Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > DIY RC Cars: A Beginner’s Guide to Remote Control Circuits
Hobbyists and designers would always like to improve their skills and know-how in electronics. Skills that make you the best in the area include mechanical, electronics, electrical, and control. The area of remote-controlled cars is the best for learning such skills.
In DIY RC Cars, you will shape your mechanical skills by fabricating mechanical structures such as the DIY RC car chassis. Your electrical skills will be sharpened through understanding electrical quantities such as voltages, current, and power, which are necessities for powering your DIY. Your electronic skills, from understanding the electronic components to making their functional circuits and soldering skills, will be enhanced through the DIY RC cars.
Finally, your DIY RC car needs to have a control mode. Your control skills are sharpened by understanding various control systems and their functions. At an advanced level, you end up understanding some programming basics. This introductory article is suitable for beginners in the DIY RC car industry.
This section will focus on how RC cars work and the essential components of remote-controlled vehicles.
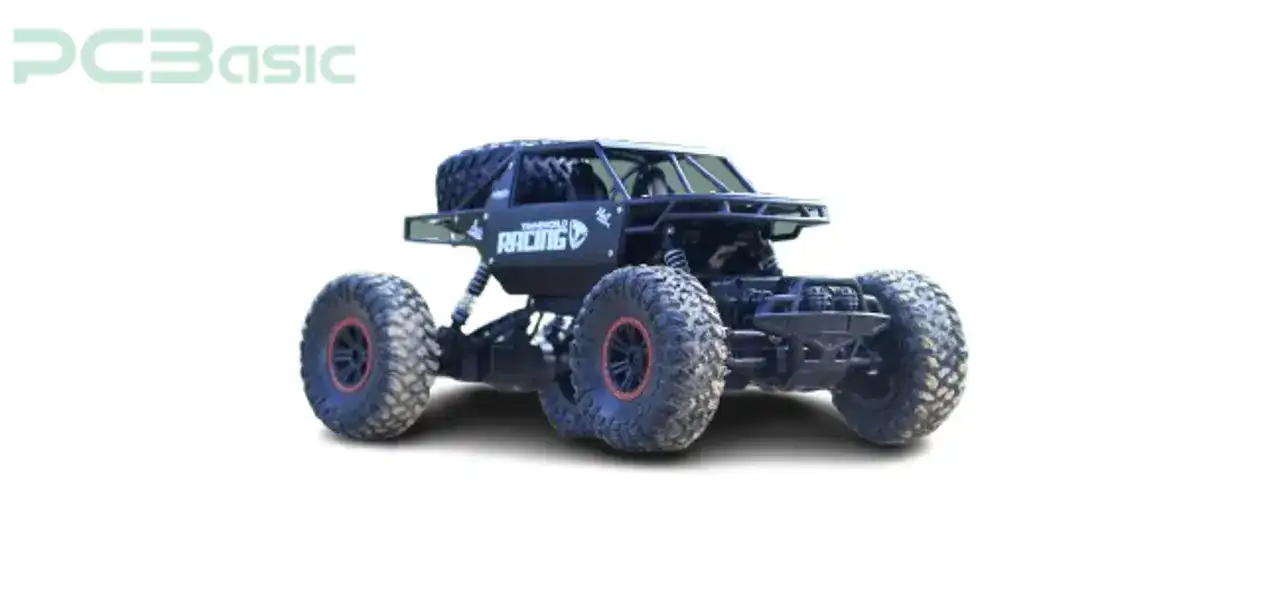

Figure 1: RC Car
RC stands for remote control. RC cars are intelligent systems that combine mechanical mobile structures with wireless communication. The system has a transmitter, wireless power, and a receiver mounted firmly on the mechanical structure. For the system to work, the receiver sends selected signals to the receiver on the RC car. The transmitter picks input from the user and then sends it to the receiver for decoding. The receiver picks and interprets all the inputs, sending the proper commands to the RC car actuators, such as servo motors, for necessary output. Your RC car comes to life with a mechanical structure and a transceiver.
Besides the mechanical structure and the transceiver, the following technology also plays the most significant role in building an RC car:
· RF: RF is an abbreviation for radio frequency, making communication between the transmitter and the receiver possible.
· LiPo Batteries: RC Cars require enough electrical DC power to operate, and Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries bring in the necessary energy.
