Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > SMD LED Polarity: How to Identify It?
Accurate SMD LED polarity is the most crucial factor in PCB manufacturing and assembly. Correct SMD LED polarity can be determined to facilitate the expected function of the specific component and eliminate failure during its usage. This is because an incorrect polarity may lead to circuit interrupts or total system interrupts. Therefore, there is nothing as important as the polarity indicators and signs.

A study showed that 35% of the total damage to PCB elements can result from incorrect connections. It has been found that this is responsible for time-related delays, increased cost, and in some cases, a substandard end product. In the electronics sector, there is an excellent example of this problem where different polarity alignments lead to system efficiency losses as well as more rework.
This article will provide a framework for learning about the SMD LED polarity, mount, marks, tests, and symbols with examples. When you finish reading it, there should be no doubt in your mind about how to approach the LED polarity or areas to avoid when using PCB. This information is highly beneficial in preventing manufacturers' problems and maintaining the quality of the product at any time.
 About PCBasic
About PCBasic
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
Recurrent in electronics, polarity refers to the qualitative identification of the direction of current in any constituent part. One needs to take into consideration that simple items like LEDs, diode or capacitors have anode and cathode. Polarity should be carried out correctly since it may lead to circuit breakdown.
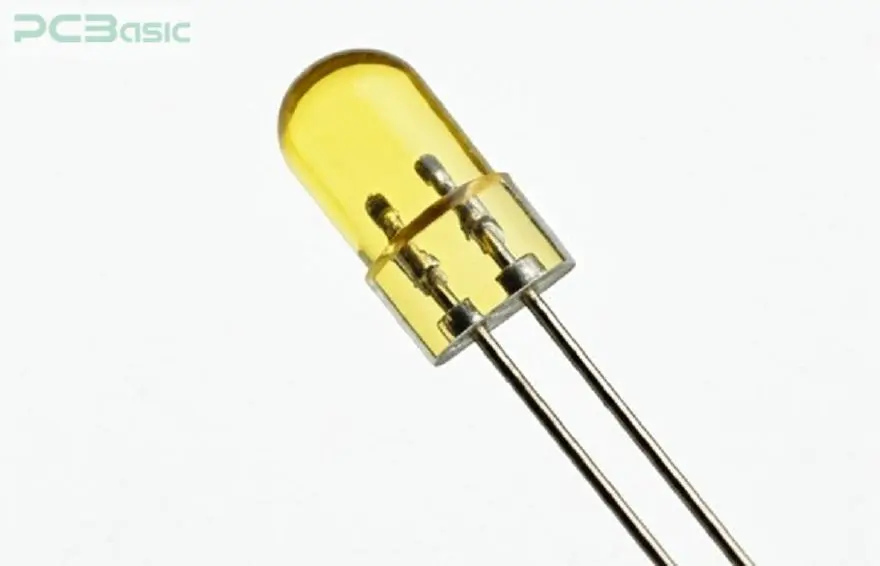
SMD LED polarity determines the direction of the current flow. Usually, the cathode of the LED is indicated by the use of dots or a flattened end of the metal lead. Understanding these polarity markings is essential for assembly procedures.
