Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > Game Emulator PCBA: Overview, Design, and Applications
A Game Emulator PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) refers to a custom-designed PCB that enables the emulation of game consoles on modern hardware. This PCBA integrates several electronic components like processors, memory, and input/output interfaces, which allow it to simulate the functions of older gaming consoles, enabling users to play retro games on newer platforms such as PCs, smartphones, or custom gaming systems.
The PCB acts as the backbone of a game emulator device, connecting and coordinating various components such as the microcontroller, memory modules, and peripheral interfaces. This integration allows the emulator to run classic video games that were originally designed for outdated or obsolete gaming systems.
Importance of Game Emulator in Modern Gaming
Game emulators provide significant value by offering backward compatibility for old games, allowing them to be played on modern hardware. This is particularly important for preserving the history of gaming, as many classic consoles are no longer in production or are difficult to find. Emulators bridge this gap by providing a means to relive old favorites on more accessible platforms.
The key benefits of using game emulators in both personal and commercial gaming include:
· Cost-efficiency: Users can play a wide variety of games without needing to purchase expensive, often rare, gaming hardware.
· Convenience: Emulators allow users to access a range of games from multiple consoles on a single device, making it easier to enjoy different games across different generations.
· Customization: Emulator software can offer additional features like game mods, graphics enhancement, and save state features that are not available on original hardware.
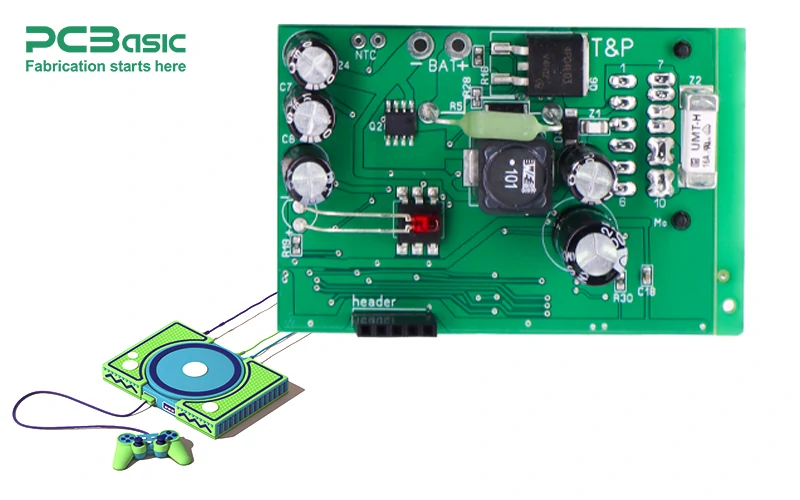
Microcontroller or Processor
The microcontroller or processor is the heart of the game emulator PCBA. It is responsible for running the emulator software, processing game data, and coordinating communication between the hardware components. The choice of processor is critical for the emulator’s performance, as it determines the speed and accuracy of the emulation. High-performance processors are essential for handling complex game logic and graphics processing.
Memory Modules (RAM, ROM, Flash)
Memory plays a crucial role in storing the emulator software, game data, and user settings. The emulator’s RAM is used to run the game and manage temporary data during gameplay. ROM is where the game’s code is stored, and flash memory is typically used for saving game progress or storing additional software. The combination of these memory types ensures that the emulator runs smoothly, with minimal lag or interruptions.
Input/Output Interfaces
The I/O interfaces provide the connections between the game emulator and the external peripherals, such as controllers, monitors, and audio systems. Common interfaces include:
· USB: For connecting controllers, keyboards, and other input devices.
· HDMI: For video output to monitors or TVs, supporting high-quality graphics.
· Audio out: For connecting to external speakers or audio systems to deliver immersive sound.
Power Supply Circuitry
The power supply is essential for the stable operation of the game emulator. Proper power distribution ensures that each component receives the correct voltage and current without noise or fluctuations. Efficient power management is crucial to prevent overheating and to support longer gaming sessions without performance degradation.
