Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > White PCBs | A Comprehensive Guide
Printed circuit boards come in a variety of colors, with the most classic and most common being the green circuit board. Different color circuit boards may not be fundamentally different in function, but their production process, visibility, heat dissipation performance and appearance effect will still be different. The choice of PCB color is not only related to the appearance and image of electronic products (especially for transparent shell products), but also closely related to product application scenarios, brand positioning, maintenance convenience and other factors.
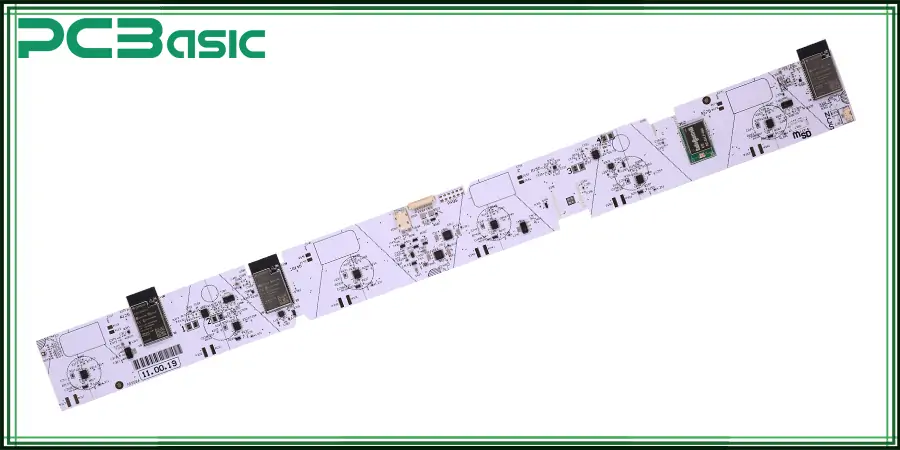

Next, in this article, I will introduce you to white PCBs. In recent years, white PCBs have gradually gained favor in a number of industries - not only for their simple and beautiful appearance, but also for their excellent performance in specific applications. White circuit board refers to a printed circuit board with a white solder resistance layer, which plays a key role in protecting the pad and improving reliability in addition to the visual appearance.
A white PCB refers to a printed circuit board that uses a white solder mask outside the surface solder pad. Its main structure is the same as the traditional green PCB, including copper coating, substrate, pad, screen printing and other parts, the only difference is that the solder resistance color of the white PCB is white. Although the color seems to be a small change, in terms of visual effects, design matching, optical applications, etc., the advantage of white PCBs is very prominent.
The color of the circuit board mentioned earlier is mainly determined by the color of the solder mask. So next, let's take a closer look at the solder mask layer! Solder mask layer is a protective coating covering the surface of PCB copper foil, common colors are green, white, black, red and so on. In addition, the solder mask has the following functions:
Prevent welding short circuit: The solder mask layer can effectively isolate non-welded areas, reduce the risk of bridging, and improve the reliability of soldering. If there is no solder shield protection during patch welding or wave soldering, there may be a short circuit between adjacent pads due to excess solder, resulting in circuit failure.
Improve product insulation performance: solder resistance ink has good insulation characteristics, can effectively prevent leakage, electric shock or static damage between the lines, so that the safety and stability of the entire circuit system can be enhanced.
Improve the appearance and recognition of the finished product: the solder mask layer gives the PCB a unified and clean appearance (green, white, black, purple, etc.), which makes the circuit board easier to identify, classify and maintain, but also convenient for subsequent screen printing and quality detection.
