Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > A Comprehensive Guide to SMT Lines and Machines
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is an indispensable core process in modern electronic manufacturing. With the rapid advancement of technology, SMT machines and SMT production lines have significantly improved the efficiency and precision of PCB SMT manufacturing, making them the most popular processes in SMT PCB Assembly. Through automated equipment such as Pick and Place Machines and SMT placement machines, manufacturers can quickly and efficiently complete the production of complex electronic products.
The core of a PCB assembly line is the highly automated SMT line, which covers the complete process from solder paste printing to component placement, reflow soldering, and final testing. Renowned brands such as Yamaha SMT Machines, ASMPT SMT Machines, Panasonic SMT Machines, and Fujitsu SMT Machines provide high-performance SMT placement machines, offering manufacturers a wide range of solutions to meet the needs of both prototyping and high-volume production.
China, as the largest global hub for electronic manufacturing, has established itself as a leader in providing high-value PCBA China services. With competitive pricing and fast delivery, China offers comprehensive PCB SMT assembly services to global customers. Whether for highly automated production lines or small-batch prototyping during the R&D phase, China's SMT machines and technological solutions are among the best in the industry. This article will explore SMT technology, types of equipment, and their key roles in modern electronic manufacturing, providing a complete guide to help you understand and choose the right SMT machines for your needs.
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is a revolutionary method used in modern electronic manufacturing that involves directly mounting electronic components onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). Unlike traditional through-hole technology, which requires drilling holes for component leads, SMT uses SMT machines and automated PCB assembly lines to streamline the manufacturing process, significantly improving speed, precision, and production efficiency.
|
Aspect |
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) |
Through-Hole Technology |
|
Component Mounting |
Components are mounted directly onto the PCB surface. |
Components are inserted through drilled holes. |
|
Manufacturing Speed |
Faster due to automated SMT machines like pick-and-place systems. |
Slower due to manual component placement. |
|
PCB Design |
Supports compact, multi-layer designs for high-density circuits. |
Requires more space, limiting circuit density. |
|
Production Cost |
Lower due to reduced labor and efficient PCB SMT assembly. |
Higher due to manual work and material costs. |
|
Application |
Widely used in consumer electronics and industrial devices. |
Often used in applications requiring durability, like power systems. |
The SMT line consists of various specialized SMT machines that perform distinct tasks to ensure efficient and high-quality PCB assembly line operations. Below is an overview of the essential equipment used in SMT PCB assembly:
Pick-and-place machines are the heart of the SMT line, responsible for precisely placing surface-mounted devices (SMDs) onto the PCB. These machines come in three main types:
Manual Pick-and-Place Machines: Suitable for prototyping or small-scale production, requiring human intervention.
Semi-Automatic Pick-and-Place Machines: Offers partial automation for medium-scale operations.
Automatic Pick-and-Place Machines: Fully automated SMT placement machines used in high-speed, high-volume PCB SMT assembly.
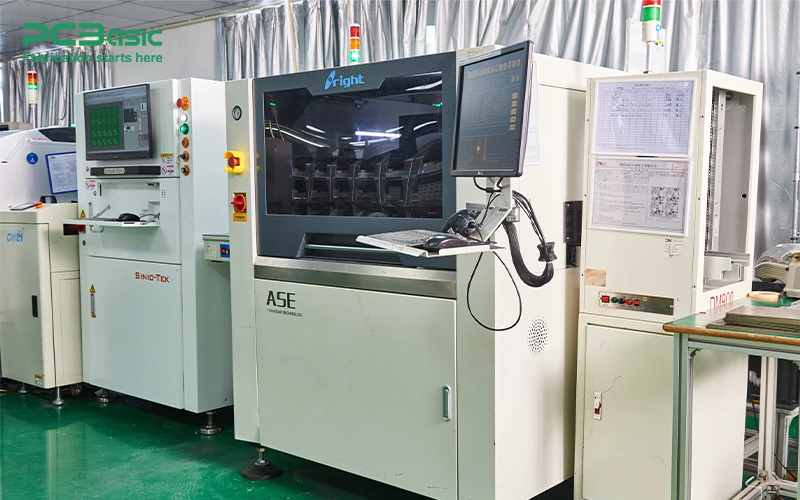

