Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > PCBA OEM Services: A Full Guide to PCB Assembly, Design, and Production
What is PCBA? PCBA stands for Printed Circuit Board Assembly. It refers to the process of assembling electronic components onto a printed circuit board (PCB) to create a functional circuit. The main components involved in PCBA are:
· PCB: The base substrate, typically made of materials like FR4 or flexible PCB, serves as the foundation for mounting electronic components.
· Electronic Components: These include resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits (ICs), transistors, and connectors.
· Soldering: A process that ensures electrical connections between components and the PCB, using techniques such as wave soldering, reflow soldering, and hand soldering.
PCBA plays a crucial role in modern electronics, enabling everything from simple consumer electronics like mobile phones and laptops, to advanced industrial equipment, automotive systems, and HDI (High-Density Interconnect) PCBs.
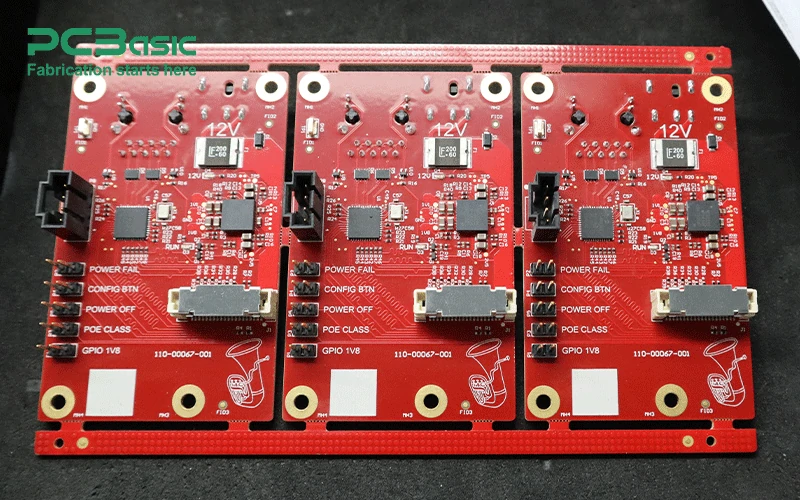
OEM stands for Original Equipment Manufacturer. In the context of PCBA, OEM refers to companies that manufacture products based on the designs and specifications provided by another company. In this case, the OEM typically manufactures the PCB boards and assembles them with electronic components to produce a finished product. OEMs in the electronics sector offer custom solutions that cater to specific client needs.
The role of OEM in the electronics manufacturing supply chain is pivotal, as OEMs handle the design, sourcing, assembly, and quality control of PCBs, offering cost-effective solutions and quick turnaround times.
PCBA OEM services provide a complete solution for companies looking to outsource their PCB assembly. This includes everything from designing the PCB layout, sourcing the components, manufacturing the multi-layer PCB boards, and finally assembling the components into a fully functional circuit board. Shenzhen PCBA OEM companies, renowned for their manufacturing expertise, are leading the way in offering OEM customized PCBA boards that meet international standards.
Step 1: Design and Specification In the first step, customers provide the design files (such as Gerber files, BOM (Bill of Materials), and specifications for components, layout, and manufacturing standards). The OEM then validates the design for manufacturability and may recommend modifications to optimize the process. The PCB layout and component placement must be carefully planned to ensure the board is functional and meets design requirements.
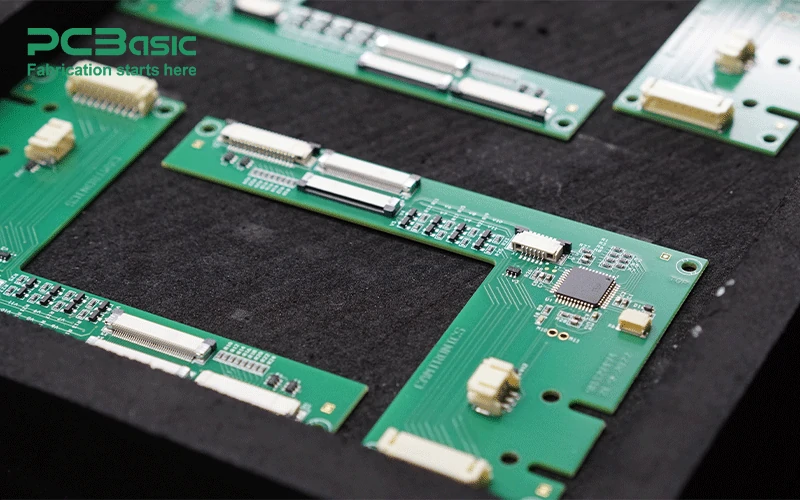
For complex designs, such as HDI PCBA or flexible PCBs, the design process becomes more intricate, requiring specialized knowledge in PCB routing and layer stacking.
