Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Miniaturization changed everything. More layers. Finer traces. Tighter spacing. But standard PCBs can’t keep up.
Enter HDI—High Density Interconnect. These boards use microvias, thin dielectrics, and advanced lamination to route complex signals in compact footprints. You’ll find them in smartphones, RF modules, medical implants, and advanced driver-assistance systems. It’s not just smaller—it’s smarter routing, better signal integrity, and higher reliability.
In this guide, we'll break down HDI PCB and microvia structures and explain why this tech drives modern high-performance electronics.
HDI stands for High Density Interconnect. But it’s more than just a compact circuit board. It’s an advanced design strategy used to squeeze more functionality into less space—without sacrificing performance. These boards use microvias, blind and buried vias, ultra-thin dielectrics, and multiple stacked layers to achieve incredibly dense routing.
You won’t find these in basic consumer gadgets. A high density interconnect PCB is critical in high-performance systems—think aerospace controls, 5G modules, LiDAR systems, neural implants, and military-grade communications. Anywhere size, speed, and reliability matter, HDI shows up.
They’re designed to handle fine-pitch components, often under 0.5 mm. That allows tighter connections, faster signals, and reduced electromagnetic interference. Traditional PCBs simply can’t support that level of complexity.
It’s not just about saving space. HDI PCB technology reduces signal loss, improves power delivery, and supports faster switching speeds. In a world driven by AI, edge computing, and compact sensor systems, HDI has become essential infrastructure—quietly powering the next wave of intelligent electronics from the inside out.
Now, let’s talk about what makes an HDI board different under the hood. Traditional PCBs have large mechanical drilled vias and relatively wide traces. HDI PCBs use:
• laser-drilled microvias,
• tighter trace spacing,
• and stacked layer technology.
The entire structure is designed to optimize every square millimeter. There’s a clear reason for that: the demand for more I/O, smaller components, and higher speed signals.
Common HDI PCBs follow a 1+N+1 structure, where:
• "N" is the number of core layers.
• The “1” on either side are the outer HDI layers connected by microvias.
It doesn’t stop there. Advanced HDI layouts use 2+N+2. It has:
• Two HDI layers on the top and two on the bottom.
• More routing channels. More room to breathe.
Still not enough? You can push it further: 3+N+3, or even higher. It’s a scalable approach. You only add layers when the design actually needs them, which keeps costs (and headaches) under control.
Any-layer HDI, also called ELIC (Every Layer Interconnect), removes the limits. Microvias can now connect any two layers directly—no need to go step-by-step. Routing becomes insanely efficient. This is how your smartphone gets all that performance packed into a board smaller than a credit card.
These boards are built using sequential lamination. That means you laminate, drill, plate, and repeat the process layer by layer. This allows ultra-precise connections between dense internal circuitry.
The structure usually includes:
• Core layer: Usually FR-4 or a high-performance laminate.
• Prepreg: Resin-impregnated fiberglass sheets that bond copper layers.
• Copper foil: For signal traces and planes.
• Microvias: Laser-drilled holes less than 150 microns in diameter, plated with copper.
All these elements come together to support BGAs (Ball Grid Arrays) with 0.4mm pitch or smaller. That’s nearly impossible with traditional via technology.
One key point: HDI isn’t just about shrinking things. It’s about enabling reliable performance in compact layouts. That requires perfect layer registration, consistent via plating, and precise alignment during fabrication.
Designers often say: if you get the stack-up wrong, the board will fail—no matter how good your layout is.
An HDI PCB stack-up is more than just an arrangement of copper and dielectric layers. It’s a carefully engineered electrical architecture. Every layer serves a function—signal, power, ground, shielding—and the via strategy ties it all together.
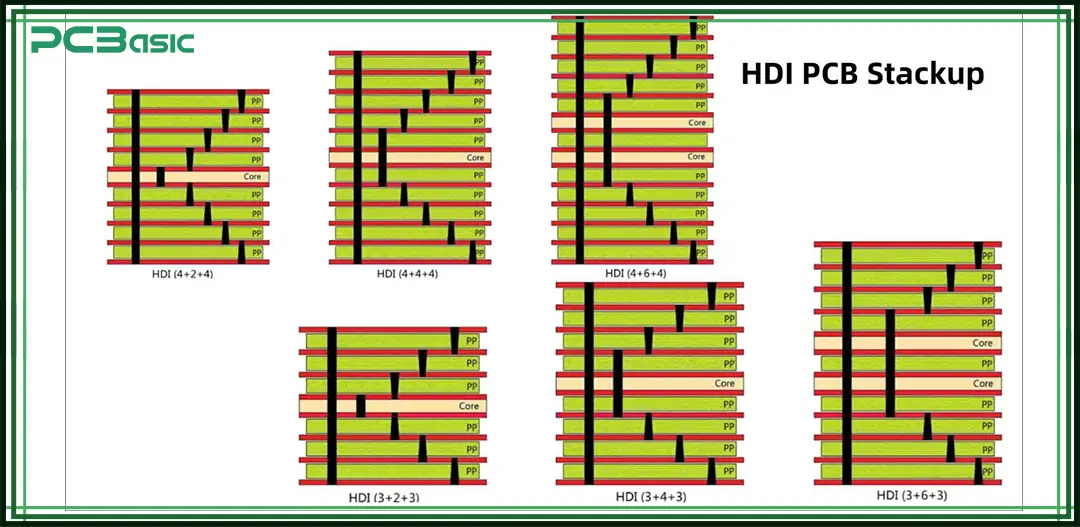
Let’s walk through a simplified HDI stack-up:
1. Top Signal Layer
2. Dielectric (Prepreg)
3. Ground Plane
4. Core
5. Power Plane
6. Dielectric
7. Bottom Signal Layer
Sounds straightforward, right? Not exactly. In HDI design, microvias and blind/buried vias create vertical connections between specific layers. You may have a via from Layer 1 to Layer 2, and a separate buried via from Layer 3 to Layer 5. Or a stacked via that goes from Layer 1 all the way to Layer 6.
These choices aren’t random. They’re based on:
• Signal timing requirements
• Impedance control
• Crosstalk minimization
• Power distribution and decoupling strategies
For high-speed digital designs—say, DDR4, USB 3.0, or HDMI—you’ll often see dedicated stripline or microstrip impedance-controlled traces embedded in specific layers. And all of this is packed into a board that might only be 0.8mm thick.
Advanced HDI PCB stack-ups can include:
• Multiple buried via layers
• Resin-coated copper foils
• Filled and capped via-in-pad structures
• Hybrid materials for specific electrical or thermal properties
One real-world example: a mobile processor PCB might use a 3+N+3 stack-up, with 10 total layers, stacked microvias, and resin-filled via-in-pad to support a 0.35mm BGA pitch.
Key takeaway? In HDI PCBs, the stack-up is a performance tool—not just a mechanical one. It determines signal integrity, EMI behavior, and even manufacturability.
At this point, it's clear HDI design is only half the battle. Manufacturing is the other. HDI boards are built through sequential lamination cycles. That means layers are pressed, drilled, plated, and bonded one at a time. Each lamination adds new routing options via microvias and buried vias. But materials matter just as much as process.
• FR-4 (High Tg variants): Cheap and reliable for moderate-speed designs.
• Polyimide: Great thermal stability for aerospace and defense.
• Rogers, Isola, Panasonic Megtron: Used in high-speed RF/microwave HDI applications.
• Halogen-free or Lead-free laminates: Meet strict environmental standards.
• High glass transition temperature (Tg)
• Low Z-axis expansion
• Tight Dk/Df tolerances for signal integrity
• Stable dielectric properties over frequency and temperature
Laser drilling also requires materials with clean ablation behavior, so the edges of microvias remain intact without debris or undercutting. Resin systems need to flow properly during lamination but cure with high rigidity.
In short, your choice of material isn't just about cost. It directly affects drillability, reliability, and RF performance.
Here’s what sets it apart:
HDI PCBs pack more routing density into less board area. That’s critical when designing for devices like wearables, implantables, or edge-AI modules. There’s no space for oversized traces or full-depth vias. Microvias and fine-line routing let you scale down without cutting features. No dead zones. No wasted space. Just an efficient layout.
Shorter signal paths. Fewer stubs. Better controlled impedance. Microvias reduce inductance, which leads to cleaner high-speed signal transmission. That’s a big deal when you're routing DDR, PCIe, USB 3.2, or HDMI signals.
Need a 12-layer board? With HDI, you might get it done in 8 layers. That’s lower material cost, reduced board thickness, and simpler lamination. Stacked microvias help in efficient layer usage, so the layout stays compact and efficient.
Smaller vias = tighter coupling. That means reduced loop areas and less radiated noise. HDI is ideal when electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) becomes critical—like in medical, avionics, or automotive applications.
Microvia-in-pad designs improve thermal dissipation. Also, more routing space allows better decoupling capacitor placement, which directly enhances power delivery.
Less drilling. No large through-holes. Better copper balance. HDI boards offer more robustness under vibration and thermal cycling—an important consideration in defense, aerospace, and EVs.
 About PCBasic
About PCBasic
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
HDI technology isn't limited to consumer electronics. It's everywhere. Here's where HDI shows up behind the scenes:
Space is the enemy. HDI PCBs help squeeze CPUs, RAM, cameras, and batteries into sleek enclosures—without performance compromise. Most modern smartphones have ELIC HDI boards with 10+ layers.
Implantable defibrillators. Wearable glucose monitors. Portable ECG. These products require ultra-small form factors and strict reliability. HDI makes them possible.
ADAS, infotainment, LiDAR control boards, and electric vehicle battery management systems all benefit from HDI layout. Especially with increasing autonomous functions, signal integrity and miniaturization are non-negotiable.
Routers, switches, and base stations need HDI boards for high-speed data routing, precise impedance control, and reduced EMI.
Defense-grade radar modules, avionics processors, and navigation controls rely on HDI’s durability and signal clarity in extreme environments.
Designing an HDI board is part science, part art. You're not just placing traces. You're managing physics—electromagnetic behavior, thermal expansion, and manufacturability constraints. That's why the HDI layout demands special attention.
Here’s what matters most in HDI PCB design.
• Microvias: Use them to connect two adjacent layers. Avoid stacking more than 3 levels unless necessary.
• Staggered vs Stacked: Staggered microvias are more reliable, but stacked allows tighter BGA escape.
• Buried Vias: Keep them isolated to inner layers. Plan their locations early to avoid routing issues.
Used in dense BGA packages, especially when pitch goes below 0.5mm. These vias must be filled, plated, and planarized properly to avoid solder wicking.
Not every fabricator can do this well. Always consult with your HDI PCB manufacturer before committing.
• Trace width: Often between 3–4 mil for HDI.
• Spacing: Keep signal trace spacing ≥2× trace width if possible to reduce crosstalk.
• For controlled impedance, simulate your stack-up using field solvers or tools like Polar Si9000.
Microvias have low aspect ratios—less than 1:1. That’s why the depth between layers matters.
Avoid placing too many microvias in one area. It can cause resin voids or uneven copper plating.
Filled and capped vias are essential for stacked structures. Use resin-filled or electroplated fill based on IPC standards.
Incomplete via fill = reliability issues = failed board in the field.
Before tape-out, run checks for:
• Drill registration
• Solder mask alignment
• Copper-to-copper clearances
• Thermal reliefs
• Via tenting or capping
The goal? Fabrication-ready design with minimal revisions.
Manufacturing HDI boards is nothing like regular PCBs. It’s multi-step, precision-driven, and highly sequential.
Here’s a simplified flow:
1. Inner Layer Imaging & Etching: Inner copper layers are patterned using photolithography.
2. Core Lamination: The etched cores are laminated with prepreg and copper foil.
3. Laser Drilling (Microvias): Laser drills sub-0.15mm vias through the top layer. UV or CO2 lasers are typically used.
4. Desmearing and Hole Cleaning: Plasma cleaning ensures debris-free via holes for reliable plating.
5. Electroless Copper Deposition: A thin copper layer is deposited inside microvias for conductivity.
6. Electroplating: Additional copper is plated to increase via wall thickness.
7. Outer Layer Imaging & Etching: Top signal layers are created. Fine traces are patterned.
8. Sequential Lamination: Additional layers are added as needed, repeating steps 3–7 for each HDI cycle.
9. Via Fill & Planarization: Via-in-pad structures are filled with epoxy resin and planarized via CNC.
10. Solder Mask and Surface Finish: ENIG or OSP surface finishes are applied.
11. Final Testing: Finally, electrical tests validate integrity.
This process may include multiple lam cycles depending on stack-up complexity. Each cycle introduces cost and time, so it must be engineered wisely.
In HDI boards, vias aren’t just holes. They’re design elements.
Here’s a quick breakdown:
Go from top to bottom. Not used often in HDI due to space wastage.
Connect the outer layer to an internal layer. Great for surface-mount component routing.
Stay completely within inner layers. Useful for keeping outer layers clean.
Laser-drilled, <150µm diameter. Connect adjacent layers. Low inductance and perfect for HDI.
Placed directly on top of one another. Enable vertical connection from top to core.
Offset by a small amount. More mechanically reliable than stacked.
Placing via directly beneath a pad. Used for ultra-dense BGAs and helps reduce inductive delay.
Each type has trade-offs in terms of cost, manufacturability, and signal performance. Your choice should align with the layout, stack-up, and component pitch.
Design is only half the equation. The hard part? Turning that design into a board that actually works—down to the micron.
That’s where PCBasic delivers.
We don’t just make PCBs. We build HDI—from tight-pitch prototypes to full production runs. Need a 1+N+1? We’ve got it covered. Running 3+N+3 or ELIC? No problem.
Why engineers choose PCBasic:
• Laser drilling precision to 75 µm
• Controlled impedance tuning
• Microvia reliability testing
• IPC 6012, ISO, and RoHS compliance
• Custom stack-up engineering
• Quick-turn HDI PCB prototyping
• DFM consultation included
We’ve helped clients across medical, aerospace, telecom, and automotive industries. Whether you need a small HDI PCB prototype or full volume production, we’re equipped to deliver.
Have a project in mind? Let’s talk.
HDI PCBs are essential today. They’re no longer just a choice—they’re the standard. When your design needs more space, faster speeds, or better signal integrity, HDI is the answer. From structure to stack-up, understanding the details is crucial for success.
Whether you're a startup or an established team, the right design and manufacturer matter. Precision is everything.
Looking for a reliable HDI PCB partner? Choose PCBasic because we know the tech and deliver quality every time.
Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
