Did you know that the United States alone produces 6.9 million tonnes of electronic waste annually? The amount of e-waste generated globally is alarming, emphasizing the need for circuit board recycling, which is crucial in managing global electronic waste (e-waste).
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are a component of most electronic devices and, thus, make up a significant portion of e-waste. They contain hazardous substances, which adds to the problem. Because PCBs are built from valuable materials such as silver or copper, recycling can help recover these materials while addressing environmental health concerns.
Innovative recycling techniques can handle several PCBs, especially those operating at low temperatures and pressures. This in-depth guide will help you discover the advantages, tips, and challenges of circuit board recycling so let's look at them.
What is Circuit Board Recycling?
Old and discarded electronic items, such as computers and mobile phones, contain PCBs that can be recovered through PCB recycling. The goal is to extract valuable metals such as gold, silver, and copper that electronic device manufacturers can reuse.
This process reduces environmental pollution created by e-waste while conserving natural resources. Before extracting the metals, PCB recycling begins with physical dismantling and chemical treatment to eliminate hazardous substances, followed by mechanical separation to recover the metals.
 About PCBasic
About PCBasic
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
Why Should You Recycle Circuit Boards?
Electronic circuit boards contain materials like plastic, metals, and fiberglass. Improper disposal of these materials can have severe environmental and health effects.
Toxic chemicals from these electronic components can leech into the soil and water, causing widespread contamination and making it crucial to recycle circuit boards properly. Here are other reasons why recycling electronic circuit boards is crucial:
Preventing Environmental Contamination
Electronic circuit boards are a significant contributor to electronic waste and landfill overflow. Recycling circuit boards can minimize the detrimental environmental impact of e-waste.
If disposed of incorrectly, PCBs can contaminate groundwater and soil, as they contain heavy metals such as lead, mercury, and other toxic substances. If incinerated without proper controls, they may even lead to air pollution by releasing toxic fumes into the air.
Recycling would reduce the waste sent to landfills and prevent toxins from contaminating the air, water, and soil.
Reducing Health Risks
Harmful chemicals in PCBs can lead to health hazards for waste management workers and communities near landfills or disposal sites. Because they degrade very slowly, PCB waste can bioaccumulate the food chain, adversely impacting human and wildlife health.
Recycling can reduce such risks by safely managing and treating hazardous substances found in circuit boards.
Economic Benefits
Recycling PCBs reduces environmental pollution and offers economic benefits by recovering metals and components that can be sold and repurposed. The process also aligns with resource conservation, reducing the need for mining.
Compliance and Regulations
Several countries regulate electronic waste disposal by enforcing strict laws. Recycling ensures compliance, reducing the risk of potential fines or legal penalties resulting from non-adherence to such laws.
What Kind of Circuit Boards Can You Recycle?
To recover metals, you can recycle printed circuit board scrap from computer motherboards, hard drives, telecommunications, and networking equipment. In broad terms, here are the kinds of circuit boards that you can recycle:
Single-Layer PCBs: Single-layer PCBs are present in TV remote controls, calculators, and toys. They are the simplest type of PCBs composed of just a single layer. Their single layer makes them easy to recycle, among other PCBs.
Double-sided PCBs: Double-sided PCBs, such as those found in printers, audio equipment, and computer peripherals, have conductive copper layers on either side of the substrate.
Multi-layer PCBs: Complex electronic circuits such as smartphones, medical devices, and computers contain multi-layer PCBs of multiple substrate layers.
Rigid PCBs: Most recycling centers accept rigid PCBs because they are the most used in electronics, commonly found in TVs, washing machines, and automotive electronics.
Flexible PCBs: You can recycle flexible PCBs in wearable devices, displays, and medical implants.
Rigid-Flex PCBs: Rigid-flex PCBs combine features of both rigid and flexible PCBs. They are used in advanced electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, and aerospace equipment.
Aluminum Backed PCBs: A metal backing present in Aluminum PCBs dissipates heat in high-power devices such as LED lights, power supplies, and automotive electronics.
What Can You Recycle from Printed Circuit Boards?
The seemingly simple printed circuit boards contain various valuable materials that you can extract through recycling.
A PCB's basic structure comprises several layers: substrate, metal, silkscreen, and solder mask. This means you can recycle several materials from PCBs, including:
● Copper: Copper can be extracted from several parts of the PCB, such as the edge trim and the etching solution. It is a precious and highly recyclable material. ● Copper: Copper can be extracted from several parts of the PCB, such as the edge trim and the etching solution. It is a precious and highly recyclable material.
●
Copper Oxide: This is a by-product generated during sludge treatment that can also be recovered.
●
Tin: Hot air leveling is commonly used to recover tin, usually found in solder.
● Precious Metals: PCBs often contain small amounts of precious metals, such as gold and silver, that can be extracted and sold.
Chemical, thermal, and physical recovery processes can help extract these materials from circuit boards. Learn about these processes in the section below.
How to Recycle Electronic Circuit Boards?
Now that we know PCB recycling is possible and an invaluable process for conserving resources and facilitating environmental protection, let's discover how PCBs are recycled.
Before we begin, it's crucial to ensure that the recycling process aligns with global directives such as the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive (WEEE) and the Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive, which specify methods for recycling PCBs.
The following are the methods involved in PCB recycling:
Physical Processing
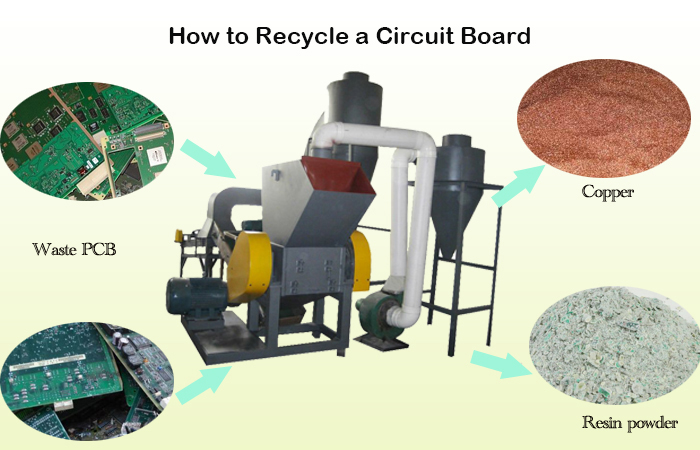
The first step to recycling PCBs is physical processing, which involves cutting the circuit board into smaller segments to extract components. The process employs drilling, sorting, and magnetic separation techniques to remove capacitors, motors, batteries, plugs, semiconductors, and other elements.
The process begins by dismantling the PCBs, which removes more significant components and hazardous materials. Then, it is followed by shredding, which involves breaking the board into smaller pieces. The goal is to increase the surface area to aid further processing.
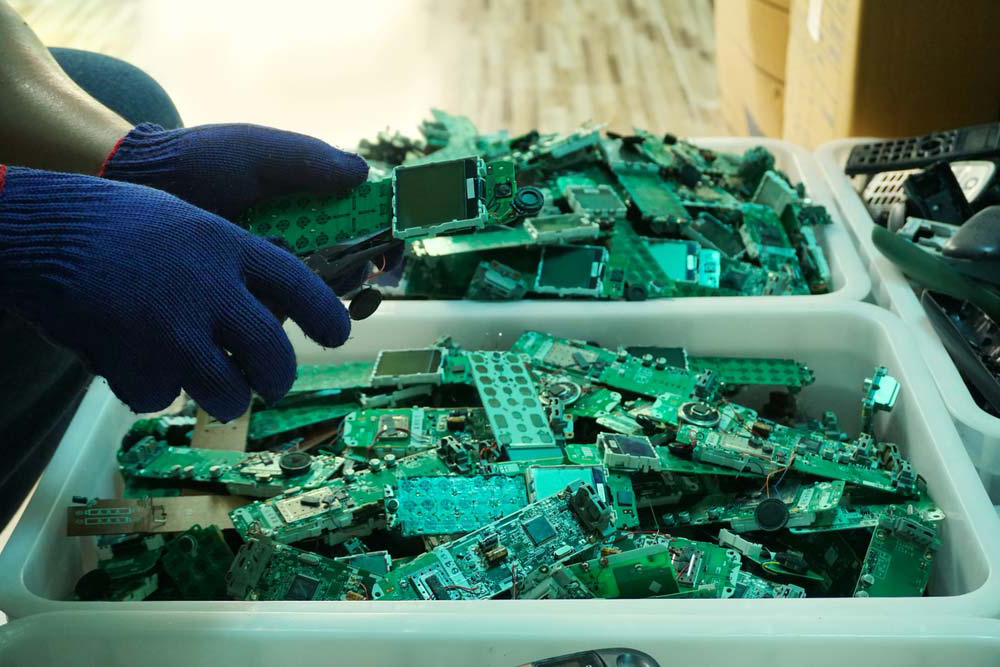

The next step is using separation techniques to segregate metallic from non-metallic materials. The following separation techniques can be used to achieve this:
● Magnetic separation: This physical separation technique uses magnets to extract ferrous metals from the shredded mix.
● Eddy's current separation: A method that leverages the different electrical conductivities to separate non-ferrous metals like copper from aluminum.
● Air separation: As its name suggests, this technique uses air flow to segregate lighter non-metallic materials from heavier metallic particles.
● Screening: It involves using screens of various sizes to sort materials based on their dimensions.
The physical processing method is the most environmentally friendly; however, it releases large amounts of dust, metal, and glass debris into the air. Prolonged exposure to a contaminated environment can cause respiratory problems. Additionally, physical processing helps extract all metal components from the circuit board.
Therefore, according to research, cryogenic temperatures are recommended for grinding PCBs before separation. This process is eco-friendly and enables the reuse of metallic and non-metallic components. The study also emphasized employing electrostatic separation, a highly efficient process that helps extract metal, middlings, and non-metallic products.
Chemical Processing
The second recycling phase uses chemical methods to dissolve the thermoset substrate of the waste PCBs. This process begins by dipping the PCB in acid, which destroys the FR-4. It involves the following steps:
The first step is immersing the circuit board materials in a chemical solution that dissolves the targeted metals. Leaching agents include acids such as hydrochloric, nitric, or sulfuric acid. These potent agents can dissolve metals commonly found in PCBs, including gold, silver, and copper.
Leaching introduces a mixture of various metals into the solution. Purification techniques separate and concentrate specific metals from the solutions. Standard purification techniques include solvent extraction, precipitation, or ion exchange.
Chemical processing generates a large amount of wastewater, which requires treatment for proper disposal. A recent study highlighted a more eco-friendly approach using small-molecule dissolution to dissolve thermosetting polymers with ester groups.
The technique allows the recycling of electronic components without harming the environment. Unlike conventional chemical methods, the remaining solution in this technique can be reused multiple times.
Thermal Recovering
Apart from physical and chemical processing, thermal recovery is another method used to recycle circuit boards. The primary thermal recovery process involves heating the PCB to a high temperature, which incinerates the FR-4. It retains the copper, which can be refined and restored.
Several other thermal recovery techniques help recover valuable materials from PCBs. For instance, circuit boards are heated without oxygen in pyrolysis, breaking down polymers and separating metallic from non-metallic components. The resulting gases can be condensed to form oil, which is suitable for use as fuel.
Gasification is a similar thermal recovery process that converts organic materials into syngas (synthetic gas) and solid residue. Syngas can be used for energy generation, while the residue contains metal.
Other techniques like incineration, which involves burning the organic components of the PCBs and reducing them to ash, release harmful emissions that can harm the environment.
Thus, thermal recovery is detrimental to the environment because it releases harmful intoxicants such as lead and dioxin.
Thermal recovery is often followed by a hydrometallurgical process that uses chemicals to leach metals from solid residue.
Refinement
Whatever method you choose, the last step is refining the separated metals to purify them. Refinement ensures that the recovered metals (such as copper, gold, and silver) meet stringent quality standards for reuse in new products.
The refinement process occurs in the following steps:
● Concentration: Materials undergo further separation to increase the purity of extracted metals. Flotation or density-based separation is used to concentrate specific metals from mixed materials.
●
Purification: Despite concentration efforts, the materials may still have residual impurities. Purification processes like hydrometallurgical or pyrometallurgical methods (such as smelting and refining) are essential. These techniques remove impurities to recover high-purity metals.
●
Recovery: In the final stage, pure metals are retrieved through chemical reduction, which converts metal ions into solid metal. Electrowinning is also used for recovery, utilizing an electric current to plate the metal onto the cathode.
Where to Recycle Your Printed Circuit Boards?
It is critical to consider that the recycling center you pick sticks to environmental regulations and recycles metals responsibly. Certifications such as e-Stewards or R2 (Responsible Recycling) indicate reputable recyclers.
Depending on your location, you can choose several channels for recycling PCBs near you. Some common channels include:
Local E-Waste Collection Centers
Most cities have designated e-waste collection centers that accept discarded electronic components, including PCBs, for recycling.
Specialized Recycling Companies
Several companies specialize in recycling electronic waste and PCBs. Sometimes, these companies also offer pickup services and hold responsibility for recycling practices.
Electronics Retailers
Electronic retailers may also feature recycling programs for electronic waste.
Private Recycling Companies
Private recycling companies specialize in recycling electronic waste, including computer circuit boards and other electronic components.
Online Platforms
Websites and other online resources are excellent platforms for searching for local companies dedicated to electronic waste recycling and other recycling locations.
Challenges of Circuit Board Recycling
Electronic circuit boards are complex devices composed of several layers, making recycling these multi-layered electronic components quite challenging. Choosing an environmentally-friendly method adds to the challenge of PCB recycling. Here are some key challenges:
Complex Materials
PCBs are made of valuable materials, inert substances, and hazardous materials, which makes the separation and recovery processes quite intricate.
Efficiency of Conventional Technologies
Traditional recycling methods lack efficiency and require harsh conditions, such as extreme temperatures (greater than 200 degrees Celcius) and pressures. These factors make conventional recycling processes detrimental to the environment.
Economic Viability
Recycling PCBs can incur significant costs, making it financially less appealing for recyclers. Although recycling aims to recover precious metals from circuit boards, this may only sometimes offset the costs.
Environmental Concerns
Recycling processes are not necessarily environmentally friendly, and there's a risk of releasing toxic substances during recycling. This includes lead and brominated flame retardants, which considerably harm the environment.
Technological Advancements
Technology is developing rapidly, adding to the complexity of recycling processes. As PCBs become highly complicated, recycling technologies must continuously adapt to handle these newer types.
Regulatory Compliance
Meeting strict environmental regulations and ensuring that the recycling processes adhere to legal standards is an ongoing challenge.
Hazardous Material
Besides valuable metals, PCBs contain harmful materials such as lead, cadmium, and mercury. These materials can adversely affect the environment and human health if not handled properly.
PCB recycling processes must employ specialized equipment and processes to eliminate and dispose of these materials safely.
Limited Economies of Scale
The PCB recycling industry is relatively smaller than other recycling industries, limiting economies of scale and leading to high recycling costs compared to paper or plastic recycling industries.
Lack of Standardization
Printed circuit boards come in various designs and feature many parts, which adds to the challenge of recycling these electrical components. Because of the wide variety of PCB designs and components, it is tough to develop standardized recycling processes.
Limited Recycling Infrastructure
Recycling e-waste is an emerging issue, and several countries need the proper facilities to recycle PCB boards. Limited infrastructure and high transportation costs make PCB recycling quite a challenge.
Tips for Circuit Board Recycling
Considering the challenges posed by PCB recycling, here are some handy tips for disposing of circuit boards effectively:
Separate Components
One way to make the recycling process seamless is to separate the components of your electronic device on your own. Disassemble the circuit board by unfastening screws, clips, and other fasteners as required.