· Servo motors: RC Cars require movement, and motor steering is one way to achieve movement. The commonly used motor for this purpose is the servo motor.
· ESC system: RC cars use the ESC (Electronic Speed Controllers) to control the vector of these cars.
These are the vital components that are needed to build an RC car:
The chassis is the backbone of RC cars. It is the structure that accommodates all other components. The component is the base of the RC cars, hosting other elements such as the suspension, motor, drive chains, batteries, and electronics.
Different chassis are designed to enable RC cars to achieve various functionalities and terrains. Off-road, on-road, drift, rock crawler, short course, and stadium trucks are just some types of chassis in RC cars. Chassis are designed using various materials, such as plastics, Aluminum, Carbon fiber, steel, and wood. Multiple materials are selected by application area, cost, benefits, and limitations.
Some critical features that make the chassis complete are the wheelbase for attaching the wheels, the ground clearance, the drivetrain, the suspension system, the battery mounting surface, the chassis layout, and the tires and wheels.

Figure 2: RC Car Chassis
The Servo motor is an electromechanical component that precisely controls the angular and linear motion of RC cars. This type of motor is used in throttle and braking to regulate speed and steering to control the direction of the RC cars.
Servo motors come in various types, from analog to digital and brushless. When choosing a servo motor for your RC car, you must consider the torque, speed, voltage consumption, size, weight, waterproofing ability, and the type of bearings used.

Figure 3: RC Cars Servo Motor
DC motors use direct current, where electrical energy is used to rotate a shaft connected to mechanical parts like gears, sprockets, wheels, belts, and chains. Various types of DC motors, such as brushed and brushless, are used in RC cars.
