Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > PCBA Components: The Foundation of Electronics Manufacturing
In the world of electronics, PCBA manufacturing is at the core of creating devices that power modern life. But what drives the functionality of a PCBA board? The answer lies in its components. This article delves into the common PCBA components, their functions, and their importance in the Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) process. We also address frequently asked questions, such as what does PCB stand for in electronics, what is a PCBA, and the differences in PCB vs PCBA.
Understanding the distinction between PCB vs PCBA is key in electronics:
When someone asks, what does PCB stand for in electronics, or what does PCBA stand for, the answer lies in this transformation. The PCB is the skeleton, while the PCBA is the fully functional body.
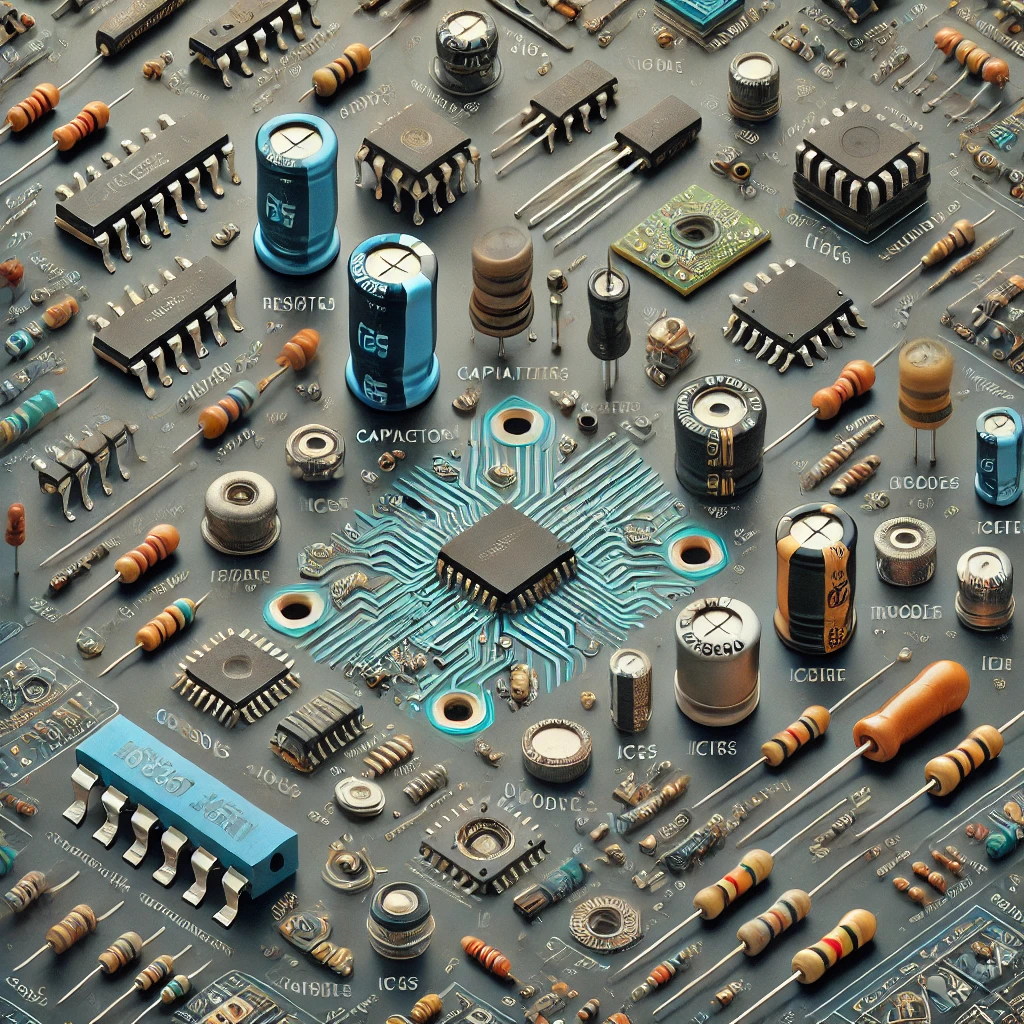
Resistors are fundamental components in every PCBA board. They limit and regulate electrical current, ensuring circuits function safely and efficiently. In PCBA manufacturing, resistors are categorized by their power ratings and resistance values, which are measured in ohms. Whether you’re learning what is PCB in electronics or studying the PCBA meaning, resistors are among the first components you'll encounter.
Capacitors store electrical energy and release it as needed. They are crucial for stabilizing voltage and smoothing power supply fluctuations. In Printed Circuit Board Assembly, the most commonly used capacitors are electrolytic and ceramic disk types. Their capacitance is measured in farads (F), while their voltage retention is measured in volts (V). Capacitors are indispensable in PCBA manufacturing, enabling seamless device operation.
Diodes ensure that electrical current flows in a single direction, protecting circuits from reverse currents. Each diode features two terminals: the cathode and the anode. This directional control is a vital part of the PCBA meaning, as it safeguards the functionality of various devices. Understanding the role of diodes helps clarify what is PCB in electronics and how PCBA boards handle power regulation.
Integrated Circuits, also known as microchips, are the brains of a PCBA board. These silicon-based components contain tiny resistors, capacitors, and transistors, enabling them to perform everything from simple tasks to complex calculations. ICs highlight the evolution of PCBA manufacturing, where compact, efficient designs are essential to modern electronics.
Transistors are semiconductor devices used to amplify or switch electrical signals. Their three-terminal design makes them easy to identify on a Printed Circuit Board Assembly. Whether in amplifiers, processors, or signal modulators, transistors play a critical role in bridging the gap between PCB vs PCBA.
While resistors, capacitors, diodes, ICs, and transistors are foundational, other components are often essential in Printed Circuit Board Assembly:
These components further illustrate the complexity and precision involved in PCBA manufacturing.
Every PCBA board relies on its components to perform specific tasks. These components define the functionality, reliability, and efficiency of electronic devices. Whether you’re assembling a simple circuit or working on advanced PCBA manufacturing, the quality and placement of components are critical.
The heart of every Printed Circuit Board Assembly lies in its components. From resistors and capacitors to ICs and transistors, these elements power the devices that shape our world. Understanding the PCBA meaning, the differences between PCB vs PCBA, and the roles of key components answers questions like what is PCB in electronics and what is a PCBA.
By mastering the fundamentals of PCBA components, you gain insight into the complex, fascinating world of electronics manufacturing.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