Step 2: Material Sourcing Once the design is validated, the next step is sourcing the required materials. This involves procuring:
· FR4 (common for standard PCBs)
· Multilayer PCB boards (for complex and high-density designs)
· Flexible PCB materials (for applications requiring flexibility, such as wearables or mobile devices)
· Electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, and ICs.
Choosing reliable suppliers is crucial to ensure quality and reduce the risk of component failures. Shenzhen PCBA OEM manufacturers are well-known for their strong relationships with global suppliers and high standards of quality assurance.
Step 3: PCB Manufacturing The PCB manufacturing process includes etching, layering, and surface finish to create the base board. The process varies depending on the type of PCB:
· Single-sided: Components are mounted only on one side.
· Double-sided: Components can be mounted on both sides of the board.
· Multilayer: More than two layers are used, with internal layers that allow for more complex circuit designs.
For high-density designs, HDI PCBs are manufactured using fine lines and micro vias, ideal for high-performance applications like smartphones and computing devices.
Step 4: Component Sourcing & Mounting Components are sourced, and the pick-and-place machine is used to position the components accurately on the PCB. Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Through-Hole Technology (THT) are used for mounting components. Automated soldering methods like reflow soldering are commonly used for surface-mount components, while wave soldering is typically used for through-hole components.
Shenzhen-based PCBA manufacturers often specialize in flexible PCBs, which require specialized assembly techniques to ensure reliability in compact designs.
Step 5: Testing and Quality Control After assembly, testing is critical to ensure that the PCBA functions as intended. Different types of tests include:
· In-circuit testing (ICT): Ensures all components are correctly placed and soldered.
· Automated Optical Inspection (AOI): Identifies visual defects such as soldering issues or component misplacement.
· Functional testing: Verifies the functionality of the assembled board.
PCBA OEM companies ensure that all boards meet the necessary quality standards such as RoHS, CE, and UL certifications, guaranteeing compliance with global regulations.
Step 6: Final Assembly and Packaging Once testing is complete, the boards are assembled into their final product (encapsulation, connectors, enclosures). Packaging is done carefully to protect the boards from ESD (electrostatic discharge) and physical damage during transportation. Proper packaging is especially important for flexible PCBs and multi-layer PCB boards, which are more sensitive than standard boards.
Full Turnkey PCBA:
A full turnkey PCBA service means the OEM handles the entire process, from designing the OEM PCBA to sourcing materials and components, assembling, testing, and delivering the final product. This is ideal for clients looking for a one-stop solution to streamline their production.
Partial Turnkey PCBA:
In a partial turnkey PCBA service, the customer supplies some components (e.g., specific ICs or connectors), while the OEM handles the rest. This option provides flexibility and can be more cost-effective for customers who have specific component requirements.
Prototype and Low-Volume Production:
OEMs also offer services for prototyping and low-volume production runs, allowing companies to test their designs before scaling up to mass production. This is especially important for companies developing new products or seeking validation for their OEM customized PCBA boards.
High-Volume Production:
For clients needing large quantities, high-volume production ensures that the PCBA OEM has the capacity and equipment to efficiently manufacture and assemble thousands of boards. With automated assembly lines and advanced SMT technology, these services cater to industries like consumer electronics, automotive, and telecommunications.
Testing and Post-Production Support:
Even after the assembly is completed, PCBA OEM providers offer post-production support like design validation, rework services, and after-sales testing to ensure the reliability and longevity of the product.
Single-sided PCBs: These are the simplest type of PCBs, with components mounted on only one side of the board. They are used in low-complexity applications where space is not a primary concern.
Double-sided PCBs: These PCBs have components mounted on both sides, allowing for a more compact design and increased functionality. They are commonly used in consumer electronics and industrial applications.
Multilayer PCBs: These PCBs consist of multiple layers of conductive material, enabling higher component density and smaller form factors. Multilayer PCB boards are commonly used in high-performance devices like smartphones, laptops, and networking equipment.
Passive Components:
Resistors: These are components that limit the flow of electrical current. They are essential in controlling voltage levels in circuits.
Capacitors: Used for storing electrical energy, capacitors are crucial for smoothing out voltage fluctuations in circuits and in filtering applications.
Inductors: These are used in power supplies and signal filtering, where they store energy in a magnetic field when electrical current passes through them.
Active Components:
Integrated Circuits (ICs): These are the "brains" of many electronic devices. ICs contain multiple transistors and other components in a small, integrated form.
