Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > What is an IC Substrate? A Comprehensive Guide
Over the years, it has been evident that integrated circuits are becoming compact and smart with the increasing demand for the miniaturization of electronic devices. Moore’s law states that the number of transistors on a chip will double every two years. These challenges led the scientists to make more sophisticated integrated circuits and IC substrates. The IC substrate is made up of resin-based materials and then this substrate is used to create tiny electrical wiring inside the chip that connects the IC with the PCB or external system. The IC substrate makes it possible for the microchip to transmit the electrical signals between the chip and the circuit board.
The advancements in semiconductor technologies, like the invention of Ball Grid Array (BGA) packages and IC substrate, make it crucial for design engineers to grasp the fundamental and core concepts of IC substrate, their manufacturing process, and how and when to use IC substrate PCBs in their design. This article will help you cover all the fundamental and core concepts of IC substrate to level up your game!
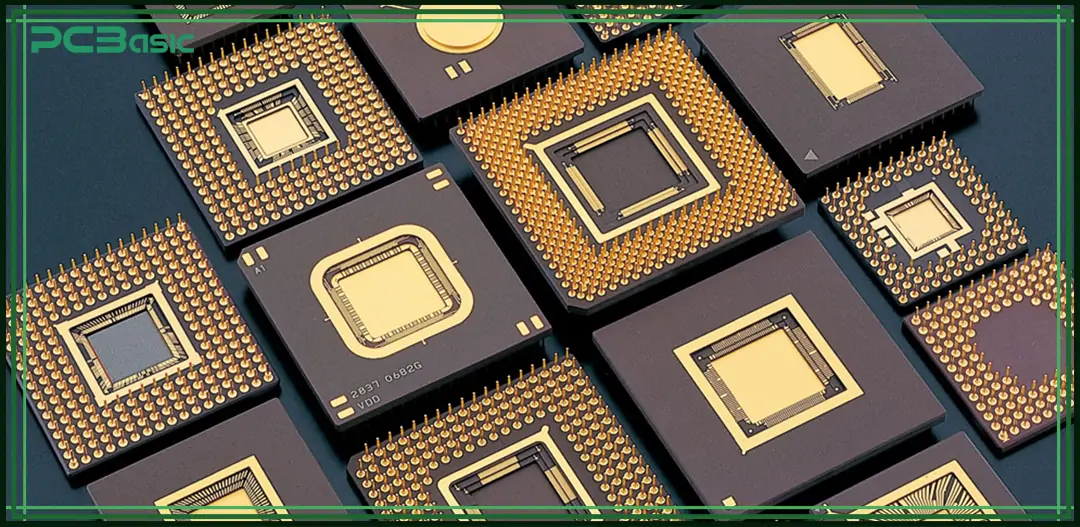
An integrated Circuit, or simply IC, is a circuit that has
transistors, diodes, resistors, and capacitors all fabricated in a small semiconductor
chip. An IC Substrate is a specialized platform that is used as a Base for the
physical and electrical support of integrated circuits. The substrate is a
material that acts as a shield for the IC and establishes the connection
between the IC and the PCB trace. This substrate is a collection of holes and
traces that form the electrical connection for the components inside the IC and
give them a path to communicate with the external world. In simple words, the IC
substrate is nothing but the internal wiring of an IC that connects the chip
with the PCB.
Different microchips have different sizes, performance, cost, packaging styles, thermal management, and cost considerations. Based on these factors, IC substrates can be classified into three main categories:
The IC substrate classification by packaging type focuses on the final structure or packaging style of the IC. Based on the packaging type, the IC substrate role changes, which divides them into different types.
1. BGA IC Substrate: BGA stands for Ball Grid Array and they use solder balls arranged in the form of an array to make an electrical connection. This type of IC substrate is specially designed to handle thermal dissipation. They are used in applications where better thermal performance and higher densities of pins are required.
2. CSP IC Substrate: Unlike the BGA packaging type, the Chip Scale Package (CSP) is used mainly for applications that require a lower pin count. These IC substrate packages are smart and lightweight, hence suitable for miniaturization products like consumer electronics, the Internet of Things, and wearable electronics.
3. MCM IC Substrate: MCM stands for Multichip Module, and as its name suggests, these IC substrates are primarily used to perform multiple tasks. Simply speaking, an MCM substrate has multiple chips combined in a single module, and each module serves a unique purpose. As the multiple chips are combined in a single package, these are suitable for applications that have space and weight constraints. The disadvantage of MCM IC substrate is that it is not suitable for harsh environments and extreme temperatures, as the multiple chips are packaged into a single module, causing heat dissipation.
4. FC IC Substrate: Flip Chip (FC) IC substrate is ideal for applications requiring low signal interference, better performance, and better thermal management. FC IC substrates good thermal management capabilities make them ideal for General processing Units (GPUs), RF communication chips, and machine learning processors.
IC substrates can be classified based on their material characteristics. Different material characteristics are utilized to achieve different functions.
1. Rigid board IC substrates: The IC substrate used to make rigid circuit boards uses resin and fiberglass material. The material characteristics of epoxy resin make it rigid and stable. They are used in traditional rigid boards such as BGA.
2. Flex Board IC Substrates: These IC substrates are made with polyimide material. They are used in applications requiring flexibility and space savings.
3. Ceramic Board IC Substrate: These IC substrates are made with aluminum material. These substrates are used in applications where high reliability is required.
IC substrates can also be classified in terms of bonding technology.