Solder paste printers are critical for applying a layer of solder paste onto the PCB pads, preparing the board for component placement by the pick-and-place machines. Accurate solder paste application ensures reliable connections during the soldering process.
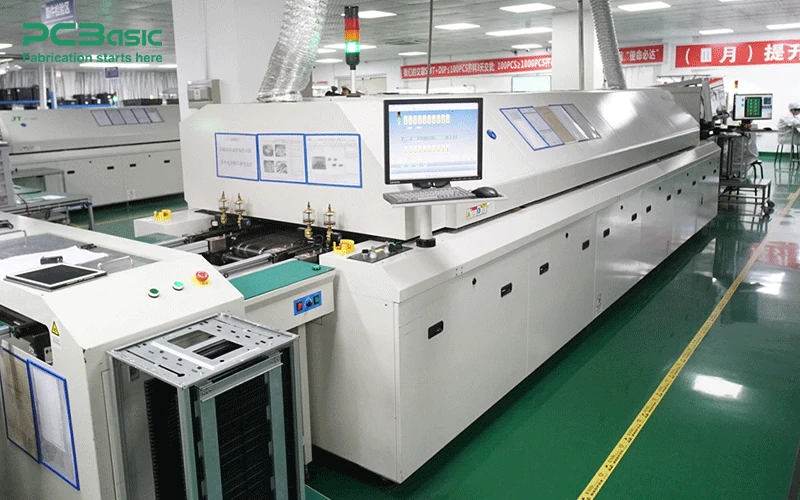

Reflow ovens heat the PCB to melt the solder paste, permanently bonding the SMDs to the board. This process is integral to the PCB assembly line, ensuring strong and durable connections for all components.
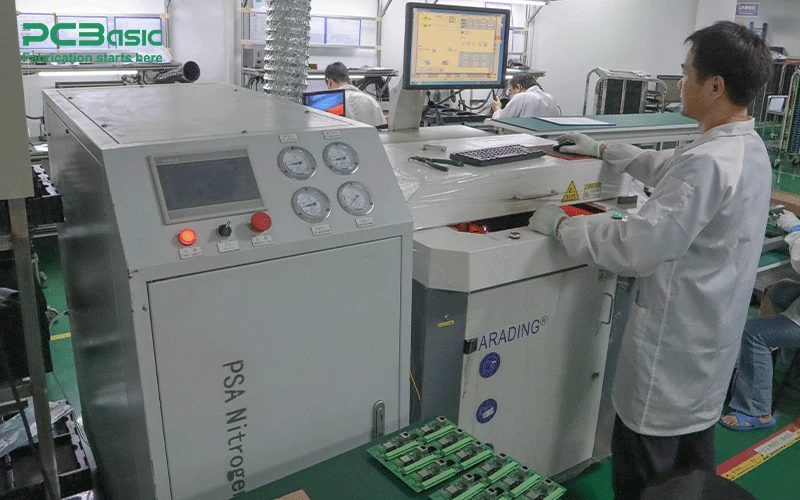

Selective soldering machines are used for through-hole components in hybrid assemblies where SMT and through-hole technologies coexist. These SMT machines precisely apply solder to specific areas without affecting nearby components.
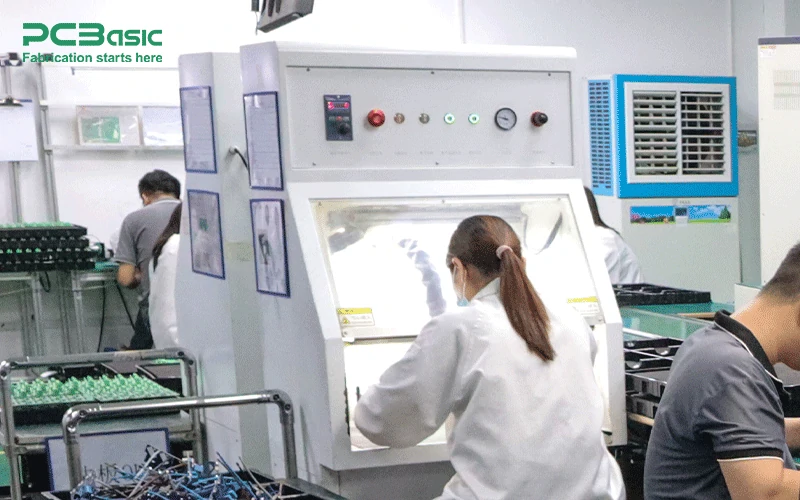

Dry ice cleaning systems are used to clean sensitive PCBs by removing contaminants and residues without causing damage, ensuring the cleanliness required for high-quality PCB SMT assembly.
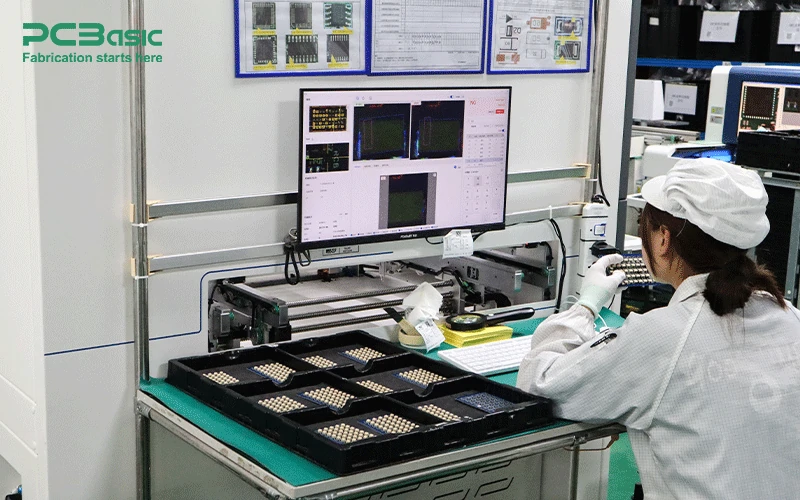

AOI machines inspect PCBs for defects such as misaligned components, solder bridges, or missing parts. These machines are divided into two categories:

Off-line AOI: Used for sample inspection or low-volume production.
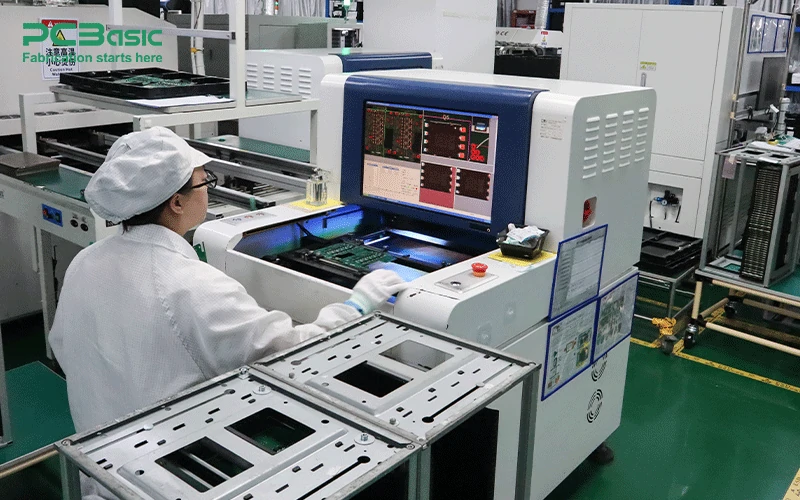
On-line AOI: Integrated into the SMT line for continuous real-time quality control.
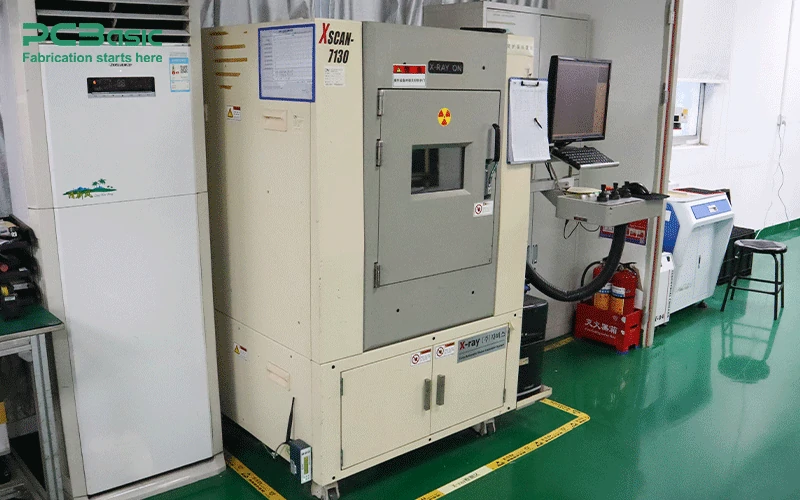

