Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > LED PCBA | A Comprehensive Guide
LED PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) are specially designed circuit boards that house and power light-emitting diodes (LEDs). These PCBs play a vital role in ensuring the efficient operation, longevity, and high performance of LED lighting systems. LED PCBs are widely used in a range of applications, including residential and commercial lighting, industrial displays, automotive lighting, and more. Whether it's for a streetlight, a digital sign, or the headlights of a car, LED PCBs provide the necessary electrical connections and heat management that make these LEDs work effectively.
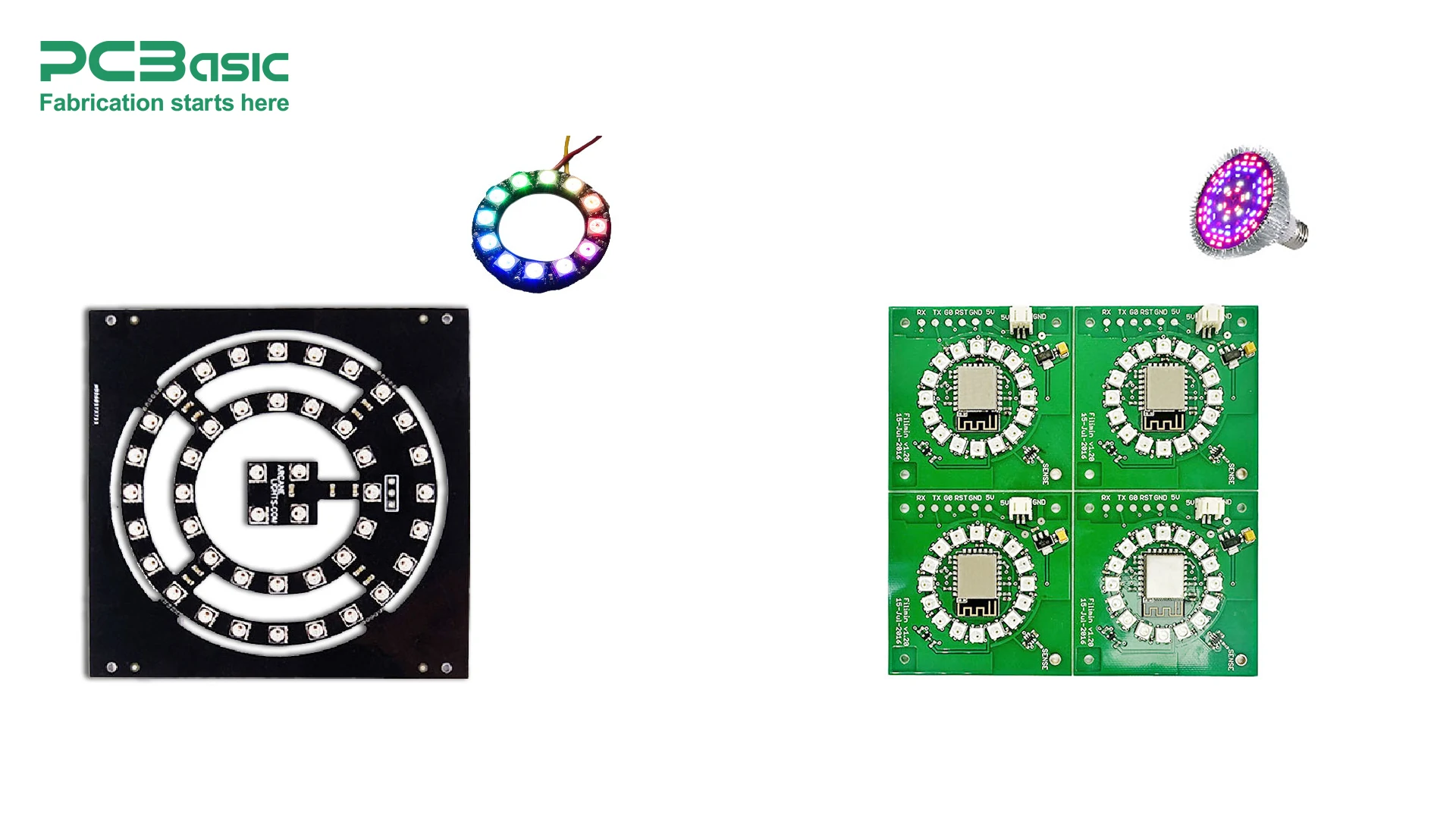
LED PCBs are at the heart of modern lighting solutions, enabling highly efficient and sustainable lighting options. These PCBs are specifically engineered to ensure optimal heat dissipation, electrical conductivity, and overall durability, all of which are essential for maximizing the lifespan and performance of LEDs. Without a properly designed LED PCB assembly, the heat generated by the LEDs could cause damage, shortening their life and efficiency. By providing a stable platform for the LEDs, LED PCBs ensure that these components remain functional over long periods and perform at their best.