To select the DC motors, consider key specifications such as motor size, number of turns, KV ratings, voltage, torque, and efficiency. The motor is used in propulsion, accessories, and steering assistance in RC cars.
The transceiver is made up of the transmitter and the receiver.
· Transmitter: The RC car operator uses this handheld gadget to send control commands to the receiver on the RC car chassis. The key features of the transmitter are frequency, mainly radio frequency, channels that determine the transmitter's functionality, and the range of operation. They come in two types: piston grip and stick transmitter.
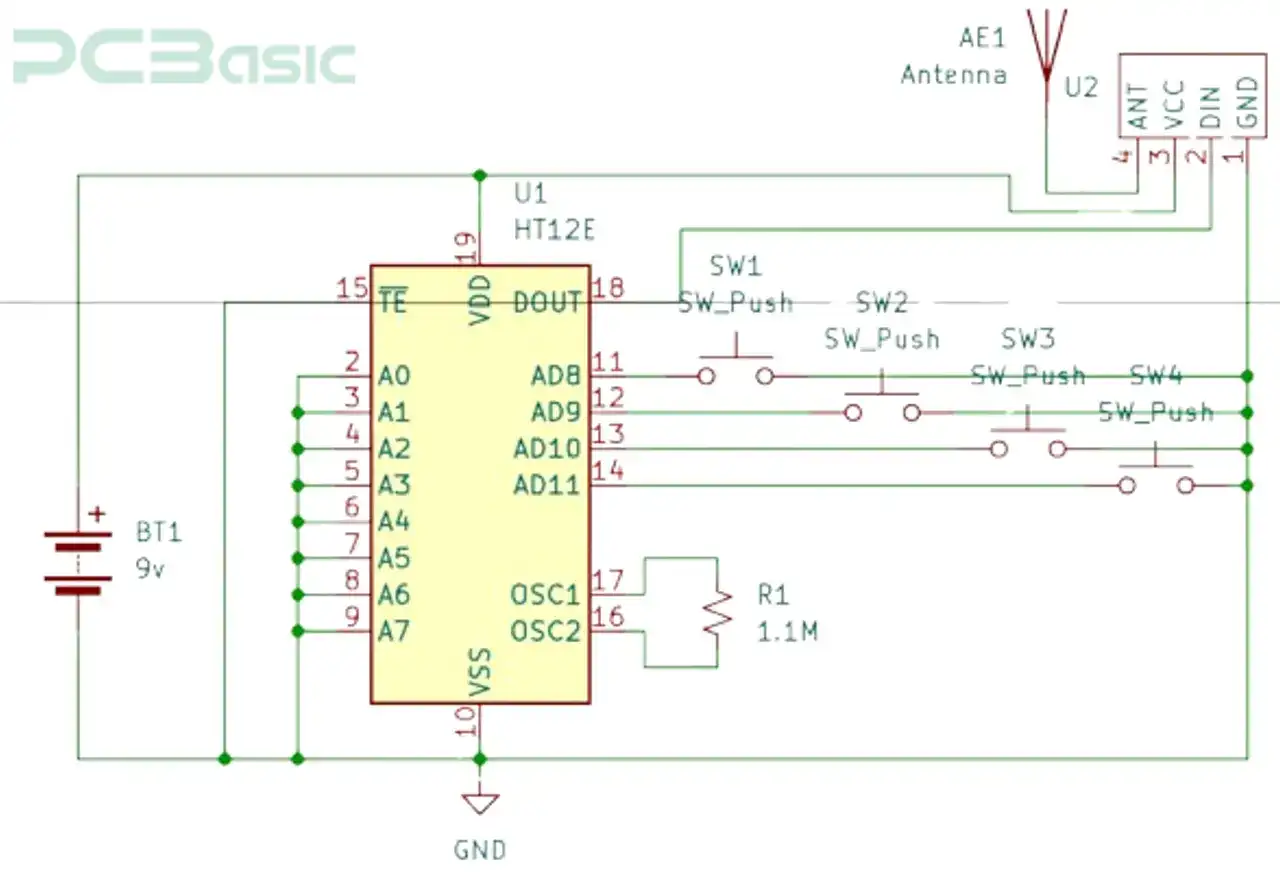
Figure 4: RC Cars Transmitter Circuit Diagram
· Receiver: This is a tiny electromechanical gadget mounted on the RC cars to receive signals from the transmitter and send them to the RC car ESC for necessary response or action. It has features such as an antenna, channels, and a compact design that can be accommodated in an RC car. It can either be a two-channel or multichannel system.
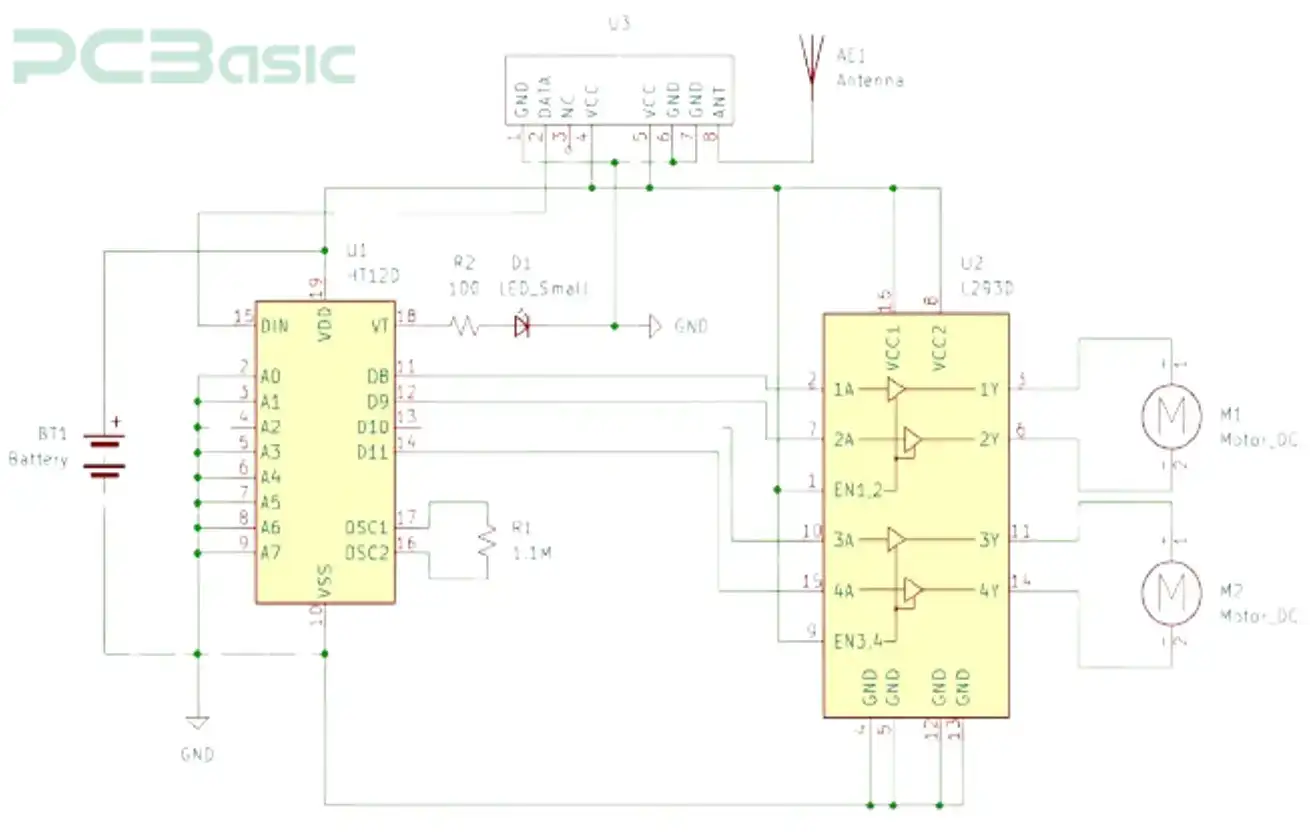
Figure 5: RC Cars Receiver Circuit
The ESC is a system used in RC cars to regulate the speed of the motors. It also controls braking, battery consumption, and the car's direction. Two types of ESC exist: the brushed ESC is used for brushed motors, and the brushless ESC is used for brushless motors.
Before selecting an ESC system, several considerations have to be made, such as current ratings, voltage ratings, battery eliminator circuits, and easy programming. Also, consider motor matching, application area, size, weight, and battery compatibility.
The battery pack powers the RC cars. A designer has to select among the existing battery packs. Four types exist: Nickel-Metal Hydride, Lithium Polymer, Nickel-Cadmium, and Lithium-Ion Battery Packs.