X-Ray inspection systems are crucial for detecting hidden defects, such as voids in solder joints or issues in ball grid array (BGA) packages, which cannot be identified through visual inspection or AOI.
ICTs test the electrical performance of PCBs by checking circuits for shorts, opens, and component functionality. These SMT machines are vital in the final stages of SMT PCB assembly to ensure the board functions as intended.
SMT loaders and unloaders automate the loading and unloading of PCBs onto the SMT line, reducing manual handling and ensuring smooth transitions between different stages of the PCB assembly line.
Docking stations facilitate the transfer of PCBs between various machines within the SMT line, enhancing workflow efficiency and reducing downtime in high-volume production environments.
In addition to the standard equipment used in an SMT line, there are several other essential machines that play a critical role in ensuring the quality, functionality, and reliability of SMT PCB assembly. These machines address specific processes in the PCB SMT manufacturing workflow, from soldering and testing to protective coatings and precision cutting. Below is a detailed explanation of these PCBA machines and their importance in the PCB assembly line.
1. Wave Soldering Machines
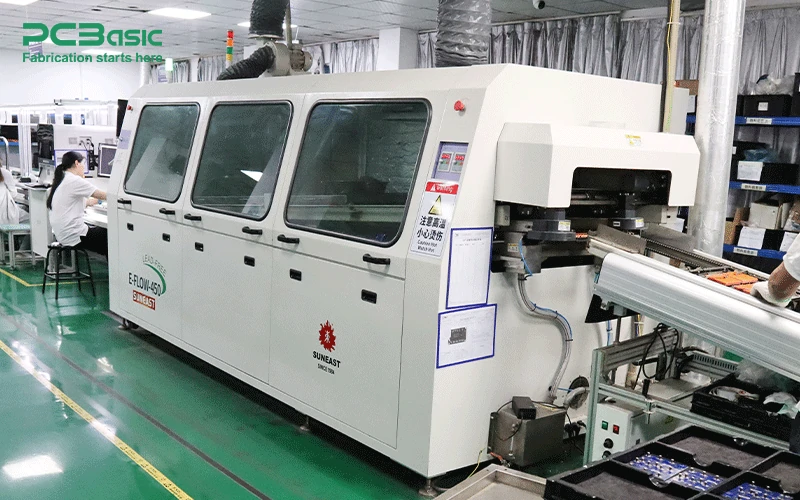

Wave soldering machines are indispensable for assembling through-hole components on PCBs. Unlike pick-and-place machines that handle surface-mount components, wave soldering is specifically designed to solder the leads of through-hole parts by passing the PCB over a wave of molten solder. This method ensures that every pin is securely soldered to the board.
These machines are often integrated into hybrid PCB assembly lines, where both SMT placement machines and through-hole soldering coexist. The combination of wave soldering and SMT lines enables manufacturers to produce complex PCBs that require multiple assembly techniques.
Key Benefits:
- High-speed soldering for large-scale production.
- Uniform solder application ensures consistent quality.
- Reduces manual intervention, enhancing efficiency in PCB SMT assembly.
2. Flying Probe Tester
The flying probe tester is a versatile testing tool used during the inspection phase of PCB SMT assembly. Unlike traditional fixtures, flying probe testers use movable probes controlled by software to test electrical connections and components on a PCB. This flexibility makes it ideal for prototyping, low-volume production, and designs that frequently change.
Flying probe testers are particularly valuable in PCB assembly lines where precision is critical, as they ensure the functionality of the assembled PCBs before they proceed to the next stage.
Applications:
- Validating connections in prototype designs.
- Ensuring circuit integrity in low-volume production.
- Testing boards assembled with pick-and-place machines for accuracy.
3. Bed of Nails Test Machine
The bed of nails test machine is another critical component of the PCB assembly line, primarily used for high-volume production. It consists of a fixture with numerous spring-loaded pins (or "nails") that make contact with test points on the PCB. These machines are commonly found in fully automated SMT lines to validate the electrical performance of PCBs.
Compared to flying probe testers, bed of nails machines are faster and more suitable for large-scale SMT PCB assembly, where repetitive testing is required.
Advantages:
- Fast testing for high-volume production.
- Ensures complete coverage of test points on the PCB.
- Seamlessly integrates into automated SMT lines.
4. Functional Test Machine
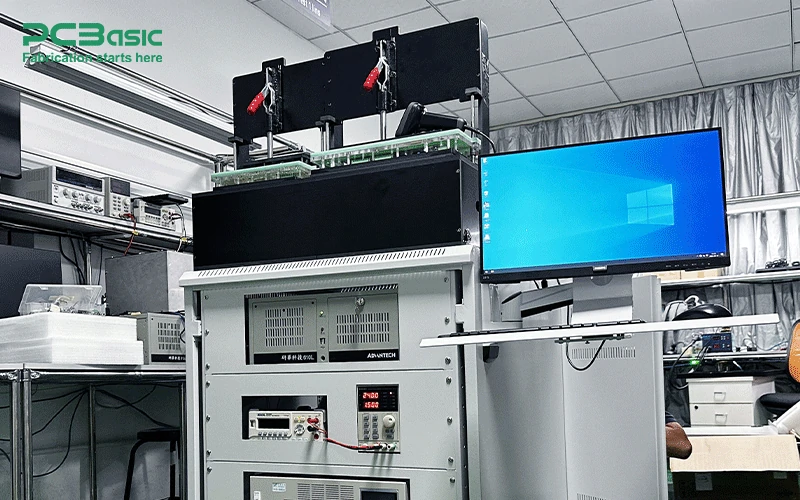