Consider Donation or Reuse
Before you consider recycling, it's best to analyze whether the printed circuit board is in working condition. If it is still usable, consider donating or repurposing it instead of recycling it. This extends the lifespan of existing electronics while minimizing the demand for new ones.
Research Recycling Options
If you are considering recycling your PCB board, it's optimal to research and compare different options based on their convenience, cost, and environmental impact. You must also consider their certifications to ensure adherence to local recycling regulations.
Find a Trustworthy Electronics Recycler
Check whether your local municipality offers electronics waste recycling programs if you're looking for a reliable electronics recycler near you. Look for a specialized electronics recycler with a reputation for circuit board recycling.
Ensure they hold proper certifications and adhere to recycling protocols for handling electronic waste.
Protect Your Personal Information
Are you recycling your old computer or a related electronic device? Make sure to erase all personal information stored on it before you recycle its circuit board. Safeguard your privacy by removing files, documents, or passwords from your old devices before giving them up for recycling.
Verify Certifications
Pick a recycling company or electronics retailer with certifications like the R2 or e-Stewards. These certifications prove that the company follows responsible recycling practices and meets environmental and social standards.
Adhere to Local Regulations
Don't forget to check your local regulations regarding electronic waste disposal. Some areas have specific rules for handling and disposing of e-waste.
Avoid Landfills
Avoid discarding them in the trash despite the challenges you may face while recycling circuit boards. They contain hazardous materials that can harm the environment if not discarded correctly, making recycling the only environmentally responsible choice.
Future of Circuit Board Recycling
Environmental protection and the adoption of sustainable practices are becoming more popular today. This means e-waste recycling is also gaining recognition as more innovative and efficient recycling methods emerge. As the volume of e-waste increases, circuit board recycling becomes extremely important in ensuring resource conservation.
Researchers strive to introduce environmentally friendly processes that can recover valuable materials from printed circuit boards (PCBs). Researchers have made several advancements in the e-waste recycling industry, including:
Small-Molecule Assisted Approach for PCB Recycling
Introducing the small-molecule-assisted approach is an exciting advancement in the PCB recycling industry. The method involves dissolving the thermosetting polymers containing ester groups commonly found in PCBs.
Unlike conventional methods, this method allows the recycling of PCBs at temperatures below 200 degrees Celsius. The small-molecule-assisted approach is efficient and environmentally friendly because recyclers can reuse the recycling solution several times.
PCB Designs That Aid Recycling
Traditional circuit boards feature intricate designs and multiple layers, making recycling difficult. Researchers have developed PCB designs that can be recycled easily into their original components. The latest designs facilitate disassembly and reuse.
Apart from altering their design, researchers are also looking into using biodegradable polymers as binders for PCBs. The goal is to increase recyclability and reduce environmental impact.
Further research focuses on combining hydrometallurgical and pyrometallurgical processes to increase the benefits of PCB board recycling. Combining multiple methods can improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
Other Emerging Techniques
Technological advancements promise significant improvement in separating and recovering valuable materials from circuit boards. Traditional methods often lead to a loss of valuable resources and can be time-consuming.
However, the latest techniques are more efficient alternatives. Some examples include electrochemical processing, bioleaching, and hydrometallurgical methods.
Electrochemical processing facilitates easier separation and recovery by employing electric currents to dissolve metals from circuit boards. Bioleaching is more eco-friendly compared to conventional techniques. It involves the use of microorganisms to disassemble circuit boards and extract metals.
Biometallugrical methods boast higher recovery rates than traditional methods. The technique involves the chemical dissolution of metals.
How to Make PCB Boards More Recyclable?
Optimizing PCB designs, processing methods, and careful material selection can enhance the recyclability of circuit boards. Some strategies that can improve PCB recyclability include:
Modular Design
A modular design approach aids in disassembling PCBs, making it much easier to separate and recover components of materials. Another advantage of using modular components is easy replaceability and upgradation. This means that a modular design would extend the lifespan of a PCB and reduce waste.