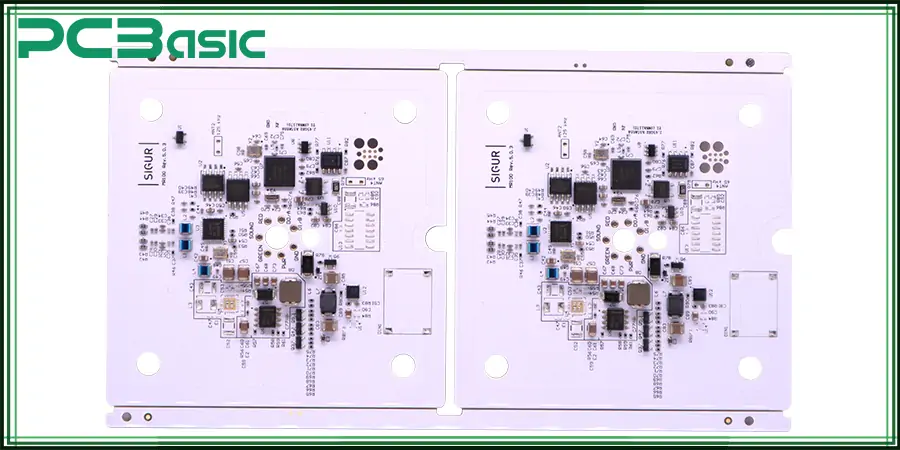
High Reflectance
Compared with dark PCB, white PCB has better light reflection performance. This performance makes white PCBs ideal for applications that require high light utilization, such as LED lighting, backlight displays, and optical systems.
Beautiful Appearance
White PCBs have a clean, modern visual experience and are widely used in high-end consumer electronics, medical devices, and smart home products, especially in product designs where the board may be visible (e.g., Motherboards designed for side or full transparent PC cases).
Brand Differentiation
For businesses that want to distinguish themselves in appearance or brand identity, the use of white PCB boards can create a unique visual style, in line with high-end or minimalist product design concepts.
Poor Contrast
The white background of the white PCB makes the copper line and the silk screen logo difficult to distinguish, which enhances the difficulty of manual detection, debugging and repair.
The manufacturing process is more demanding
The white solder resistance layer is prone to discoloration (such as yellowing) during reflow or UV exposure, which can affect aesthetics and performance if the material formulation or process control is not appropriate.
Limited supply of materials
White solder resistance materials are not common, and not all PCB factories routinely have white solder resistance materials. This is likely to lead to longer delivery times or higher costs for small batch white PCB production.
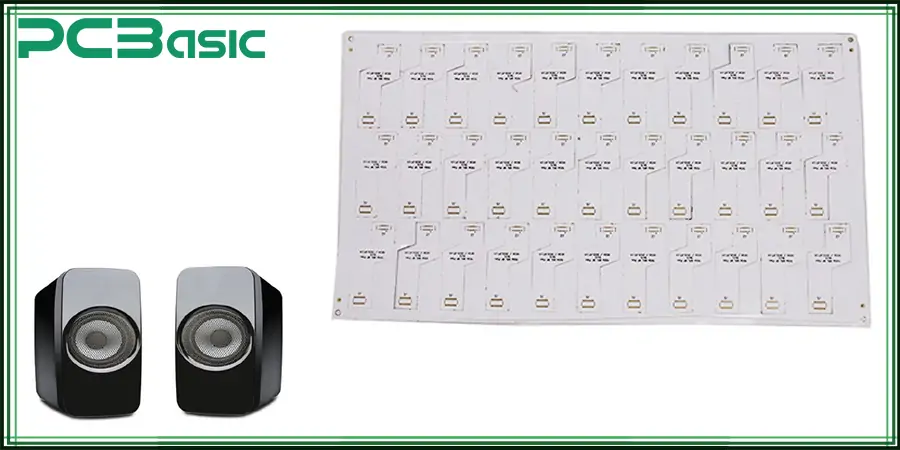

The application of white PCB is very wide. Because of its high reflectivity, it is widely used in LED lighting products; the reflection efficiency of light is improved, and the overall light efficiency of LED lighting products will also be enhanced. Because of the beauty of white, white circuit boards are widely used in high-end consumer electronics products (such as personalized computer hosts have many white PCB motherboards), which is already an important carrier of differentiated appearance design. At the same time, white PCB motherboards are also widely used in on-board display and lighting modules in electric vehicles and autonomous driving systems to enhance the internal visual experience. In short, white PCBs are becoming more and more common.