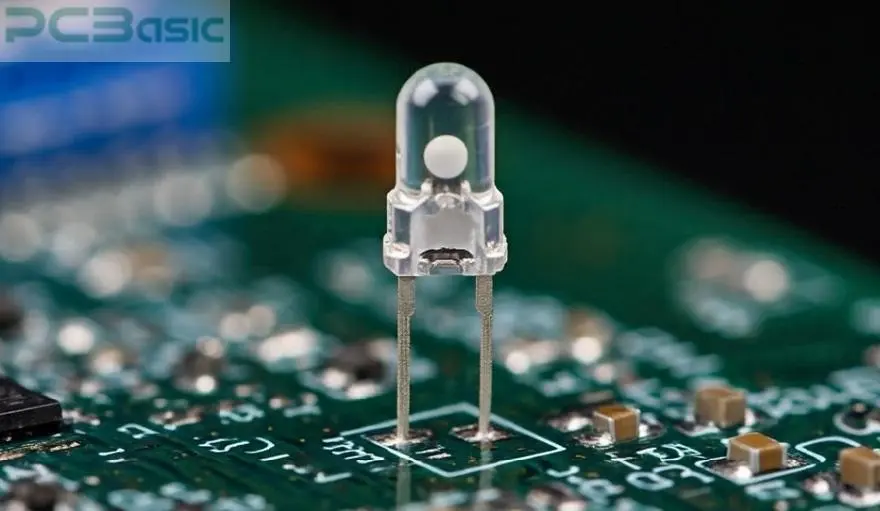
Accurate SMD diode polarity minimizes damage to the component and achieves a failure rate reduction of up to 35%. Diode polarity marking on the PCB reduces cases of wrong placements, leading to enhanced production quality on the PCB diodes.
To identify SMD LED polarity, one first needs to know what anode and cathode are.
1. What is an Anode?
An anode is the positive electrode of an LED. Through it, current can enter into the LED from the power source to make the device glow.
2. What is a Cathode?
The cathode is the negative terminal of the LED, through which current is outflowing when exiting through the anode. The step is to determine which of the leads is cathode since putting the LED in the wrong polarity will damage it.
Some Approaches:
1. Length of the Leads: A convention is that the anode is always the positive electrode, which is the more extended terminal; the cathode is the negative electrode, the shorter terminal.
2. Notch or Flat Edge Markings: As most of SMD LEDs come in packages with no distinguishable flat on the cathode side, polarity is often marked with a flat edge.
3. Multimeter Testing for Polarity: Polarity can be tested using a multimeter – when the positive probe of the multimeter is connected to the anode, the LED should turn on.
4. Schematic Symbol Clarification: In the symbolic diagrams, the arrow pointing out of the symbol shows the direction of the cathode.
These methods help in assessing the SMD LED polarity correctly to avoid some disastrous errors on PCBs. Another point would be that an LED polarity's orientation needs to be stated so that there are no mistakes on the assembly line.
SMD LED polarity marking on the PCB is crucial since it guides users on the proper manner of device installation. In some cases, one can distinguish a dot, notch, or flat plane on the body of the LED, and this points towards the cathode. Such visual instructions are essential, especially for technicians who use the product. This makes it easy for them to elaborate on how they can relate to anode and cathode. Hence, it avoids problems that arise from wrong polarity on some of the components used.
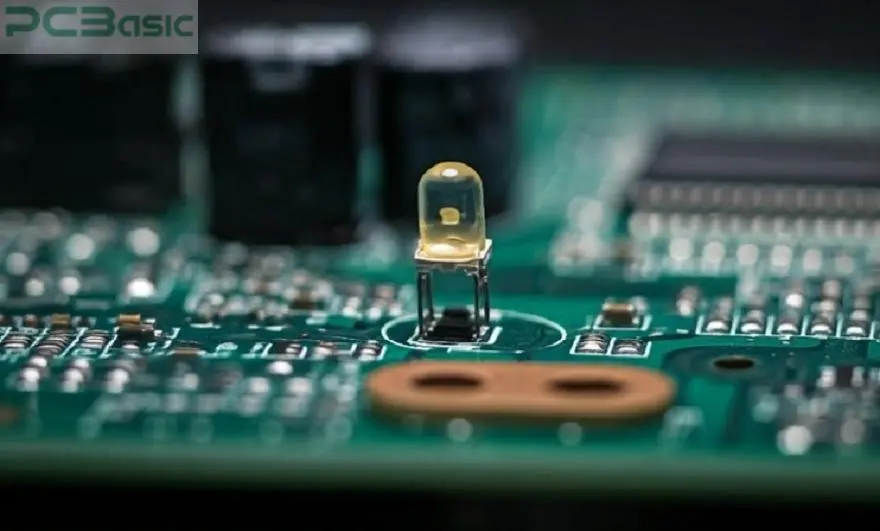
Aside from evident stamps, diode polarity marking on the PCB should also be labeled so that polarity is evident with the positive and negative poles. It can be used as standard symbols for the identification of such terminals. Failure to appreciate and abide by such markings poses a significant risk to achieving efficient utilization of PCB assembly. It can also help in improving the reliability as well as performance of the final product.
Many operational and hardware-related issues can arise if LED pairing is not conducted correctly.
1. No Illumination or Dimming: The immediate consequence of wrong SMD LED polarity is that the LED either does not emit light or only has a low brightness. The disruption of flow is caused by LEDs being built in a certain current direction. This confuses the design of the LED if you swap the anode and cathode. Also, the LED can indicate flicker or work irregularly depending on certain conditions; therefore, the performance is unpredictable.
2. Potential Component Damage: Satisfactory connections of polarity enhance LED efficiency and lead to less damage to the parts of the PCB. If it is maintained continuously, the problem of reverse voltage causes thermal stress to arise. This can lead to the LED being burnt out or the circuits being damaged. Under severe circumstances, this leads to short circuits, while in electronic assembly, it translates to a wider failure.
Thus, SMD LED polarity is critical as the efficiency of electronic devices depends on this polarity.
The SMD LED polarity must be correct when assembling to avoid some problems affecting functionality. Here are some concise methods:
LED Orientation and Placement on PCBs:
Make sure that the anode is correctly situated regarding the second terminal- the cathode whose own symbol is placed on the PCB. In this way, mistakes can be avoided and there is uniformity in terms of the placement of the facilities, through using placement guides.
Avoiding Common Mistakes in SMD LED Assembly:
1. Flat Edge and Notch Misinterpretation: You should be able to read the flat edge or notch on the LED properly to get the polarity connections right.
2. Cross-referencing Schematic Symbol: Before soldering, check the schematic symbols for the SMD LEDs to define the anode and the cathode ends.
3. Importance of Clear Markings on PCB Layout: Make proper use of clear polarization markings on the PCB to point towards the correct LED polarity. Preventing the installation of mismatched devices also helps standardize such terms to avoid confusion.
These methods help to reduce many problems associated with polarity. Consequently, it increases the reliability of products in general.
Knowledge about the polarity is a crucial requirement for SMD LEDs. It is also crucial for diode direction marking and SMD components such as SMD diode polarity and SMD capacitors polarity. It is very important to understand the polarity of the SMD diode and the SMD capacitor since improper connection of them is fatal to all devices.
SMD diodes control current and its direction, thus polarity identification is critical.
1. How do you Determine the SMD Diode Polarity?
It has a band on the SMD diode that points to the cathode.
2. SMD Diode Identification of Polarity on PCB
Diode polarity marking on PCB typically has a symbol or a flat line which is used to point at the cathode. Careful markings help to install circuits correctly, thus increasing reliability.

The capacitors also call for specific polarity to have the best performance as needed.
1. How to Identify SMD Capacitor Polarity?
The capacitors also call for specific polarity to have the best performance as needed. For SMD capacitor polarity, check for a stripe or flat bar on it. This bar reflects polarity and in case there is no stripe present; use a multimeter to confirm polarity.
2. SMD Capacitor polarity symbol on printed circuit board
Identification of the negative terminal is crucial. The capacitor polarity symbol on the PCB prevents wrong polarity connections.
Cost reduction and improved device reliability can be achieved by observing standard diode polarity marking on PCB and capacitor polarity symbols on PCB.
The life and the efficiency of the electronic devices depend upon SMD LED Polarity. Thus, it is an important parameter to take into consideration. Many problems could arise due to a faulty LED polarity, i.e., lighting dysfunction, damage to the components of the electronic devices, and assembly problems. There are various measures that manufacturers can take with an aim of avoiding polarity problems. These methods include multimeter testing as well as looking at the orientation symbol of capacitors on PCBs. In other words, the correct polarity marking aids the developers in gaining quick and easy assembly, hence getting devices that are more effective for use and have long service delivery.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