Rigid LED PCBs are commonly used in applications where the PCB is fixed and not subject to bending or shaping. These types of LED PCBs offer solid mechanical strength and long-term reliability, making them ideal for stationary applications, such as lighting fixtures or industrial equipment.
Flexible LED PCBs are designed for applications that require bending or shaping. These PCBs are often used in signage, automotive lighting, or custom lighting designs where flexibility is a key factor. Flexible LED PCBs offer versatility in design and are particularly useful for intricate or curved lighting solutions.
Aluminum LED PCBs, also known as metal core PCBs, are specifically engineered for high-power LED applications that require excellent heat dissipation. The aluminum base provides superior thermal management, ensuring that the LEDs do not overheat during operation. This type of PCB is widely used in high-intensity lighting systems, such as automotive headlights and industrial lighting, where heat management is critical.
Ceramic LED PCBs are known for their high thermal conductivity and electrical insulation properties. The ceramic base material ensures efficient heat dissipation, making these PCBs ideal for high-performance or specialized LED applications. Ceramic PCBs are often used in environments that require high thermal resistance, such as in high-power LEDs for industrial or medical applications.
SMD (Surface-Mount Device) LED PCBs are designed to house SMD LEDs, which are soldered directly onto the surface of the PCB. This type of PCB is widely used for compact and space-efficient lighting designs. SMD LEDs are smaller and more flexible in layout, allowing designers to create more intricate and lightweight LED assemblies. SMD LED PCBs are commonly used in applications such as backlighting, signage, and small-area lighting systems.
LEDs are the core components of any LED PCB. They emit light when an electrical current passes through them, making them essential for various lighting applications. There are several types of LEDs used in PCB LED assemblies, including SMD LEDs, COB (Chip-on-Board) LEDs, and traditional through-hole LEDs. Each type offers different advantages depending on the application, with SMD LEDs being particularly popular for compact, efficient designs.
Ceramic Base: Ceramic provides excellent heat resistance and is used in applications where high temperatures are present. Ceramic bases also offer good electrical insulation, which is important in maintaining the safety and stability of the LED PCB assembly.
Aluminum Base: Aluminum is widely used in LED PCBs because of its superior ability to conduct heat away from the LEDs. Aluminum LED PCBs, or Metal Core PCBs, are particularly useful in high-power LED applications, ensuring that the LEDs stay cool and perform reliably.
Rigid PCB: Rigid PCBs are the standard base used in most stationary applications. They are non-flexible and offer good mechanical strength, making them ideal for applications where the PCB needs to be mounted in a fixed position. Rigid PCBs are commonly used in everything from household lighting to industrial systems.
Metal Core PCB: Metal Core PCBs, especially those made with aluminum, offer superior thermal performance compared to traditional FR4-based PCBs. These PCBs are crucial in high-power LED applications where heat buildup can compromise the performance and lifespan of the LEDs. Metal Core PCBs help ensure that the LEDs remain cool, even under intense usage.