Material Selection
It is essential to pick materials that can easily be recycled and have a minimal environmental impact. Instead of using traditional PCB substrates, it is optimal to use eco-friendly alternatives such as bio-based or biodegradable materials. Proper material selection simplifies the recycling process while reducing the use of non-renewable resources.
Standardization
Standardizing PCB designs and manufacturing processes makes circuit board recycling seamless and ensures consistency across PCB manufacturing industries. Using standardized components and materials makes recovering valuable resources from PCBs much easier.
Labeling and Identification
Lack of labeling and identification creates problems during the sorting and separation process of PCB recycling. Clear labeling allows recyclers to identify and sort valuable materials quickly.
Education and Awareness
Educating designers, manufacturers, consumers, and recyclers about the importance of circuit board disposal encourages sustainable practices. Raising awareness about the impact of e-waste on the environment and available recycling options is crucial to pushing stakeholders to dispose of circuit boards correctly.
Closed-loop Systems
Close-looped recycling systems would reintegrate recovered materials from circuit boards into new electronic products, reducing waste generation. Thus, establishing close-loop systems promotes circularity, ensuring that resources remain within the production cycle.
Investment in Research and Development
Continued research and development initiatives encourage stakeholders to improve PCB recycling technologies and explore more eco-friendly recycling processes.
FAQs About PCB Recycling
1) Are Circuit Boards Recyclable?
Yes, circuit boards are recyclable, although the process can be complex considering the variety of materials they contain. Circuit board recycling will allow you to extract valuable metals like copper, which can be reused with enough purity.
2) How are Circuits Recycled?
Circuit board recycling is a multi-step process that extracts valuable metals from circuit boards, reducing the environmental impact of e-waste. The process starts with dismantling the circuit boards to remove valuable components from devices like CPUs, RAMs, and connectors.
It is then shredded into smaller pieces, after which separation techniques such as magnetic and eddy separation segregate the circuit board into metallic and non-metallic fractions. After the recovery process, recyclers refine the metals for reuse when manufacturing new electronic devices.
3) Is there Money for Recycling Circuit Boards?
Yes, you can generate money from recycling printed circuit boards depending on processing volume and efficiency. However, the profit generated depends on the market prices of recovered metals, including gold and copper. Higher-grade boards product more profit than lower-grade ones.
4) What Can You Do With Old Circuit Boards?
Old circuit boards can be utilized in several valuable ways, including recycling, selling, donating, or reusing them in DIY projects. Some companies purchase electrical components, and you can make a small profit by selling them.
Old circuit boards are excellent resources for DIY projects. Everyday items you can make from old circuit boards include jewelry, guitar picks, stationary holders, etc.
5) Are Circuit Boards Eco-friendly?
No, considering printed circuit boards' traditional manufacturing and disposal process, they are not eco-friendly. They lead to e-waste, when disposed of, a growing global issue that contributes to contamination that can harm the environment and human health.
Despite ongoing PCB recycling and using biodegradable materials for manufacturing circuit boards, PCBs are only partially eco-friendly. A lot more research is needed to reduce their environmental impact.
6) What Components of Electronic Circuits can be recycled?
Several components of electronic circuits can be recycled to minimize e-waste and conserve resources. Circuit boards often recycle metals such as copper, silver, and gold.
Plastics and glass used in electronic devices can be recycled and repurposed. Besides these materials, electronic circuits contain components like resistors, capacitors, and switches that can be recycled and reused.
Conclusion
PCB recycling is an essential process for environmental protection. It aims to recover valuable materials from printed circuit boards while minimizing environmental impact. Several recycling methods can extract these metals from circuit boards, including physical, chemical, and thermal processing.
These techniques enable recyclers to reuse resources from electronic waste, eliminating the need for mining and extracting additional materials for electrical manufacturing processes. Circuit board recycling is, therefore, an invaluable technique for overcoming environmental hazards.

 About PCBasic
About PCBasic