Transistors: Acting as switches or amplifiers, transistors are fundamental to modern electronics and are used in signal processing, power regulation, and logic circuits.
Sensors: These detect physical quantities like temperature, pressure, or motion and convert them into electrical signals that can be processed by other parts of the circuit.
Surface-Mount Technology (SMT):
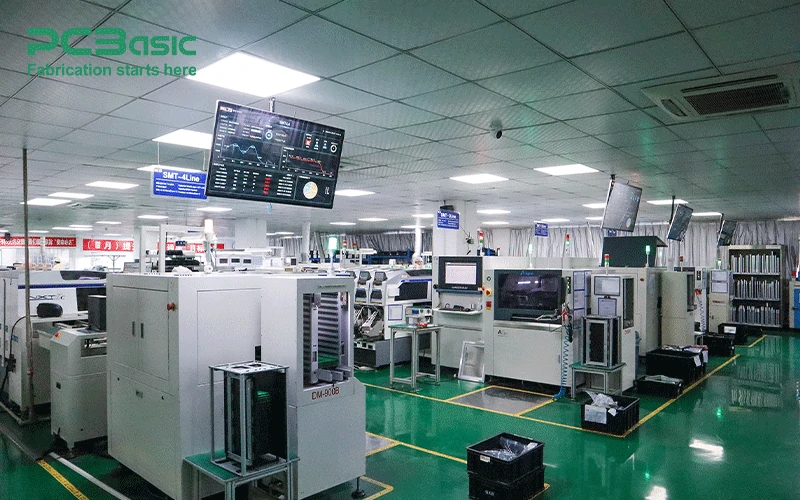

SMT is the most commonly used method for assembling components on PCBs, especially for OEM PCBA services. It involves mounting components directly onto the surface of the PCB using automated machines. SMT allows for higher component density and more compact designs, which is crucial in consumer electronics and mobile devices.
Through-Hole Technology (THT):
THT involves inserting components with leads through holes in the PCB and soldering them on the other side. It is mainly used for larger components that require more robust mechanical connections, such as connectors, switches, and heavy-duty resistors.
Mixed Technology:
In some cases, a combination of SMT and THT is used. This is known as mixed technology and is often required when a design involves components that are best suited for each technology.
Wave Soldering:
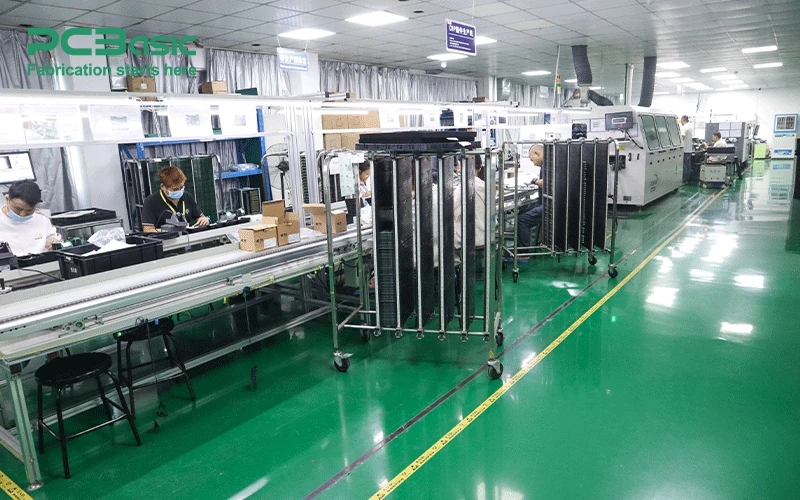

Wave soldering is typically used for THT components. The PCB is passed over a wave of molten solder that coats the exposed leads of the components. This method is efficient for mass production and ensures a reliable bond for components.
Reflow Soldering:
Reflow soldering is used in SMT assembly. The PCB with surface-mounted components is passed through a reflow oven, where the solder paste melts and forms solid solder joints between the components and the PCB. This method is ideal for high-density boards with small components.
Hand Soldering:
While not as automated as wave or reflow soldering, hand soldering is still used for small-volume runs, repairs, and rework. It requires skilled technicians to manually apply solder to specific points on the PCB.
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI):
AOI systems are used to detect defects in PCB assembly by capturing high-resolution images of the board. The system compares the images with the design files to identify missing or misplaced components, poor solder joints, and other assembly errors.
X-ray Inspection:
X-ray inspection is used for inspecting Ball Grid Array (BGA) and other complex assemblies. It enables manufacturers to see through the PCB and examine solder joints beneath the components, which are not visible with AOI alone.