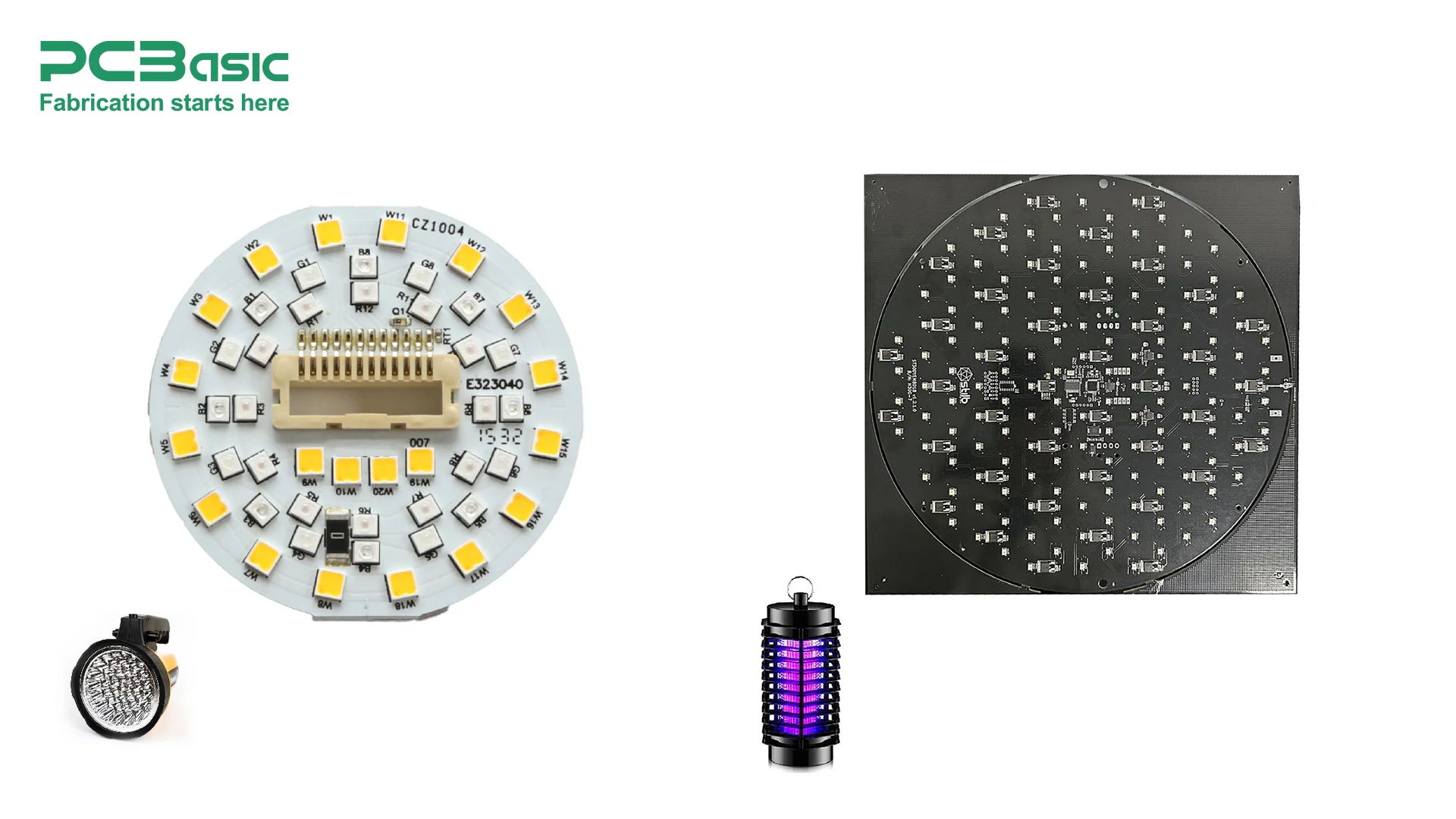
The manufacturing process of LED PCBs begins with the design phase, where an initial schematic design and layout plan are created. This step is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and effective heat management. CAD tools are used to create a detailed PCB layout, specifically designed to accommodate LED components such as SMD LEDs. Prototyping helps refine the design before mass production, ensuring all elements are in place for efficient operation.
Choosing the right base material for the PCB is critical to the overall performance of the LED PCB assembly. Materials like aluminum, ceramic, or FR4 are selected based on their thermal, electrical, and mechanical properties. For instance, aluminum PCBs are chosen for their excellent thermal conductivity, making them ideal for high-power LED applications. Ceramic PCBs are selected when high thermal resistance and insulation are required.