Functional test machines, or FCTs, are essential in validating whether a finished PCB operates as intended under real-world conditions. These machines simulate the actual working environment of the PCB, testing its functionality after it has been assembled using pick-and-place machines and soldered in the SMT line.
Functional test machines are indispensable in PCB SMT assembly for ensuring that the final product meets performance and reliability standards before being shipped to customers.
Typical Tests Performed:
- Power-up tests to check voltage and current levels.
- Functional verification of individual circuits and components.
- Final validation of the entire PCB assembly.
5. Steel Mesh Laser Cutting Machine
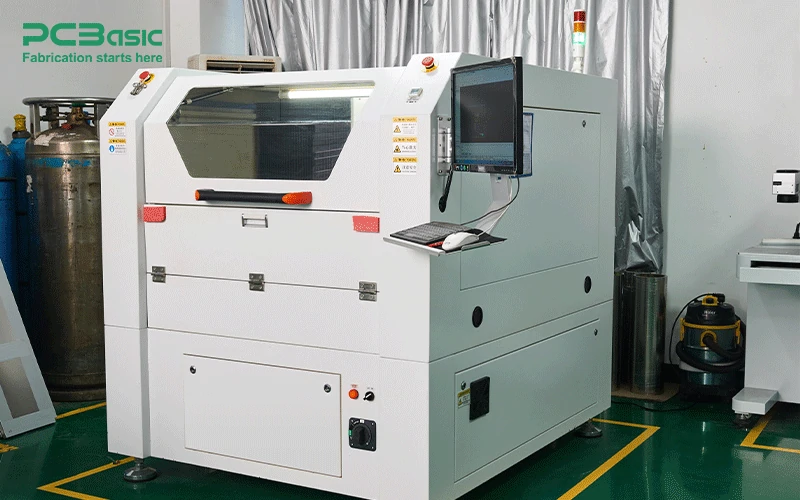

Steel mesh laser cutting machines are primarily used to create high-precision stencils for solder paste application in the SMT line. The stencils produced by these machines ensure that the solder paste is applied accurately to the PCB, which is crucial for the successful operation of pick-and-place machines and subsequent reflow soldering.
These machines contribute to the efficiency and precision of SMT PCB assembly, as accurate solder paste application is a foundational step in the PCB assembly line.
Key Features:
- High precision cutting for complex stencil designs.
- Rapid production of custom stencils for prototyping and mass production.
- Essential for maintaining the accuracy of SMT machines.
6. Three-Anti Paint Machine
Three-anti paint machines are used to apply conformal coatings to PCBs, providing protection against moisture, dust, and corrosion. These machines are often integrated into the final stages of the PCB assembly line to enhance the durability and reliability of the finished products.
The conformal coating applied by three-anti paint machines is particularly critical for electronics used in harsh environments, such as automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications.
Benefits:
- Extends the lifespan of PCBs by protecting them from environmental factors.
- Ensures consistent application across all assembled PCBs in an SMT line.
- Compatible with boards produced by SMT placement machines.
The SMT line and its associated SMT machines are at the core of modern PCB SMT assembly, enabling manufacturers to produce high-quality, reliable, and cost-effective electronic products. By integrating advanced equipment like pick-and-place machines, wave soldering systems, and functional test machines into the PCB assembly line, manufacturers can ensure efficient workflows and superior results.
Choosing the right SMT machines and technology is crucial for achieving optimal production efficiency and maintaining product quality. Global brands like Yamaha, ASMPT, Panasonic, and Fujitsu have revolutionized the industry with their innovative SMT placement machines and solutions. Moreover, PCBA China has become a global leader in providing high-quality and cost-effective manufacturing services, leveraging state-of-the-art SMT machines to meet diverse customer needs.
As the demand for compact, high-performance PCBs continues to grow, the evolution of SMT lines and machines will remain a driving force in the electronics manufacturing industry. By investing in the right equipment and processes, manufacturers can stay competitive and deliver cutting-edge products to the market.
 About PCBasic
About PCBasic
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