In-Circuit Testing (ICT):
ICT is used to test each individual component on the PCB to ensure it is correctly placed and functioning. It checks for issues such as open circuits, shorts, and incorrect component values.
Functional Testing and Validation:
This testing method involves powering up the assembled board and testing its overall functionality. The board is subjected to real-world conditions to ensure it performs as expected under normal operating conditions.
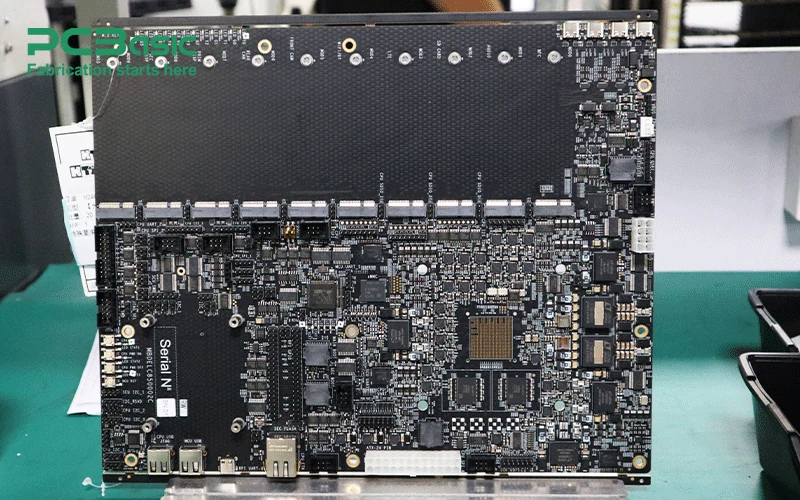
Reduced Manufacturing Overhead: By outsourcing the PCB assembly process, companies can significantly reduce overhead costs associated with in-house production, including equipment, labor, and facility maintenance.
Economies of Scale: PCBA OEM services benefit from economies of scale, which lower the unit cost for high-volume production. China OEM manufacturers, for example, are known for their ability to produce large quantities at competitive prices.
Access to Lower-Cost Component Sourcing: OEMs typically have strong supplier relationships that allow them to procure components at lower costs, passing those savings on to customers.
Faster Prototyping and Testing: Shenzhen PCBA OEM providers(like PCBasic) specialize in rapid prototyping and testing services, helping clients bring their products to market faster.
Streamlined Production Process: By handling all aspects of the PCBA process—from OEM PCBA designing to assembly and testing—OEM partners ensure a more efficient and seamless production timeline.
Quicker Iterations and Revisions: When revisions are needed, the flexibility of OEMs to adapt quickly allows for faster iteration cycles and faster time-to-market for new products.
Access to Specialized Manufacturing Expertise: PCBA OEM providers bring years of specialized experience in designing, sourcing, assembling, and testing PCBs, ensuring a high level of expertise is applied to your project.
High-Quality Control Standards: PCBA manufacturers are often certified under international standards such as ISO 9001, ensuring that quality control processes meet rigorous global standards.
Compliance with International Standards: Many PCBA OEM partners adhere to RoHS, CE, and UL compliance, ensuring that products meet the necessary environmental and safety regulations.
Tailored Solutions: OEM customized PCBA boards are designed to meet specific requirements, whether for flexible PCBs, multilayer PCBs, or HDI PCBA.
Ability to Handle Small to Large Volume Production Runs: From prototyping small batches to handling large-scale production, OEMs provide flexibility for businesses of all sizes.
R&D, Marketing, and Branding: By outsourcing manufacturing to PCBA OEM, customers can focus on their core competencies such as research and development, marketing, and product branding.
Offloading Manufacturing Responsibilities: Businesses can delegate complex manufacturing tasks to experienced OEM partners, reducing internal workload and improving efficiency.
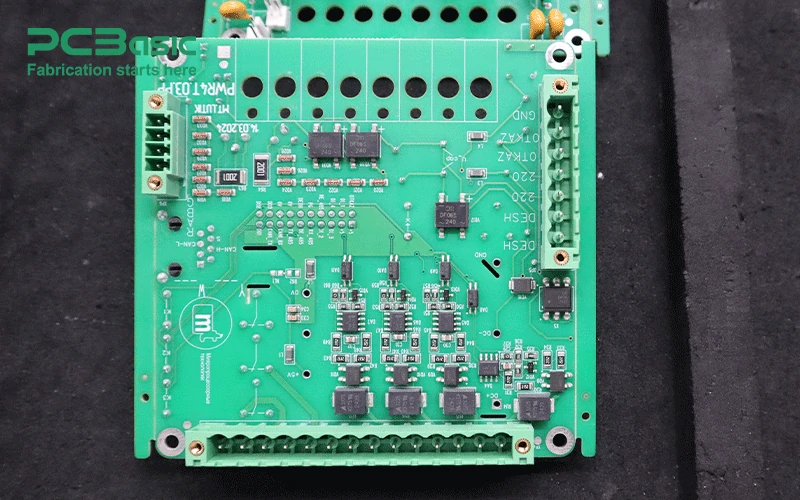
Selecting the right PCBA OEM partner is a critical decision that can directly impact the success of your product development and manufacturing. Here are key factors to consider when evaluating a potential partner for your OEM PCBA needs:
A reputable PCBA OEM partner should have a robust manufacturing capacity that aligns with your production requirements, whether you're looking for prototype assembly, low-volume production, or high-volume manufacturing.
Assess the equipment and technology they employ. Do they have the necessary SMT (Surface Mount Technology) lines, THT (Through-Hole Technology) machines, and pick-and-place machines for precise component placement? For complex designs such as HDI PCBA or flexible PCBs, it's essential that the OEM has experience and advanced capabilities in handling these technologies.
Advanced technology like automated optical inspection (AOI), in-circuit testing (ICT), and automated soldering systems is crucial for ensuring high-quality PCBs with minimal defects.
Not all PCBA OEMs are equipped to handle all types of PCBs. If you're working with multi-layer PCB boards, flexible PCBs, or complex HDI PCBs, ensure that your potential partner has experience with these specific types.
Evaluate their track record with specific electronic components—whether they are capable of sourcing high-quality components and assembling advanced components like microchips, power management ICs, or connectors that may be part of your design.
ISO 9001 is a standard for quality management systems that indicates an OEM’s commitment to delivering products that meet customer requirements consistently. Look for ISO 9001 certification to ensure your OEM partner follows structured quality control procedures.
ISO 14001 certification shows that the OEM has implemented environmentally responsible practices, which is increasingly important as businesses and consumers demand sustainability in manufacturing.
RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) certification ensures that the PCBA complies with environmental standards by limiting the use of certain hazardous materials in the manufacturing process. If your product will be sold in the European market or used in industries with strict regulatory requirements, RoHS compliance is essential.
CE Marking indicates that the PCBA complies with European Union health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
UL Certification is necessary for ensuring the safety and reliability of your OEM PCBA in critical applications, particularly in industries like automotive, medical devices, and telecommunications.
Clear communication is key to a successful partnership with your PCBA OEM. Ensure they offer project management support throughout the process, from the initial PCBA designing phase to final production.
A good partner should be responsive, proactive, and able to provide updates on the status of the project, lead times, and any potential issues that may arise.
After the production process, the right PCBA OEM partner should be able to provide comprehensive after-sales services. This includes technical assistance, troubleshooting, and the ability to manage repairs and rework if necessary.
Evaluate the OEM's ability to provide long-term support, as your product may require modifications, updates, or maintenance over its lifecycle.
One of the main considerations when choosing a PCBA OEM is balancing cost and quality. While it's tempting to go for the lowest cost option, it’s important to remember that quality issues such as faulty assembly or poor component sourcing can lead to delays, higher repair costs, and even reputational damage.
Assess the long-term value: A reliable OEM PCBA partner may offer a slightly higher upfront cost but can reduce costs in the long run through improved reliability, fewer defects, and faster time to market.
Choosing the right PCBA OEM partner is one of the most important steps in the successful development of your electronic products. The key factors in making this decision include:
· Evaluating the OEM's manufacturing capabilities and technology to ensure they can handle your specific PCB requirements.
· Verifying quality certifications like ISO 9001, RoHS, and UL, to ensure the PCB meets industry standards.
· Assessing customer support and communication efficiency to ensure smooth project management and after-sales service.
· Balancing cost and quality to get the best value for your investment.
A reliable PCBA OEM partner can be a game-changer for your business, enabling faster time-to-market, better product quality, and lower overall costs. They can provide the OEM customized PCBA boards you need while offering the necessary expertise in multi-layer PCB boards, flexible PCBs, and other advanced technologies like HDI PCBA.
In conclusion, the future of PCBA OEM services is bright, offering immense potential for companies that partner with the right OEM to bring innovative products to life. Whether you're looking for high-quality Shenzhen PCBA OEM solutions or need specific HDI PCBA expertise, choosing the right partner can make all the difference in delivering successful, market-leading electronic products.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
