Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > LGA vs. PGA: What's the Difference and Which is Better?
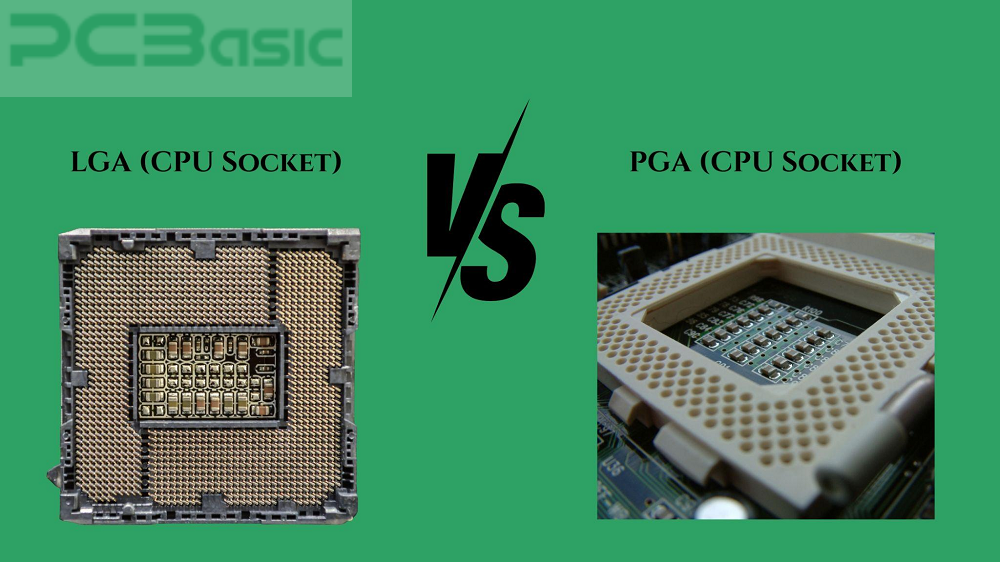
The most critical decisions when configuring or replacing a computer are the CPU choices and, accordingly, the matched socket type. Anyhow, attachment of the CPU to the motherboard is possible only due to a CPU socket, which mainly depends on system compatibility and performance. There are two most popular sockets, namely, LGA and PGA. However, it's worth noting that BGA (Ball Grid Array) is also used in embedded systems, though it's less common for consumer-grade CPUs.
LGA and PGA are opposites, especially for any gadget freak and a manufacturer of OEM or contract involved in PCB assembly. Intel LGA sockets protrude the contact pins from the motherboard. At the same time, those used by AMD set these pins directly onto the CPU. Such structural differences will take their toll on eventual installation procedures, durability, and general system performance. It's also important to mention that AMD has recently transitioned to LGA with their latest AM5 socket, marking a shift in their traditional PGA-based designs.
We'll break down the pros and cons of socket types and give you clear comparisons, so you know you're making the right choice for your needs. Whether hobbyist or pro, knowing which socket is suitable for what you do will increase the efficiency and longevity of your build.
 About PCBasic
About PCBasic
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
The socket of the CPU is the most essential component, which connects it to the CPU while allowing the power and data transfer between the two. It only performs the interface between the processor and the rest of the computer. The form of the socket is designed to provide a secure connection during which the CPU can effectively communicate with the system.
There are so many kinds of CPU sockets; each of the CPU socket types is designed to be used with a specific processor type. Among the most commonly used are LGA and PGA—LGA has contact pins on the motherboard, whereas PGA has pins on the CPU. Such a type of CPU socket plays a pretty important role in compatibility and system performance. The correct type will determine whether the CPU sits correctly and operates efficiently with the motherboard.
Generally, besides determining compatibility, the socket type affects how good, upgradable, or long-lasting the whole system would be. It is then essential to know about these differences between socket types when building or upgrading a PC for specific tasks—very heavy gaming or professional applications.
