Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > Everything You Want To Know About Stitching Vias
Stitching vias are not complex. They are just little holes within a printed circuit board (PCB). These holes join various layers of the PCB board. You can consider it as small conduits. They ensure the proper functioning of your circuit.
Stitching vias are very important in modern PCB design styles. They assist in maintaining good signal quality and strength. They improve fast circuits with high frequency—Stitching Vias smooth signal functions without causing any error.
Let’s think of PCB as a multi-layer structure. These layers each have a purpose, but something must mediate them all. What are vias? In simple terms, in PCB, the vias are like the dowels or rods that hold the layers from moving apart. They form conduits for signals to flow. The purpose of installing vias is to guarantee its performance. You must know that in any electric device, uninterrupted current flow is everything.
So if you consider its technical side, vias are round holes. PCB manufacturers drill them on circuit boards. Subsequently, they have a copper coating. However, it is important for you to understand the functions of these layers. Vias provide a smooth connection among these layers. If there are no signals, or the signals are poor, the device won't work properly.
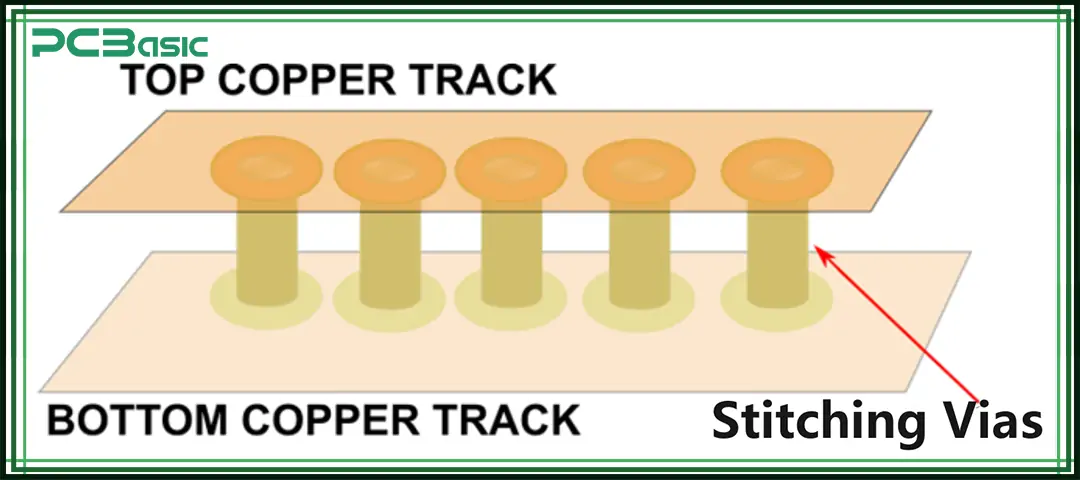
You have already read that vias are the basic source of providing electric connection to pcb layers. These vias are of different types. Moreover, they have a critical role in printed circuit board design. In this section, you will read which type of vias is best for your project.
A PCB is not a simple machine. It comes with several traces and other useful components. These parts make your circuit board strong and keep it connected to the power source. In constant ground stitching, PCB companies add extra vias to multiple parts.
Thermal Via Stitching improves heat sinking power on the board. All these Vias in large ground planes increase the area of carrying heat hence it runs cooler.
Shielding Via Stitching is used in PCBs due to EMI issues, especially on high-frequency RF or MS signal circuits. It is formed from single or multiple rows of ground stitching vias stitched around the area of a huge copper plane in the region of high-frequency track.

Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
Although stitching vias are small, they hold massive benefits in PCB design. Now, it is high time to focus on the major advantages of their usage.
Accuracy of signals also plays a decisive role to manufacture any electronic device. Recently, many people have found that if the signals transmitted get distorted, their devices need to be repaired. Ground stitching vias and via shielding help to give good and distinct signal patterns.
Making holes connected to one another, called stitching vias, ensures that messages can travel without stopping. Stitching vias, and also holes on a printed circuit board (PCB), reduce the chance of signals getting cut off or causing major disturbances. Embroidering vias are important for your gadget to work properly because they keep the signals complete, especially when you have high-speed circuits.