In the last paragraph, we have introduced the solder mask layer that causes the different colors of the circuit board. Now, let's take a look at the difference between white PCBs and other colored PCBs.
|
Category |
White PCB |
Green PCB |
|
Appearance |
Modern, clean look |
Traditional, standard appearance |
|
Reflectivity |
High, ideal for LED and lighting applications |
Average reflectivity |
|
Visibility |
Low contrast, not ideal for manual inspection |
High contrast, easy to inspect and repair |
|
Manufacturing |
Higher technical requirements, limited materials |
Mature process, widely available materials |
|
Typical Use Cases |
LED lighting, visible consumer electronics |
General industrial and consumer electronics |
|
Category |
White PCB |
Black PCB |
|
Appearance |
Clean, futuristic, tech-oriented look |
Premium, minimalist, professional |
|
Reflectivity |
High, suitable for lighting designs |
Low (absorbs light), not ideal for optical use |
|
Visibility |
Traces and pads are hard to distinguish |
Very low contrast, difficult to inspect |
|
Thermal Behavior |
Good (depends on material) |
Poorer heat dissipation, absorbs heat quickly |
|
Typical Use Cases |
Lighting products, visible PC builds |
High-end DIY PCs, visible enclosures |
|
Category |
White PCB |
Blue PCB |
|
Appearance |
Clean, neutral |
Stylish, distinctive |
|
Reflectivity |
High, good for optical use |
Average reflectivity |
|
Visibility |
Low contrast, harder for inspection |
Moderate contrast, easier to inspect |
|
Market Adoption |
Niche, application-specific |
Mid-range, seen in custom electronics |
|
Typical Use Cases |
LED panels, optical modules |
Industrial control boards, custom electronics |
|
Category |
White PCB |
Purple PCB |
|
Appearance |
Clean, futuristic |
Unique, highly distinctive |
|
Reflectivity |
High |
Average |
|
Visibility |
Low visibility for manual inspection |
Moderate contrast, attention-grabbing color |
|
Material Cost |
Moderate (custom solder mask required) |
Higher cost, less commonly stocked |
|
Typical Use Cases |
Medical, lighting, optoelectronics |
Premium custom electronics, small-batch designs |
How to choose the right color PCB? The following aspects are some factors that can be considered when choosing colors:
|
Evaluation Criteria |
Description |
Recommended Suggestions |
|
1. Function vs. Aesthetic Design |
Choose PCB color based on whether the product prioritizes performance or appearance. |
For functionality, choose green; for aesthetics, choose white, black, blue, or custom colors. |
|
2. Inspection & Maintenance Efficiency |
PCB color affects pad/trace visibility, impacting manual or automated inspection. |
Green offers high contrast and easier inspection; white and black are harder to inspect. |
|
3. Product Type & Operating Environment |
Different industries or usage scenarios require different PCB colors. |
Use white for LED lighting and medical devices; avoid black in high-temperature conditions. |
|
4. Brand Customization Needs |
Select PCB color to match brand identity and enhance visual appeal. |
White or black for DIY PC builds; blue or vibrant colors for educational kits. |
If the product involves light reflection, aesthetic design, consumer visibility, etc., choosing a white PCB is very reasonable. Examples include the following industries: LED industry, computer/gaming equipment, industrial control equipment, medical equipment, automotive electronics.
The choice of board color is not only a choice of design, but also a choice of functional advantages in some specific applications. Whether you're designing lighting modules, next-generation medical devices, or aesthetically pleasing consumer electronics, a white PCB board may be a more appropriate solution. If you are considering transitioning from a green or black PCB to a white PCB board, please contact PCBasic, a manufacturer with over 16 years of industry experience!

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote