Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > Ammeter vs Voltmeter vs Multimeter
In circuit measurement, we always use a series of measuring tools to know the properties of the circuit, such as ammeters, voltmeters, multimeters and so on. Although all the instruments are used to measure the amount of electricity in a circuit, they differ in their function and use. In this blog post, let’s take a closer look at what an ammeter is, what an ammeter measures, what a voltmeter and a multimeter are, and finally, a comprehensive comparison between them.
An ammeter is a device used to measure the current in an electrical circuit. Current, in simple terms, is the flow of electric charge in a conductor, such as a wire. Its unit is “ampere” (A), so the name “ammeter” derives from the unit “ampere”.
Then what does an ammeter measure? It actually measures the rate at which electric charge flows through a circuit, which is the magnitude of the current. There are several units of current that an ammeter can measure, common ones being amperes (A), milliamperes (mA), and microamperes (µA). The unit used depends on the size of the circuit you’re measuring: if it’s a household circuit, it's usually amperes; for a small electronic device, it may be milliamps or microamps.
The ammeter works by connecting it in series to the circuit. That is, the ammeter must be connected to other components in the circuit so that the current can flow through it. It is like a tool to “sense” the flow of current in a circuit. When the current passes through, the ammeter can measure the amount of charge flowing and show the size of the current.
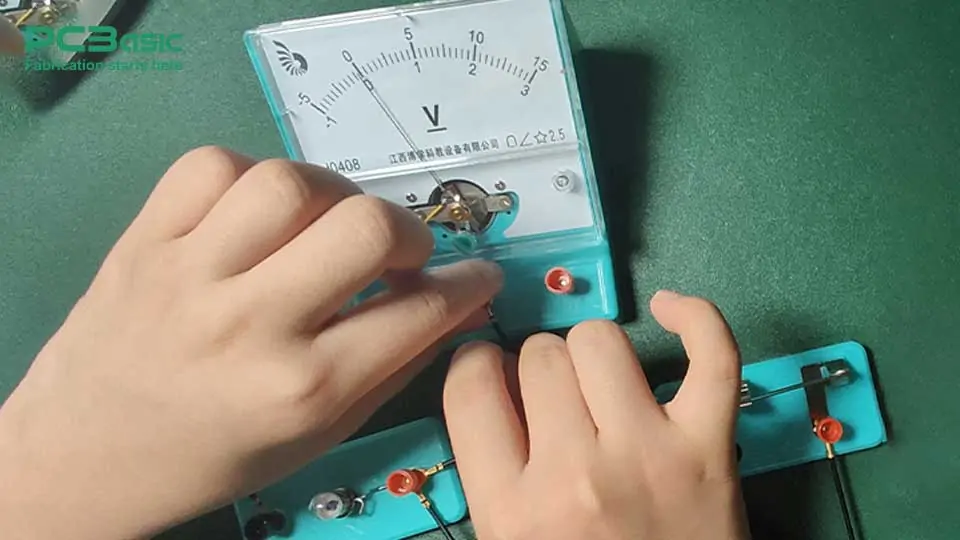

A voltmeter, on the other hand, is a tool used to measure the voltage or potential difference between two points in a circuit. Voltage can be understood as the “pressure” or “force” that drives an electric current through a conductor. It acts as the “drive force” of the current, allowing the charge to flow through the circuit.
So, what is a voltmeter used for? It helps you measure the voltage at two ends of different components in a circuit, such as resistors, batteries, or power supplies. For example, if you want to know the voltage of a battery, or whether the power supply is working properly, the voltmeter can help you know the information.
Unlike ammeters, voltmeters are not connected to the circuit in series but are connected in parallel between the two points where you want to measure voltage. The advantage of this is that it can accurately measure the potential difference (voltage) between these two points without affecting the flow of current. In other words, when the voltmeter measures the voltage, the current will not be disturbed, and the current in the circuit can still flow normally.
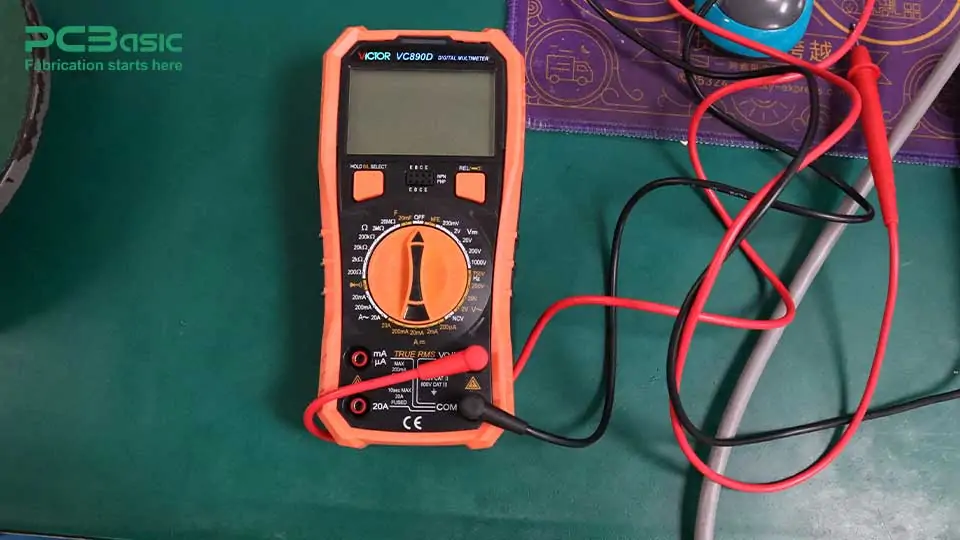

A multimeter is a very practical tool that integrates three functions: ammeter, voltmeter, and ohmmeter (for measuring resistance). So, it can measure not only current and voltage, but also resistance. In short, a multimeter is a multifunctional measuring instrument that can help us solve a lot of problems in electrical testing and troubleshooting.
So, what exactly is a multimeter used for? It can be used to measure current, voltage and resistance in a circuit. For example, you can use it to check the voltage of a battery, measure the current in a circuit, or check the resistance value of a resistor. Because it integrates these functions, multimeters are often used for the detection of various electronic devices and circuits.
Unlike dedicated ammeters and voltmeters, multimeters offer greater flexibility. Users can switch between different measurement modes as needed, either to measure current or voltage, or to check resistance. This makes the multimeter a very handy tool, especially when you need to quickly diagnose circuit problems.
The connection of the multimeter and the circuit is determined according to the value that the user needs to test. When measuring current, the multimeter is connected to the circuit in series like the ammeter; when measuring voltage, it is connected to the circuit in parallel like the use of a voltmeter. When measuring resistance values, the multimeter also needs to be connected in parallel to both ends of the component where the resistance is to be measured.
Above, we have respectively understood the definition and function of an ammeter, a voltmeter and a multimeter. So, let's take a closer look at the differences between these three instruments. Here, we will compare the ammeter, voltmeter and multimeter in detail in tabular form:
|
Attribute |
Ammeter |
Voltmeter |
Multimeter |
|
Function |
Measures current |
Measures voltage |
Measures current, voltage, resistance, and other electrical quantities |
|
Connection |
Connected in series with the component being measured |
Connected in parallel with the component being measured |
Can measure current in series or voltage/resistance in parallel depending on the setting |
|
Unit of Measurement |
Amperes (A) |
Volts (V) |
Amperes (A), Volts (V), Ohms (Ω) and others, depending on the selected function |
|
Internal Impedance |
Low impedance (close to 0 ohms) |
High impedance (close to infinite) |
Varies, typically low impedance for current measurement and high impedance for voltage and resistance |
|
Typical Use |
Measures the current passing through a circuit |
Measures the potential difference in a circuit, such as the voltage of a battery or power supply |
General-purpose testing tool for measuring current, voltage, resistance, and sometimes other parameters (e.g., frequency, capacitance) |
|
Description |
Current flows through the ammeter, and the instrument registers the amount of current. |
The voltmeter measures the potential difference between two points without direct contact with the current. |
A versatile tool that can measure various electrical parameters by selecting different modes. It’s commonly used for troubleshooting and diagnostics. |
Ammeters and voltmeters are both essential tools in the field of electronics, but their functions are different. An ammeter is used to measure current, while the voltmeter is used to measure voltage. Understanding the difference between an ammeter and a voltmeter is crucial for anyone who works with circuits. In addition, the multimeter provides a versatile alternative by combining the functions of both devices, making it an invaluable tool for a wide range of applications.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
