistic as possible to easily identify and draw when working a circuit board. For example, the zigzag line means the resistance in the flow of current while the parallel line used in a capacitor represents the plates on which charges are stored. All these features are an immediate representation of the physical characteristics and actions of the components.
Standardization and Universality
These are internationally recognized symbols such as the IEC, IEEE, and others. This ensures that the symbols are universally understood, regardless of geographic or cultural differences. The physics of each of them remains the same making these standardized symbols convey the essence in the best way.
Physical Representation of Function
Here are examples of some component symbols that represent the meaning behind their design.
● Resistor: The interrupted line means opposition to the flow of current, which in turn means it can convert energy into heat.
● Capacitor: The parallel lines reflect the physical plates that hold electricity in an electric field.
● Inductor: The loops symbolize the coil wire through which electric current flows and produces a magnetic field.
Likewise, every circuit symbol has relevance to its working or functionality.
Dynamic Components
Symbols of several components including diodes and transistors show the directional or switching nature. For example, in the symbols for NPN and PNP transistors, the arrow indicates the current direction. The arrow for the NPN points away to show that the current flow is out of the emitter. On the other end, the arrow in a PNP transistor points toward the inner side, an indication that the current flow is into the emitter.
Visualization in Circuit Behavior
Through the application of the symbols denoting current, voltage, and energy storage, engineers can be able to have a mental picture of how the parts in the circuit will perform. This is especially important in design and always when trying to improve or solve a problem.
Practical Applications
A practical use is also taken into account in the design. In the more sophisticated applications like Printed Circuit Boards, and integrated circuits, among others, symbols must not only reflect physical principles but also be easily distinguishable.
Through circuit symbol design, theoretical concepts can be easily translated into practical applications. These symbols are not merely drawings; they represent some basic concepts in electricity and magnetism and, therefore, become indispensable tools in the field of electronics.
Circuit symbols provide many advantages that simplify the design, analysis, and troubleshooting of electrical systems. They provide a simplified and standardized representation of the components for effective communication, leading to enhanced efficiency during circuit work. Some of the main benefits include:
Simplified Representation
Circuit symbols transform complicated parts into basic graphics that are simple to draw. This makes it easier to plan and arrange circuits since less clutter makes complex diagrams less confusing as well.
Universal Language
These circuit symbols have been standardized everywhere by organizations like the IEC and IEEE. This symbol makes it universally standardized in the sense that engineers, technicians, and students in various parts of the world can read and work on circuit diagrams without being influenced by language barriers or misunderstandings.
Faster Design and Analysis
Circuit symbols also help engineers sketch circuit designs quickly for rapid prototyping and analysis. They are simple and easy to use in circuits without causing any complexity. This accelerates the creation process, enabling effective brainstorming and problem-solving.
Detect errors and troubleshoot
It is much easier to see the symbolic pathway of a circuit when it has been visualized. Debugging is easier because a person can see everything is connected cleanly.
Efficient Communication
Drawing circuit diagrams with standardized industrial symbols allows for better communication not only between team and departmental members but also between different companies. This is the case in multi-authored designs where the need to read and change the layout may be accomplished by persons other than the originator.
Education and Learning – To a Higher Degree
For students just starting in this area of study and beginners to electronics in general, circuit symbols are simple representations of information made to explain complicated electrical ideas. They provide learners with the ability to think about how each piece works together without getting lost in extraneous detail.
Consistency and Accuracy
Using symbols helps maintain uniformity in the way circuits are presented across various documents and projects. This cuts down on the chances of errors that may be created because of conflicting or ambiguous representations in diagrams.
Save Space in Diagrams
Because they take up such a small amount of physical space, circuit symbols can be used to make clean and detailed circuit schematics. This is especially important in design formats such as the PCB, where components often overlap one on top of another.
Understanding Circuit Behavior
Symbols represent not only physical components but also refer to their function and behavior. For instance, the arrow shows the circuit the direction of the current, thus helping the engineers to perceive how this circuit works.
Documentation and Standardization
Circuit symbols play a vital role in documenting electronic designs. This documentation would be archived and could later be referenced as needed for future projects, maintenance, and upgrades, resulting in continuity and reliability!
In other words, circuit symbols are powerful tools for making circuit diagrams and then applying them on a physical level, making them very useful in electronics and electrical engineering. Their capacity to streamline, normalize, and increase the design’s attributes creates excellent worth for professionals and learners.
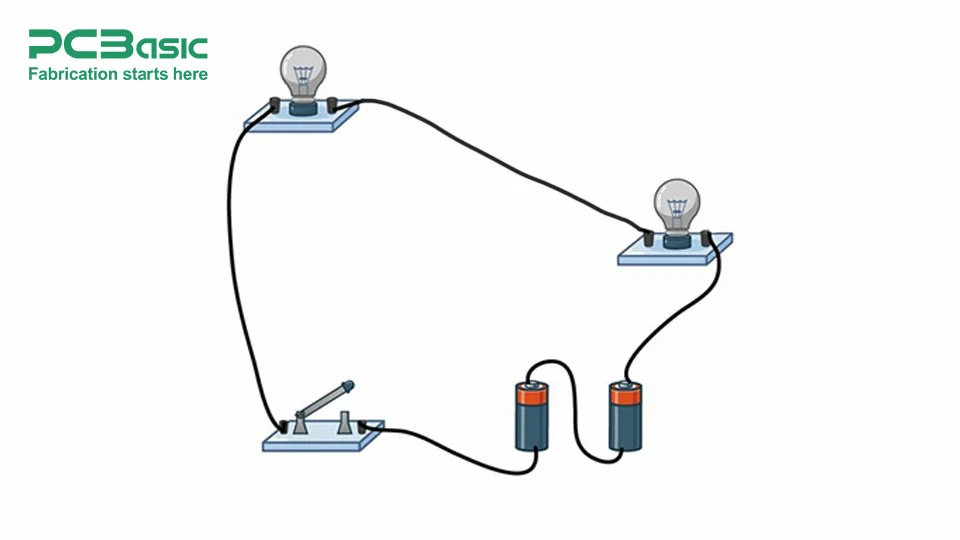
Circuit symbols are the base of electrical and electronic design, establishing a standardized language to increase the clarity of complicated systems and communication between industries. From aiding faster design and analysis to better troubleshooting and stimulating educational growth, circuit symbols offer far-reaching benefits. Detailed structures presented uniformly may allow certain circuits to be easily understood, passed from one designer to another, and improved. Today, these symbols retain their significance because they bridge the gap between technological theorization and implementation. Knowing these symbols is crucial for any person who deals with electronics in any way because those standardized symbols help to make every project completely accurate, effective, and creative.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