Before choosing the correct battery, a designer must consider its voltage capability, battery pack capacity, battery discharge rate, charger compatibility, and battery size and weight.

Figure 6: RC Cars Batteries
RC cars can be quickly built from prefabricated kits. Kits are a collection of perfectly selected components that offer performance and compatibility. Below is a list of the most common RC kits for beginners.
· Basic kits: These consist of wheels, chassis, and motors and require straightforward assembly.
· Advanced kits: Besides the features available in basic kits, this one has more features, such as programming ability, more advanced motors, such as servos, more customized chassis, and higher performance.
Before choosing your RC car kit, several factors have to be considered, such as:
· Level of your skills: Simpler RC car kits with detailed, instructive information should be an option for beginners.
· Cost: Advanced RC kits are more expensive than basic RC kits. Beyond cost, advanced kits bring in better performance, durability, and customization.
· Purpose: As stated earlier, RC cars have several classifications. You decide if you want a racing, off-road, or multi-terrain car.
You must understand their control to create remote control circuit diagrams for RC cars. The control is based on data exchange between the transmitter and receiver.
The remote control circuit for RC cars works through the following working principles:
· By pressing any button on the transmitter circuit in Figure 4, signals are sent to the encoder.
· The encoder picks the signals and converts them to a serial format, then sends them to the receiver through the RF transmitter shown in Figure 5.
· The RF receiver mounted on the RC car picks up the signals and delivers them to the decoders.
· The decoder interprets the signal and triggers the action on the motor as per the received data from the transmitter.
· Transmitter system:
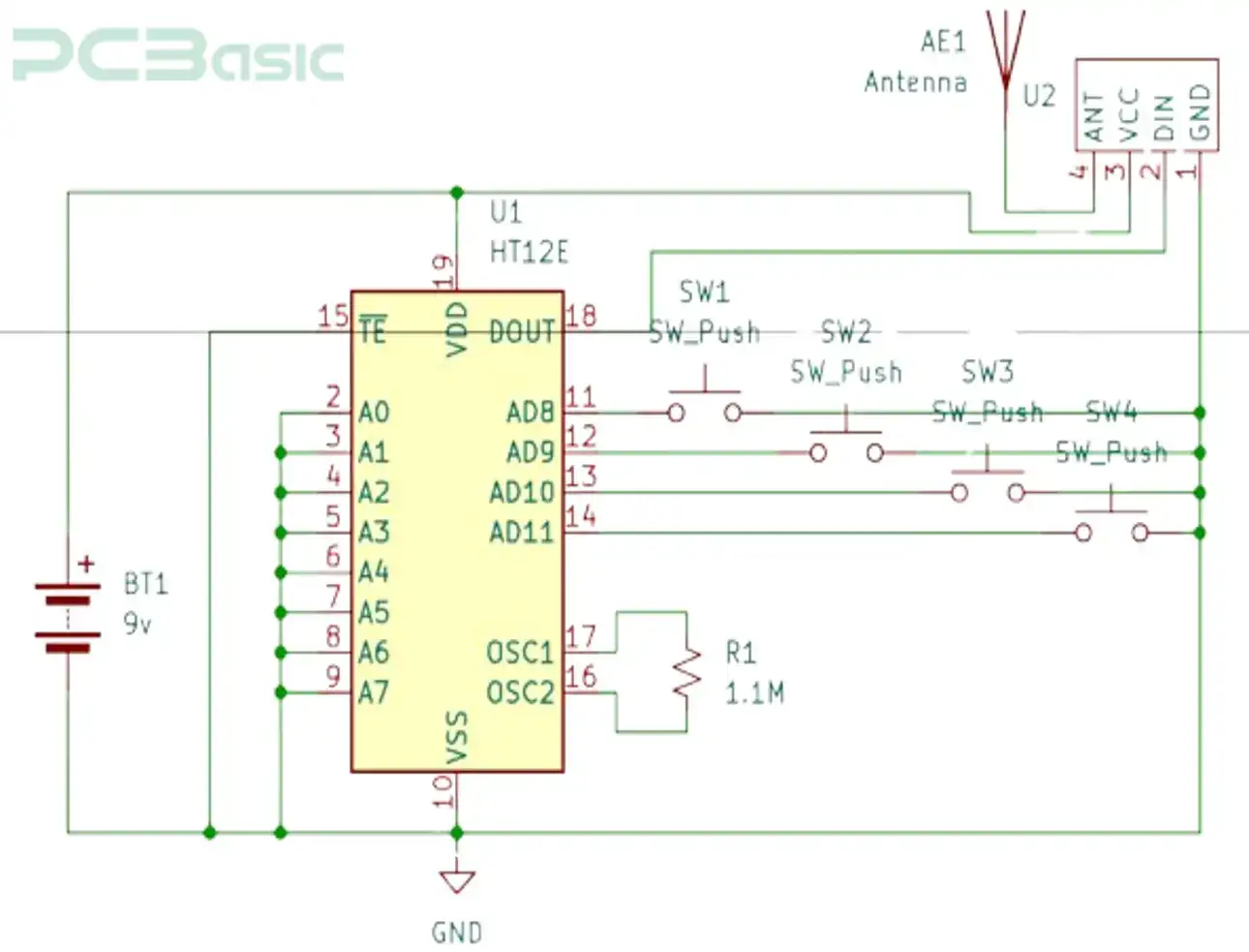
The transmitter system includes components listed below:
1. Joystick or buttons for user input.
2. Encoder IC e.g., HT12E
3. RF transmitter module, e.g., 433MHz
4. Power supply, e.g., 9V battery.
The following steps are used in assembling the transmitter:
1. Connect the switch button to an encoder IC, HT12E. The HT12E converts the user input to binary. Each press on the push button should give a unique output.
