Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > PCB Assembly Manufacturing Process | Circuit Board Assembly
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are the building blocks of modern devices that are increasingly found in the electronics industry. From smartphones to industrial equipment, PCBs are indispensable, serving as the critical framework for interconnecting electronic components. PCB manufacturing refers to making the bare board, and PCB Assembly (PCBA), on the other hand, takes these bare boards and turns them into fully functional electronic components.
Keep reading to explore PCB assembly manufacturing and commonly used techniques in depth.
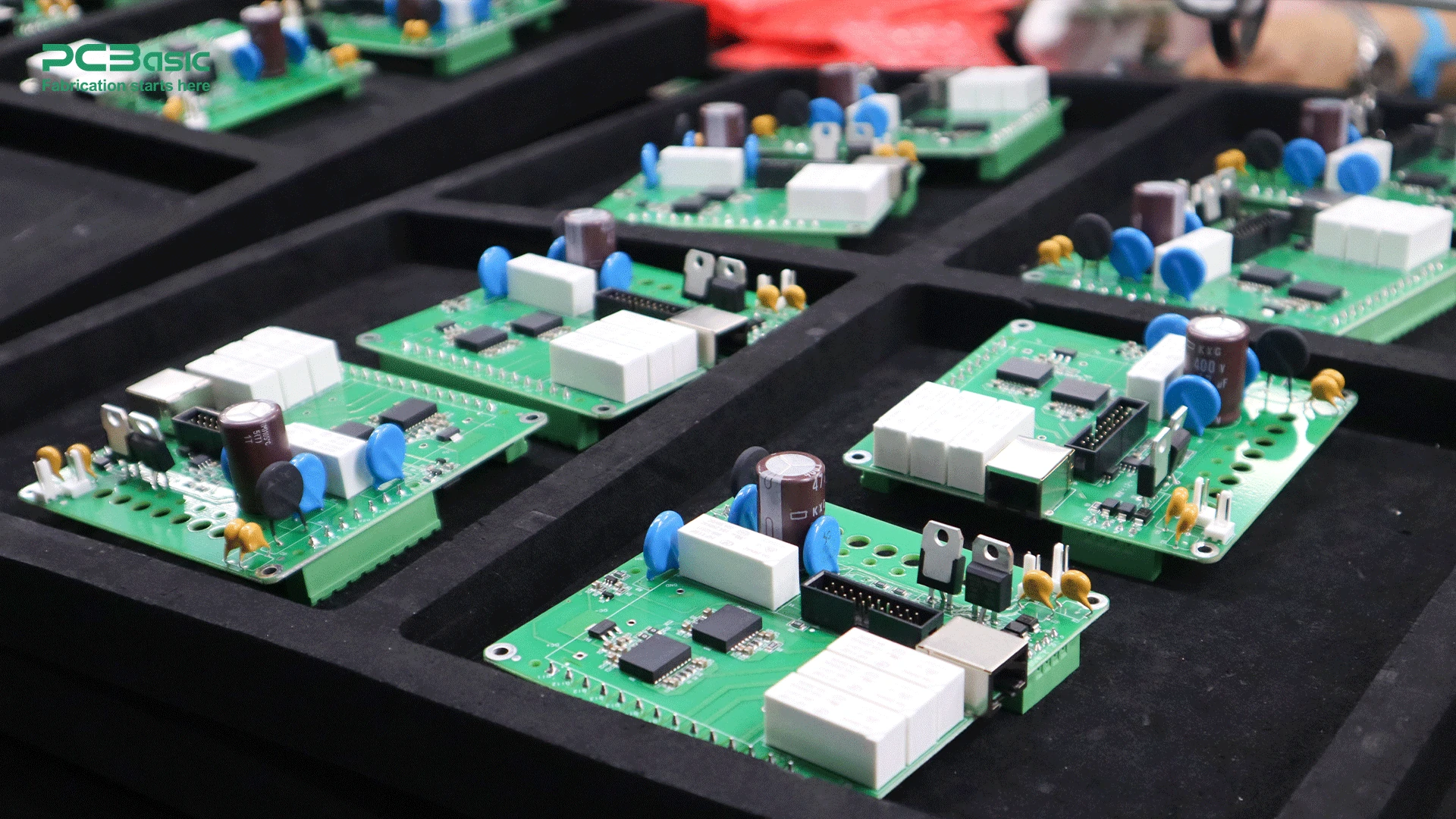
Since PCB is the basics of PCBA, we need to learn about the basic knowledge of PCB manufacturing before PCB assembly manufacturing.