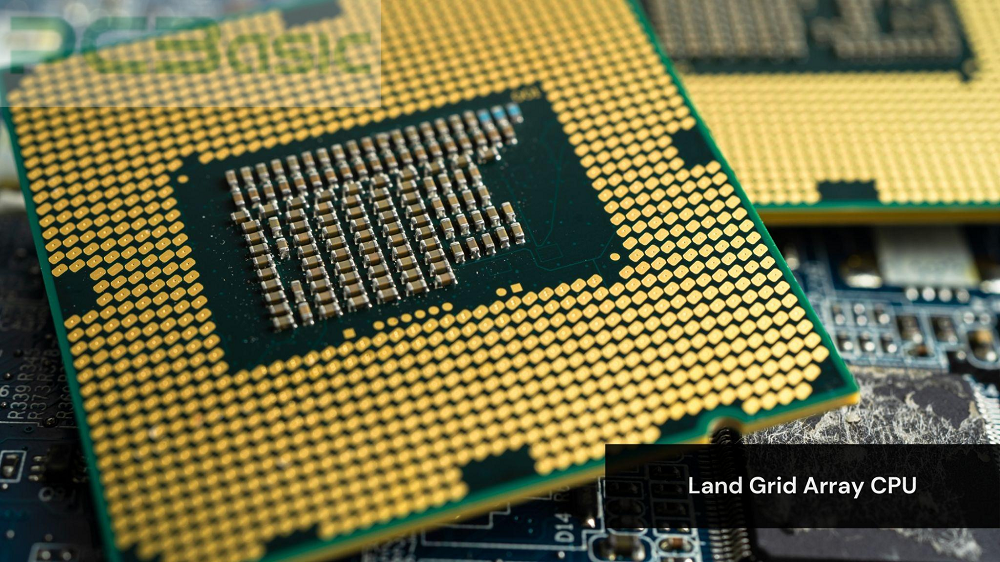

The LGA socket is a socket in the CPU where its pins are placed in the motherboard rather than on the processor. That is to say, in LGA, the contact pads of the processor sit on the pins of the motherboard, thereby touching the motherboard's pins to create a tight and efficient connection, unlike most other CPU types, such as the PGA where the pins are located on the processor.
LGA processors can be supported for a much greater number of pins, which is very useful for more complex processor types, thus enabling much faster data transfer and power delivery. Therefore, LGA has taken significant positions in most high-performance systems and servers. Among the leading manufacturers of central processors, Intel uses LGA sockets within most of its CPUs, including the highly popular Intel Core series. It’s also notable that AMD has adopted LGA for its higher-end processors like the Thread ripper and EPYC series and, most recently, the Ryzen 7000 series with the AM5 socket.
Although the LGA socket is suitable for power pins, the motherboard pins are very fragile and should be handled carefully during installation.
Advantages:
LGA has a much higher level of pin density and, hence, can deliver power and transmit data much more effectively. Therefore, it is very much suited for applications with higher performance. Secondly, it improves power stability, which is always adverse in case of power-related failures at a high level of application load. This is why land grid array processors are mainly employed in server environments and high-end systems where reliability is the most essential feature.
Limitations:
LGA design has its fair share of difficulties, however. The installation process is relatively more challenging, based on the fragile socket pins on the motherboard. The socket has to be handled with utmost care; if the pins get damaged, the CPU fails to function, and in extreme cases, permanent damage to the motherboard occurs. Thus, LGA sockets are not geared towards novice use compared to the other types of CPU sockets available. The LGA sockets are fittingly appropriate for experts, but the risk of damage is one significant limitation.
Hence, whether or not this LGA socket will be used in their system depends on its pros and cons for an informed and safe decision.