Audio/Video Processing Circuitry
Game emulators must process both video and audio signals to provide an immersive gaming experience. Audio circuitry ensures high-fidelity sound, while video processing circuitry manages rendering graphics and handling visual output. These components need to be optimized for high resolution and smooth frame rates to accurately reproduce the original game’s graphics and audio.
Cooling Mechanisms
Given the high-performance demands of game emulators, thermal management is vital to prevent overheating, especially when running demanding games or during extended gaming sessions. Effective cooling solutions, such as heat sinks, fans, or thermal pads, help maintain optimal temperatures, ensuring the stability and longevity of the components.
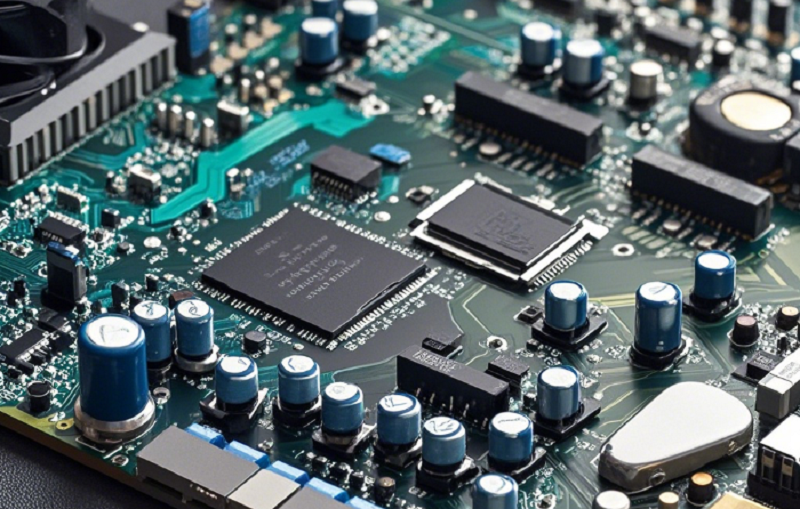
Signal Integrity
Signal integrity is crucial for game emulators, as high-quality graphics and sound require clear and reliable signal transmission. Poor signal integrity can result in graphical artifacts, audio distortion, or general system instability. Careful PCB layout design, proper grounding, and shielding are essential to minimize signal loss, interference, and crosstalk, ensuring that the emulator delivers high-fidelity outputs.
Power Distribution and Efficiency
Efficient power distribution ensures that power is provided consistently and reliably to all components. A well-designed power plane minimizes noise and reduces the chance of power-related issues that can affect the emulator's stability. Designers must carefully consider the voltage requirements for different components, such as processors, memory, and I/O interfaces, to ensure that power is distributed efficiently and without interference.
Connectivity and Compatibility
Ensuring compatibility with a wide range of gaming peripherals and video/audio devices is a key design consideration. The game emulator PCBA must support various controllers, displays, and sound systems commonly used by gamers. Using widely accepted standards such as USB and HDMI guarantees that the emulator will be compatible with most devices, improving the user experience.
Emulator Software Compatibility
The hardware design must support various emulator software platforms, such as RetroArch and MAME, which can emulate games from a variety of legacy consoles. The game emulator PCBA needs to provide the necessary processing power and memory to ensure smooth operation of the software. Additionally, designers need to ensure that the board’s architecture can handle different emulation scenarios and software configurations.
Thermal Management
Effective thermal management is essential to prevent overheating, especially in powerful systems that simulate the performance of older game consoles. Heat sinks, fans, and other cooling solutions must be strategically placed on the PCBA to dissipate heat from critical components like processors and power supply circuits. This ensures that the emulator runs smoothly even during extended use.
Component Selection
The selection of durable and reliable components is critical for ensuring the long-term performance of the game emulator. Components must be able to withstand the demands of continuous use without degrading or failing. Factors such as component ratings, thermal tolerance, and reliability in various environments should guide component selection to ensure the emulator can deliver reliable performance over time.