PCB manufacturing is a process involving designing, fabricating and testing bare boards. These multi-layer structures are composed of copper traces, insulating materials and substrates to create an efficient electrical pathway for signal transmission between electronic components. These advanced circuits enable seamless interaction between components and form the basis of modern electronic devices.
When designing circuit boards, designers utilize computer-aided design (CAD) software to create detailed designs. They often use software such as Altium Designer, KiCad, or Eagle to generate a complete PCB schematic and layout design, including later component placement, signal routing, board layers number and configuration.
After the design of the circuit board is completed, in order to verify whether the design of the circuit board is feasible, whether the signal is complete, and to ensure that it meets the specified electrical and mechanical standards, the designer also needs to conduct simulation tests on it.
After making sure the board design works, it moves into the fabrication and manufacturing stage. During this phase, the design is transformed into a physical PCB through a series of precise steps, including photolithography, etching, drilling, lamination, and surface finish.
Once the circuit board manufacturing is completed, it undergoes a series of rigorous tests to ensure its quality. Common PCB testing methods include electrical testing, visual inspection, and reliability testing.
After completing the above steps, the production of circuit boards is complete. These tested circuit boards then proceed to the PCB assembly manufacturing stage, where components are installed and soldering processes are applied to transform them into fully functional electronic modules.
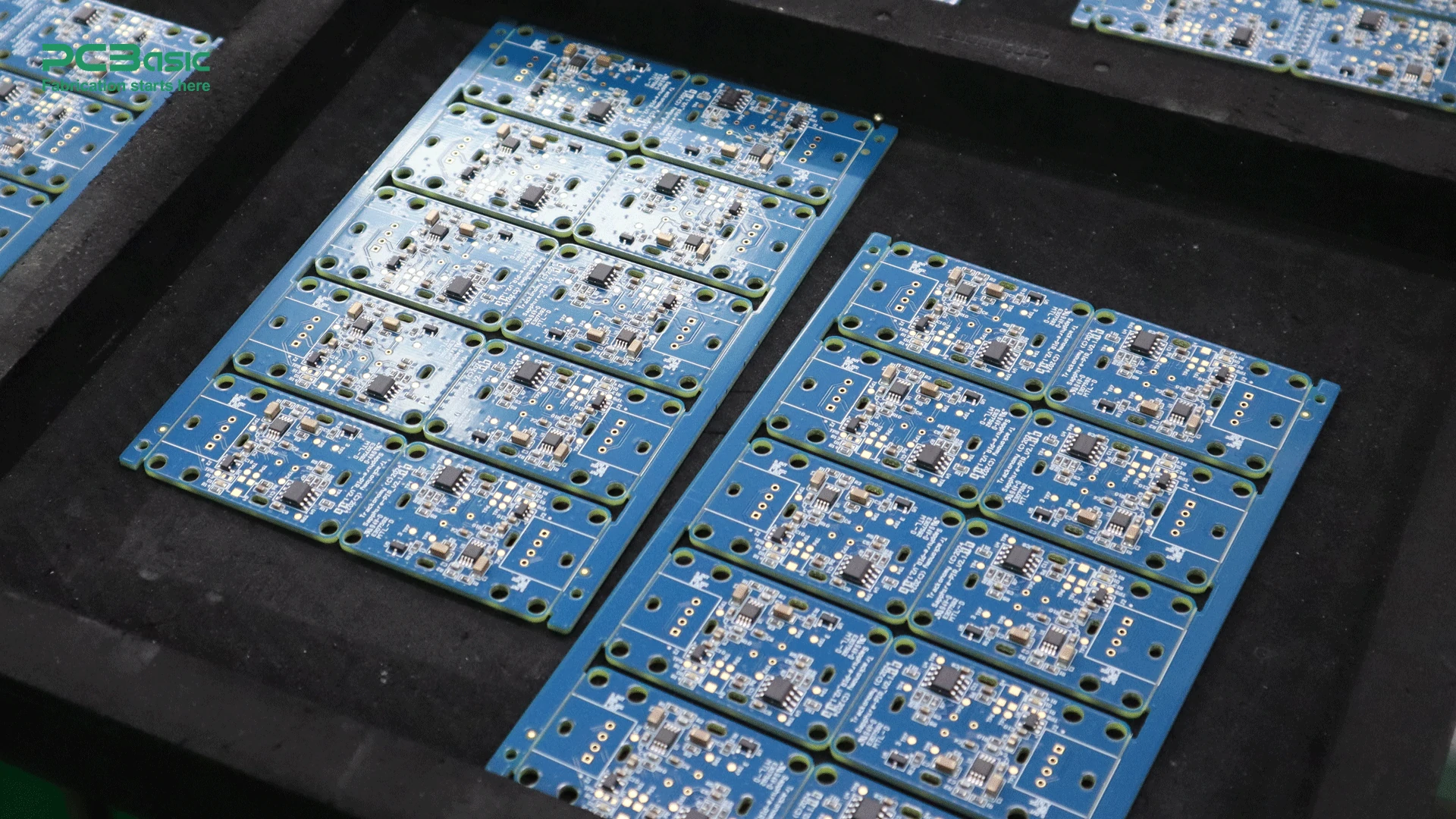
PCB assembly manufacturing is a complex and diverse process for the centralized installation of electronic elements such as resistors, capacitors, diodes, or microchips onto the already manufactured PCB. The core of PCB assembly manufacturing is not only concerned with the connection of electronic elements, one of its key features is to integrate these electronic components into the circuit board through a series of complex processes and technologies, so as to achieve complete electronic circuit functions. In other words, PCB assembly manufacturing is an important bridge between PCB manufacturing and finished electronic equipment, which directly affects the performance, reliability and functionality of electronic products.
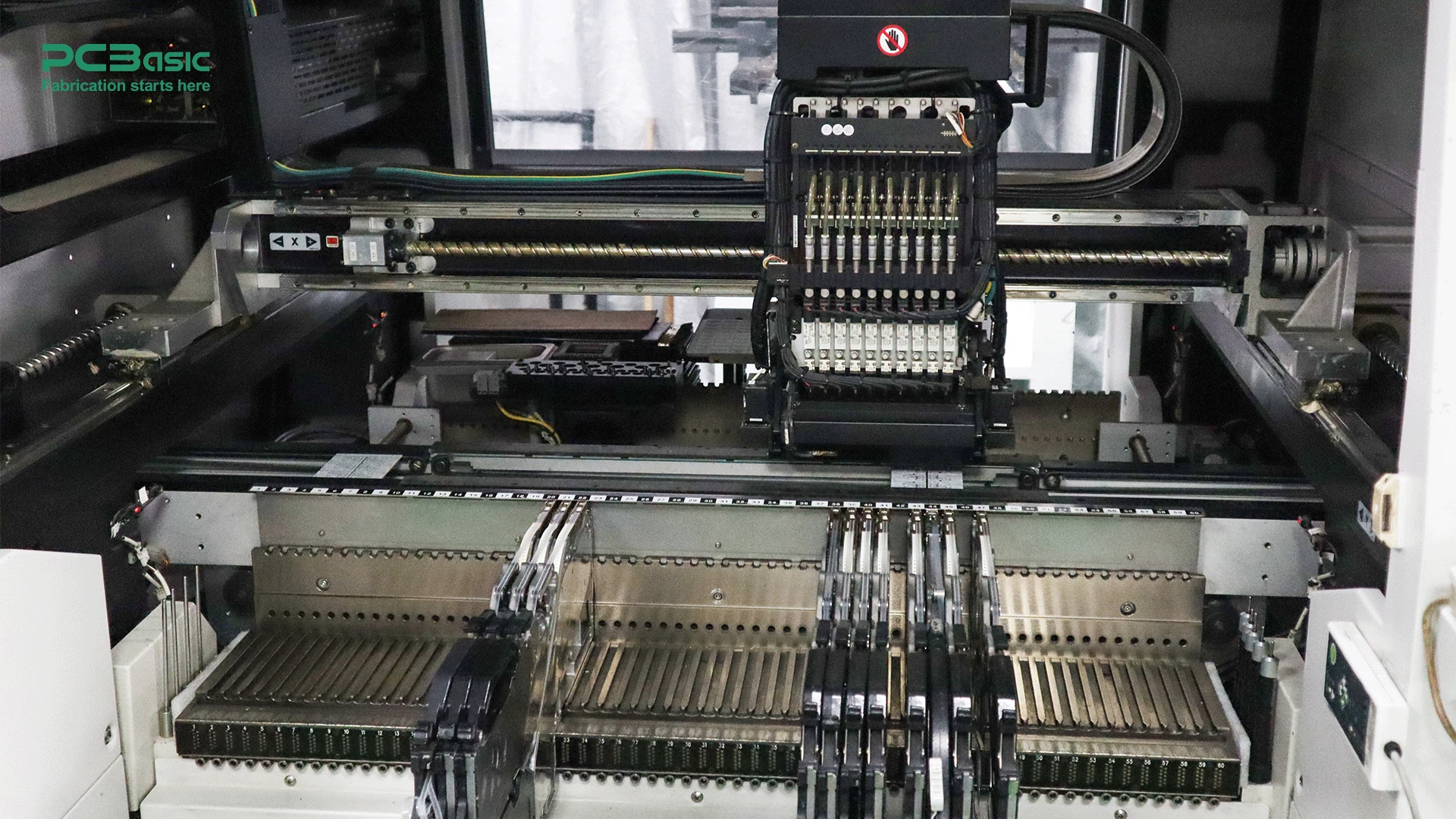
In the PCBA manufacturing process, while improving the manufacturing speed, the precision of the production is also crucial, because these factors directly determine the quality and production efficiency of the assembled products. Especially with the development of times, people's demand for miniaturized, high-performance and multi-functional electronic equipment is increasing, and advanced assembly technology is particularly important. Surface mount technology, through-hole technology and mixed assembly are common in the PCB assembly process.
SMT (Surface Mount Technology) is the most common and widely used method of modern PCB assembly, using the automated pick-and-place machines to directly mount electronic components onto the surface of the PCB. The emergence and popularity of this technology has greatly improved the production efficiency of PCB and the design flexibility of electronic products.
Through-hole technology (THT) is a traditional and mature PCB assembly method used to assemble components with pins. During through-hole assembly, the pins of the electronic components are inserted into pre-drilled holes on the PCB and are soldered to the other side of the board.
Mixed assembly is a method of combining SMT and THT when assembling a circuit board. By combining the advantages of these two technologies, mixed assembly can meet the multiple demands of modern electronics for high density, high performance and mechanical stability.
The PCB assembly process is critical to product performance, and ensuring accuracy and precision in the assembly process is critical. Let's take a look at the common steps of PCB assembly.
Solder paste application & Component mounting: If SMT is used for PCB assembly, the first step is solder paste application. In this process, the solder paste is applied to the position of the PCB where the components need to be assembled, and then the components are accurately placed on the circuit board by the automatic pick-and-placement machine.