1. Wire Bonding: The simplest type of bonding is wire bonding, in which wires are threaded from the microchip using a machine.
2. FC Bonding: Flip chip bonding is typically done using the polymer adhesive. This method uses solder balls to facilitate the interconnections of chip and board contacts.
3. TAB Bonding: Tape automated bonding is done using pressure-sensitive adhesive by attaching the chip to the flexible substrate.
There are several key functions that an IC substrate serves. The following are some of the important key functions of the IC substrate.
1. The IC substrate acts as a bridge that connects the microchip and PCB by making electrical connections.
2. It provides mechanical support to the chip.
3. IC substrate plays a key function in managing heat dissipation and preventing overheating.
4. The IC substrate protects the microchip from external environmental conditions.
5. Their small size and light weight help designers manufacture smart devices.
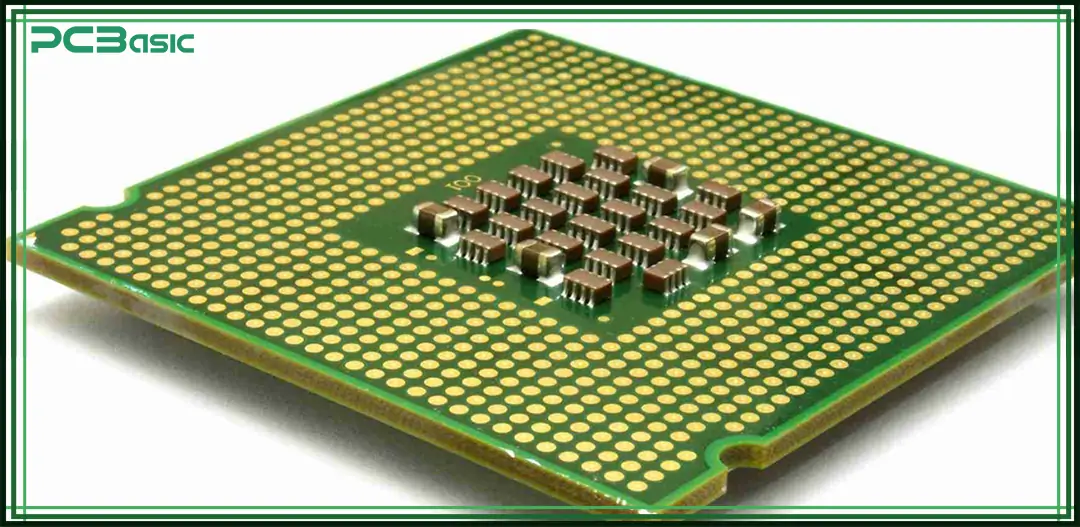
The IC substrate manufacturing process is a complex process that is being done in an extremely clean environment with no dust particles.
1. Material Selection: The very first step in the IC substrate manufacturing process is to choose the material. Normally, BT resin, ABF materials, or sometimes polyimide are used depending on the requirements.
2. Copper Patterning and Plating: The second and most critical step is the creation of electrical circuits on the substrate. Ultraviolet light and photoresist are utilized for the circuit design pattern. The developed pattern is then passed through the etching process to form the conductive paths.
3. Lamination: The final IC substrate is made by stacking and bonding multiple layers of materials together.
4. Drilling: Now, the holes and vias are drilled in IC substrate to make the way for electrical connections. The vias enable the electrical signals to pass through different layers.
5. Surface Treatment: The IC substrate is passed through the oxidation resistance process to protect it from environmental conditions such as moisture and temperature.
6. Quality Inspection: After the fabrication of the IC substrate, it goes through comprehensive quality testing to ensure that it performs as per the set specifications.
IC substrates are the fundamental blocks of IC technology. They are extensively used in all types of applications in which ICs are used.
1. Consumer Electronics: The IC substrates are widely used in consumer electronics products, such as they are used in mobile phone processors, due to their lightweight and high performance. Similarly, they are used in other consumer electronic devices, including memory devices and digital cameras.
2. RF Technologies: The RF technologies require high frequency and high-speed transmission, e.g., 5G. IC substrates are used in RF modules to meet these requirements while maintaining signal integrity.
3. Military Industry: Military applications like drones, missiles, and aircraft are operated in harsh environmental conditions. IC substrates used in these applications make them fit to withstand environmental conditions.
4. Automotive Electronics: Modern vehicles are becoming dense with electronic systems like navigation modules and autonomous driving systems. The IC substrate provides the way forward for implementing these technologies in modern vehicles.
5. Medical Devices: The IC substrate makes it easy for the designers to make extremely smart and compact devices like pacemakers for heart patients and other diagnostic equipment.
When designing the integrated circuits, it is important to consider important factors that can entirely alter the final results of your design.
1. Material Characteristics: The material characteristics can greatly alter the overall performance of the chip. It is important to know the exact material composition and substrate characteristics for your IC package.
2. Thermal Management: Thermal dissipation is an important parameter that must be taken into account while designing the IC substrate.
3. Signal Integrity: Signal integrity is a critical design parameter that must be considered in the design process of the IC substrate to ensure it is free from signal loss.
4. Reliability: The IC substrate must be reliable and withstand harsh environmental conditions.
The world is shifting towards miniaturization, and the IC substrate provides a way forward to achieve this milestone. The IC substrates are the fundamental components in integrated circuits. The IC substrates are the internal wiring of the IC that connects the chip with the PCB. Understanding IC substrate types, their manufacturing process, and design considerations is important for engineers to manufacture and design state-of-the-art integrated circuits.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