A solid ground plane in circuits works similarly to a good starting point for your circuit. It makes sure all operations work properly. Maintenance of this foundation is largely made possible through stitching vias.
In electronic boards or PCBs, ground planes are connected with stitching vias. These are on different layers of the board. This connection helps prevent ground bounce. A ground bounce happens when signals lose their path for returning. A sturdy ground plane stops noise and other issues from coming into your circuit.
Temperature is a harmful adversary for electronics and equipment. It builds up layers that can damage parts and shorten how long your device works properly. Through thermal via stitching, one can adequately control heat.
Sewing vias assist in spreading out heat across the PCB. They allow the warmth to move from hot spots evenly. This avoids overheating and keeps your components cool and secure all through.
PCBs need to be tough. They are under mechanical strain due to such factors as bending, vibration, and at times shocks. Through holes via plugging enhances the physical stability of a board.
Stitching vias provide an enhanced capability to the PCB. They are used to interconnect different layers. It minimizes the possibility of cracking or breaking. This boosts the actual strength your PCB can take without getting damaged by physical force.
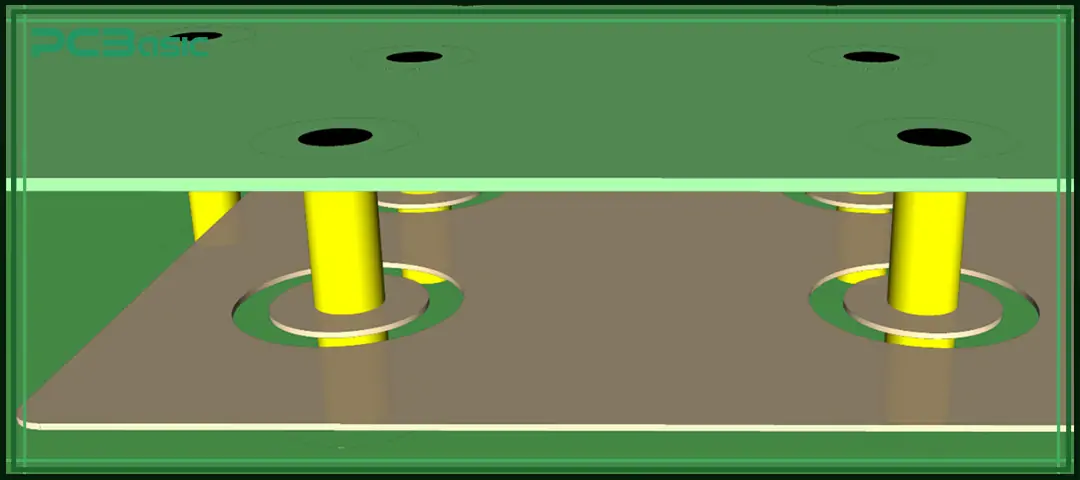
Stitching vias control via impedance. They are important in fast circuits. Stitching Vias keeps it steady in high-speed circuits. Here is why stitching vias matter for via impedance.
● Stitching vias keep signals clear.
● They make signal paths smooth and steady.
● Stitching vias link ground points near the main via.
● They stop unwanted signals from interfering.
● Stitching vias reduces signal noise.
● They also keep signals from crossing to other paths.
● This helps in tight circuit spaces.
● They are important in high-speed circuits.
Via Stitching is a technique to stitch larger copper areas on different layers. It makes vertical connections through the board structure. This process is useful in achieving low impedance and shorter return loops.
|
Characteristics |
Via Stitching |
Via Shielding |
|
EMI Protection |
It is good at high frequencies |
It blocks electromagnetic radiation |
|
Complexity |
You need more vias |
It has a higher via count |
|
Frequency |
It is good for high-frequency applications |
Decent for frequency ranges |
|
Flexible Design |
You can easily apply it |
Careful planning is necessary |
|
Cost |
Production cost is a little high |
High cost |
In the end, you have read every basic thing about vias in PCB. In summary, before you design a PCB, vias are crucial so you can make a PCB for required applications. PCB manufacturers can easily control signal quality, noise, and stability.
PCBasic is a top-rated circuit board manufacturer. Our company incorporated the latest technology to install quality vias the following design. We can provide PCB with a faster turnaround time.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