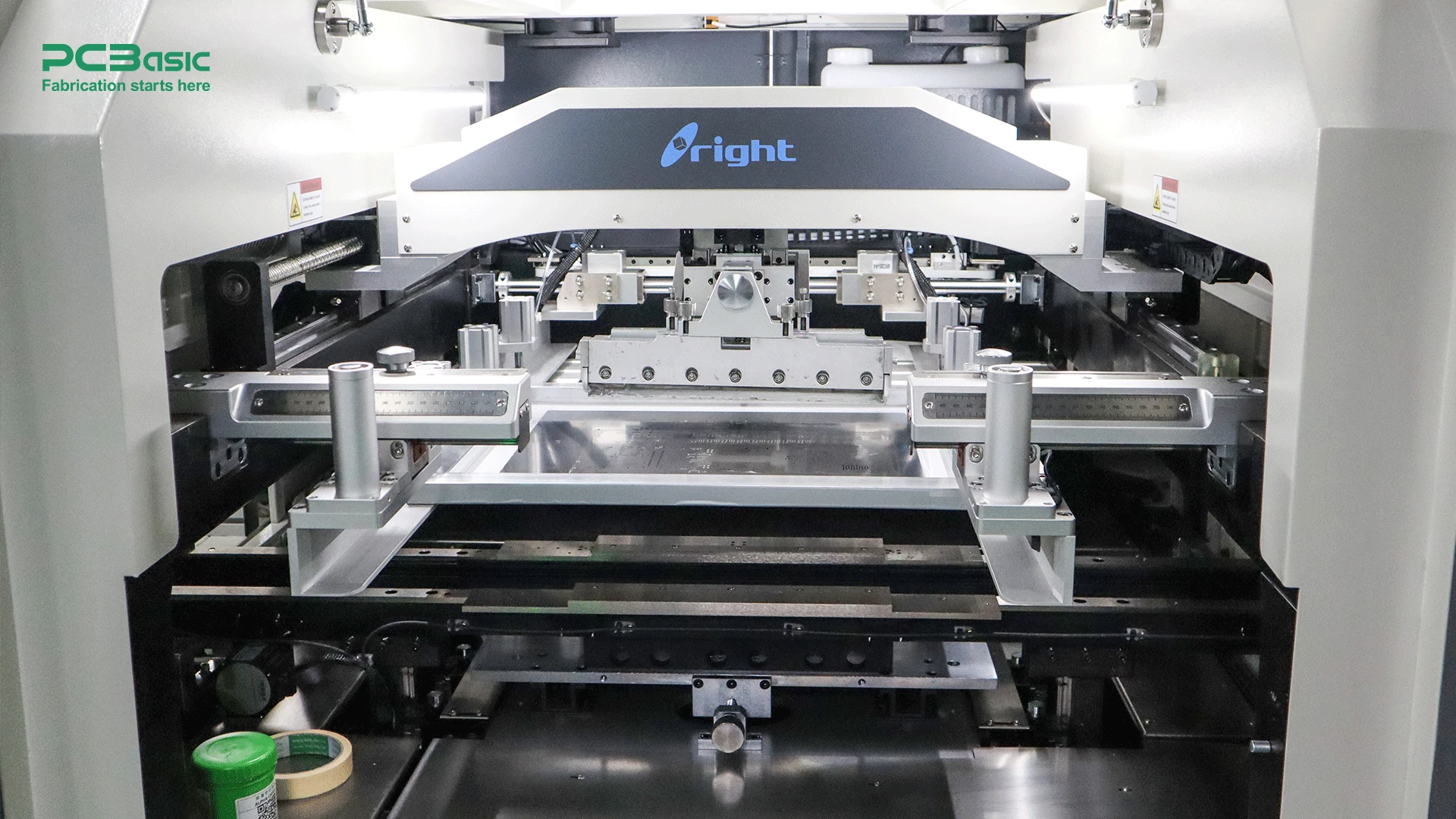

Insertion: If through-hole assembly is used, the component leads must first be inserted into the corresponding pre-drilled holes on the circuit board.
Soldering: When the components are ready on the circuit board, they need to be fixed by soldering. If SMT is used, the reflow soldering oven will be used, and the PCB will be heated in the reflow oven, melting the solder paste and fixing the components; if the THT is used, a wave soldering oven will be used to connect the through-hole elements to the PCB through a molten solder wave.
Inspection and testing: After the assembly of the circuit board, in order to inspect the solder effect and ensure the quality of the circuit board, it is necessary to inspect the assembled circuit board. Automatic optical inspection (AOI) and X-ray are commonly used. After checking the quality of the circuit, it is also necessary to test whether the circuit functions as expected, including electrical testing, thermal analysis and signal integrity.
After all the above steps are completed, a whole PCB assembly manufacturing is completed.
Circuit board assembly manufacturing plays an important role in the electronics industry, it is the key to the successful operation of electronic equipment. By integrating advanced technologies such as SMT, THT, and mixed assembly technologies, modern PCB assembly achieves high precision, reliability, and efficiency to meet the growing demand for miniaturized, high-performance, and versatile electronic products.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