Once the PCB layout is finalized, solder paste is applied to the board using a stencil and automated soldering machine. The paste serves as a medium to hold the SMD LEDs and other components in place. The components, including LEDs, resistors, capacitors, and connectors, are precisely placed onto the PCB using pick-and-place machines. This step ensures that all components are positioned correctly for soldering.
After component placement, the PCB is passed through a reflow oven. The solder paste melts during the oven’s heated process, creating electrical connections between the SMD LEDs and the PCB pads. Reflow soldering ensures that the LEDs and other components are securely attached to the PCB, forming reliable connections for optimal performance.
After soldering, the LED PCB assembly undergoes rigorous inspection and testing. Optical testing ensures that the LEDs are properly mounted and function as expected. Functional testing checks the electrical performance of the board to verify the proper operation of each component. In addition, technologies like X-ray and AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) are used to detect hidden defects, such as poor solder joints or misaligned components, ensuring the quality of the final product.
Effective heat dissipation is crucial for maintaining the longevity and performance of the LED PCB. As LEDs generate heat during operation, the PCB design must prioritize thermal management. Metal core PCBs, like aluminum LED PCBs, and ceramic-based PCBs are commonly used due to their superior thermal conductivity. These materials help to efficiently transfer heat away from the LEDs, preventing overheating and ensuring stable performance.
The PCB layout must be designed with optimal trace widths and copper thickness to handle the required electrical current. Adequate electrical conductivity ensures that the power supplied to the LEDs is sufficient and stable, enabling the LEDs to function efficiently over their lifespan.
The LED density refers to the number of LEDs placed per unit area on the PCB. It is important to balance this density to ensure even light distribution and avoid excessive heat buildup, which could negatively impact performance and lifespan. A well-thought-out LED layout ensures that the light output is consistent, and thermal management is maintained.
High-quality LED PCBs should be designed to withstand environmental factors like moisture, vibration, and temperature fluctuations. Choosing durable materials and ensuring that the design is resistant to physical wear helps prolong the life of the LED PCB, ensuring long-term reliability in various applications.
LED PCBs are widely used in LED strip lights, panel lights, and backlighting for displays. These lighting solutions are energy-efficient and offer a long lifespan, making them ideal for both residential and commercial applications.
LED PCBs are used in automotive lighting, including headlights, tail lights, and interior lighting. These PCBs help provide bright, durable lighting that enhances the safety and aesthetics of vehicles.
LED PCBs are found in LED TVs, monitors, and handheld devices. They enable the production of slim, efficient displays that are energy-efficient and provide high-quality illumination.
Digital billboards and other signage solutions use LED PCBs for high-quality illumination. The high brightness and long lifespan of LED PCBs make them a popular choice for outdoor and indoor advertising displays.
LED PCBs are also used in medical tools and equipment, providing precise illumination for surgeries, diagnostics, and other medical applications. The energy-efficient nature of LED lighting ensures reliable performance and reduces heat generation in sensitive environments.
One of the main advantages of LED technology is its energy efficiency. LED PCBs consume significantly less power compared to traditional lighting technologies and produce less heat. This makes them ideal for applications where energy conservation is a priority.
LED PCBs are compact and lightweight, which makes them easy to integrate into space-constrained applications. Whether it’s in consumer electronics or automotive lighting, the slim profile of LED PCBs enables innovative designs without compromising performance.
While the initial investment in LED PCB assembly may be higher than traditional solutions, the long-term savings are significant. LED PCBs offer cost-effective lighting solutions due to their lower energy consumption, longer lifespan, and minimal maintenance costs. Over time, these factors contribute to a reduction in overall operational costs.
In summary, LED PCBs are a cornerstone of modern lighting technology. With their unique ability to manage heat, deliver efficient electrical conductivity, and provide reliable durability, LED PCBs are used in a wide range of applications from commercial lighting to automotive systems. By understanding the manufacturing process, key design considerations, and applications of LED PCBs, you can ensure that your LED lighting solutions are optimized for performance, energy efficiency, and longevity.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