2. Attach the output from the HT12E to HT12D TO THE RF transmitter module.
3. Using a stable power source, power the RF transmitter module. Confirm that the wiring has been done perfectly.
4. Test your circuit by observing the signal being transmitted.
· Receiver System:
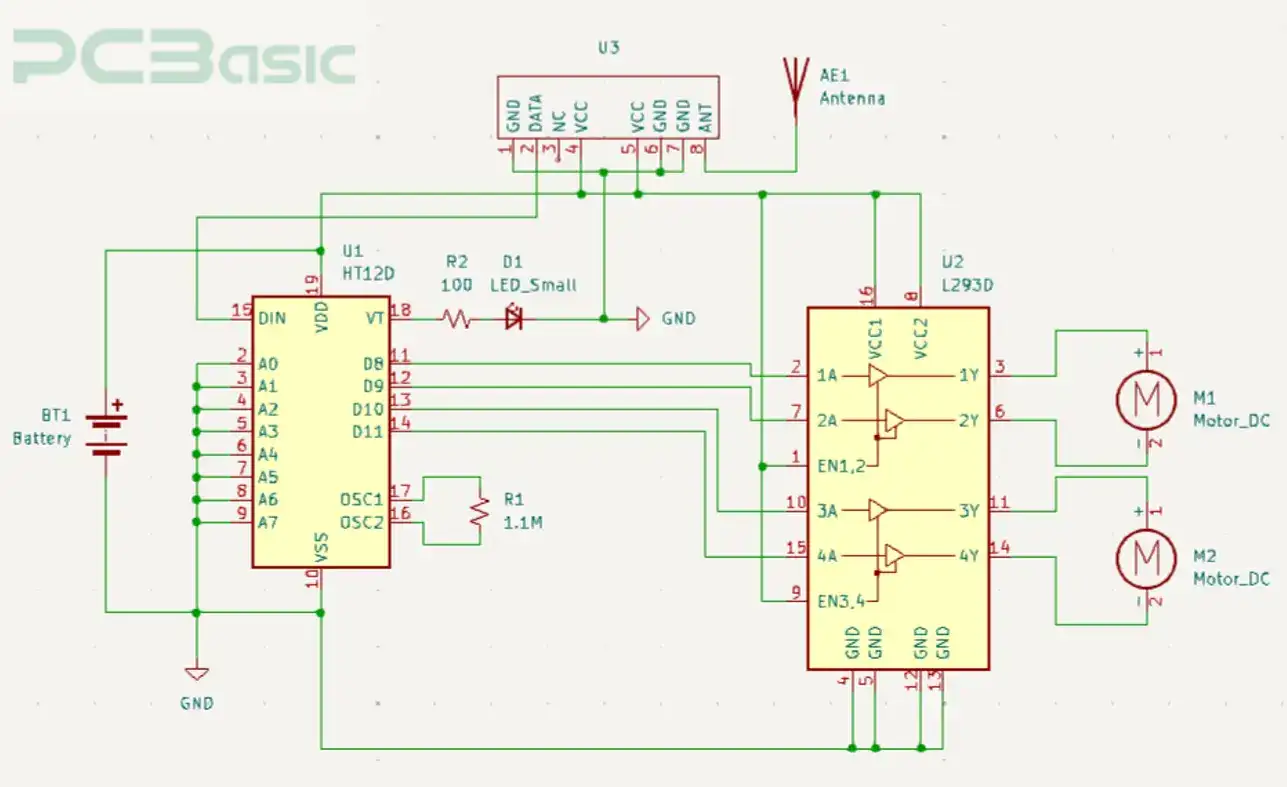
RF receiver circuit is made up of the following elements:
1. RF receiver module
2. Microcontroller,
3. Decoder e.g. HT12D
4. Motor driver
5. Motors
6. Power source.
The following steps are used in assembling the receiver:
1. Connect the receiver to the HT12D decoder IC. Following the schematic above, make sure the pinouts are well configured.
2. Integrate the decoder with the microcontroller. Write code on the microcontroller to interpret the received signals to control the motors.
3. Wire the motor driver ESC, then power it with the provided power supply.
4. Test your receiver to work accordingly.
Mechanical, electrical, and programming issues are challenges designers encounter in every design process. The design of the RC cars is no exception. The following are some common issues you might encounter and how to resolve them while dealing with RC cars.
· Non-responsive motor: In RC cars, a non-responsive motor is caused by loose connections, faulty ESC, or low power supply. To resolve this, verify your wiring, confirm your battery voltage rating and charge capacity, inspect the ESC system, and verify if the motor is functioning as expected.
· Steering malfunction: This can be caused by either transmitting wring signals or a damaged servo motor. To resolve, start by testing motor functionality, then recalibrate the delivered signals.
· Signal Interference: Sometimes, your RC car has poor transceiver pairing or different devices operating on the same radio frequency range. These changes can be solved by changing your system's operational frequency or ensuring the RC car has a perfect transceiver pairing.
· Components overheating: The change is caused by a poor cooling system or an RC car being used for long durations. By adding heat sinks and fans to the overheating components, the problem can be resolved.
Creating your own RC car is an exciting process that will help you gain many skills. It combines both creativity and technical know-how. To buy your remote-controlled car, you must know the necessary components and systems, such as receiver, transmitter, ESC, and RC car troubleshooting techniques. Advanced designers can consider designing their products from scratch and order for manufacturing through PCBasic. At PCBasic, quality and better customer care services are provided.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