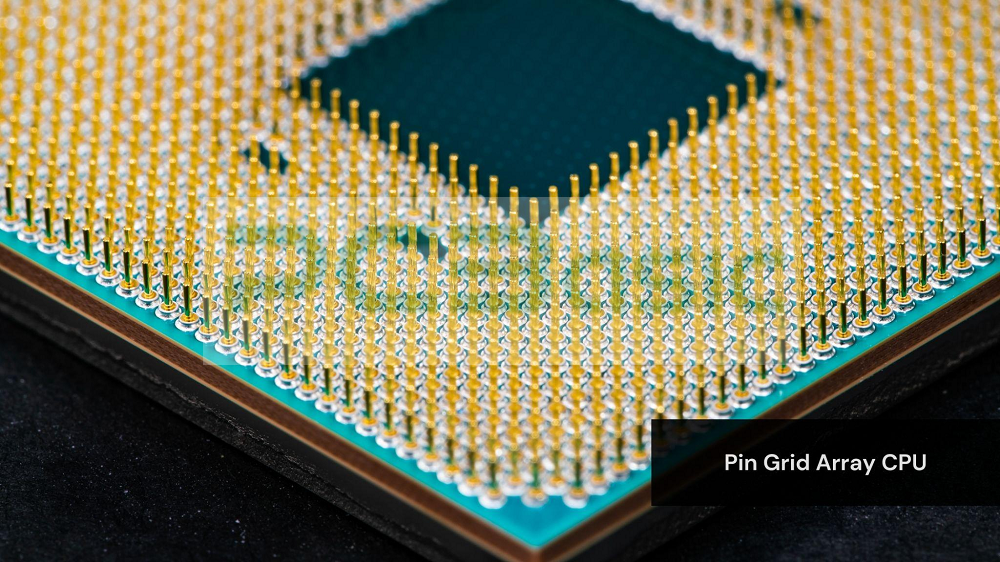
The CPU socket comes in one style, Pin Grid Array, or PGA; this processor has pins sticking out at the bottom that plug into holes in the motherboard socket. This contrasts with LGA, where the motherboard has the pins rather than the CPU. The tasks of the PGA processor design are to connect the CPU to an accessible location to replace or remove without hurting the motherboard.
Apart from this, AMD processors are also very popularly known for using pin grid array sockets, and even the popular models like AM4 were used in most consumer and gaming builds. However, it’s important to note that AMD is transitioning from PGA to LGA for their new AM5 platform.
The PGA design of the processor is simple to install but will be a bit costlier, though the pins of the processor may bend easily if not handled with utmost care. However, PGA will remain the first choice for customers who desire a reliable, easy-to-install product that will satisfy the demands of CPU sockets of low-cost and mid-range systems.
Such is the basic yet more efficient design that has made PGA unreplaceable in the market of CPUs, primarily for AMD-based computers, though this might change as AMD shifts towards LGA.
Advantages:
The PGA socket attaches faster. Since pins are present on the CPU, aligning is simpler. Thereby, it's less likely to be typed in error. Besides that, the PGA version of a processor is generally easier to manufacture and implement and, therefore, advantageous for budget-conscious users. It is faster and unlikely to damage the motherboard when attaching the CPU after its pins have been damaged to replace one.
Limitations:
The pins of a PGA CPU can bend and even break when handled; that's a nonfunctioning CPU. PGA sockets are larger and have fewer pins than LGA sockets, which have a far smaller number of connections and, consequently, even lower potential for performance. For users requiring high-density connections, LGA is generally the better option. However, AMD’s shift to LGA with AM5 suggests a new direction. Almost all consumer-level AMD processors used to employ the PGA design.
Although the PGA and LGA sockets are different types, their strength is different when it comes to usage. The LGA sockets are applied mainly on Intel processors with pins on the motherboard to achieve higher pin density. It is critical in high-performance systems such as gaming rigs and enterprise servers. It brings stability and offers strength and efficiency in transferring data. Installing might be a little tricky, and for beginners, there's a chance of bending the motherboard pins.
However, AMD primarily used PGA until their latest AM5 platform switched to LGA. They used to place the pins on the processor itself. Much less expensive and far easier to install, these configurations were prized by many frugal users and home deployments. It is not always comparable to LGA for potential performance; however, PGA is dependable and, for most mundane applications, more than adequate. The design is forgiving when installing the PGA, but pins on the processor are fragile and more likely to break if not handled carefully.
The socket type mainly depends on the performance requirements, cost, and feasibility. LGA is the best choice for those applications in which reliability and power delivery efficiency are highly important, especially for high-performance CPUs. Though LGA is advanced compared to PGA, it is relatively expensive. However, since the pins are on the motherboard, not the processor, the danger of damaging the CPU during installation is reduced.
With AMD’s shift toward LGA for its latest Ryzen and Thread ripper processors, both Intel and AMD are increasingly relying on LGA for future-proof systems. Socket type is, therefore, vital during the production of PCBs and the assembly of computers since it can greatly affect performance and compatibility levels.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