Retro Game Emulator PCBA
Retro game emulator PCBA is designed specifically for emulating classic gaming consoles, such as the NES, Sega Genesis, and SNES. These PCBs typically use less powerful processors and memory configurations compared to modern systems but are optimized to replicate the hardware behavior of older consoles. The goal is to run legacy games with high accuracy, preserving the original gaming experience while providing modern conveniences like HDMI output or wireless controller support.
Modern Game Emulator PCBA
Modern game emulator PCBA is built to emulate more recent gaming consoles like the PlayStation, Xbox, or Nintendo Switch. These systems require more powerful hardware and software emulation due to the complexity of modern games. The PCBA for these emulators must support high-definition graphics, 3D rendering, and larger memory capacities. It also integrates more advanced features, such as high-fidelity audio, faster processors, and enhanced connectivity to ensure a seamless experience with newer gaming systems.
Cross-Platform Emulator PCBA
Cross-platform emulator PCBA supports multiple gaming systems, allowing users to emulate a wide variety of consoles, both old and new, on a single device. These versatile emulators can run games from systems like NES, Sega Genesis, PlayStation, and Xbox, providing the user with a unified gaming experience. Cross-platform emulators often involve sophisticated software that can adapt to the unique hardware configurations of each platform, and the PCBA design needs to handle different system requirements, such as power and video processing, efficiently.

Home Entertainment Systems
Emulator PCBA is commonly integrated into home consoles or media centers to enable retro gaming on modern TVs and monitors. These systems allow users to play classic games from their old consoles using contemporary hardware. They often support multiple emulators and games from various platforms, offering a wide library of games in a single, convenient system. With the right connectivity options, such as HDMI and USB for controllers, these emulator setups become a popular addition to entertainment systems, blending nostalgic gaming with modern technology.
Arcade Game Machines
In the commercial arcade industry, emulator PCBA plays a significant role in running classic arcade games. By using emulator PCBs, arcade machines can offer a wide variety of games without the need for multiple original game boards. These machines often feature retro-styled cabinets but with modern hardware that runs game emulators for a variety of classic titles. This allows arcade operators to easily switch between games and offer a broader selection of titles, enhancing customer experience while reducing hardware costs.
Educational Tools
Game emulator PCBAs are also used in educational settings for game development courses, coding workshops, and retro gaming lessons. Students can learn programming and system architecture by understanding how game emulators work. The emulator serves as a practical tool for understanding how different hardware interacts with software, allowing learners to experiment with and develop their own emulation projects. Additionally, game emulators are often used in computer science education to teach coding, algorithm development, and game mechanics.
Portable Devices
Game emulator PCBA is frequently integrated into handheld gaming devices for portable retro gaming experiences. These devices provide gamers with the ability to play their favorite old-school games anywhere, without requiring bulky original hardware. Thanks to the compact and efficient design of emulator PCBAs, these portable systems can easily accommodate a range of classic games and controllers, offering a convenient and nostalgic gaming experience on the go.
Virtual Consoles
Cloud gaming and virtual consoles are rapidly growing sectors where emulator PCBA plays a role in streaming games to users over the internet. Emulators integrated into virtual console systems allow players to access a wide range of games from various platforms without needing to own the original hardware. By using emulator PCBA, cloud gaming platforms can stream retro games to users via devices like smart TVs, computers, and smartphones, providing easy access to legacy games without the need for physical game cartridges or consoles.
Why Choose PCBasic for Game Emulator PCBA?
PCBasic, with its expertise in PCB assembly, is a trusted partner for designing and manufacturing high-quality, reliable, and customizable PCB assemblies for game emulators. Our experience in handling complex designs, ensuring signal integrity, and providing efficient power distribution means that we can deliver emulator PCBAs that are both durable and performance-driven.
Partnering with PCBasic for Your Gaming Needs
PCBasic offers comprehensive support in the design, manufacturing, and integration of emulator PCBA for various gaming applications. Whether you are a developer looking to build your own emulator system or a manufacturer looking for reliable assembly services, PCBasic provides a full range of solutions to help you bring your game emulator projects to life.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
