Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > 3.3K Resistor Color Code | Everything You Need to Know
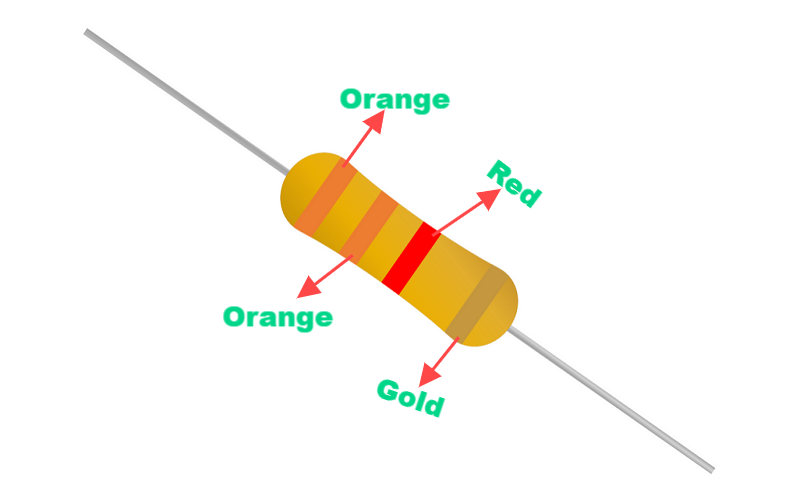
3.3K resistors (3300 ohms) specifically refer to resistors with a resistance value of 3300 ohms, which are commonly used in consumer electronics, automotive and industrial equipment. See the picture below:

Such resistors play a key role in circuits for limiting current, dividing voltage or protecting other components. Its resistance value is identified by the color code of the resistance. The common 3.3K resistor color code is orange, orange, red and gold. Depending on the material (e.g., carbon film, metal film, wire-wound resistor…) and construction, 3.3K resistors can be used in applications with different power and accuracy requirements.
The resistance value of the 3.3k resistor is 3300 ohms, which means that the resistance that the resistor can produce in the circuit is 3300 ohms, and this value also indicates the resistance that the resistor can apply in the circuit, that is, the size of the current flow through the circuit. The tolerance (the allowable deviation range of the actual resistance value of the resistor, usually expressed as a percentage) determines the deviation between the actual resistance value of the resistor and the nominal value. Smaller tolerances mean higher accuracy and are more suitable for circuits that require precise control of current and voltage.
Common tolerance levels for 3.3K resistors are ±5%, ±1%, and ±0.1%.
The power class is important for a 3.3k resistor, because the power class determines the maximum power the resistor can withstand, which also determines the application scenario it is suitable for.
Common power levels for 3.3K resistors: 1/4W, 1/2W.
Different types and styles of resistors are suitable for different applications. The main types of resistors are fixed resistors and variable resistors (such as potentiometers), and common styles of resistors are axial resistors and surface mount resistors (SMDs), each of which has its advantages and disadvantages.
 About PCBasic
About PCBasic
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
Common 3.3K resistor materials mainly include the following:
Types
Material structure
Advantages
Disadvantages
Carbon Film Resistor
A thin carbon film is deposited on a ceramic substrate
Low price and simple production process
Poor precision and heat resistance
Metal Film Resistor
Deposit a thin film of metal (e.g., nichrome) on an insulating substrate
High accuracy (±1% or less tolerance), good stability and low noise
Higher cost
Wirewound Resistor
A high-resistivity metal wire, such as nickel-chromium alloy, is wound around an insulating ceramic matrix.
It can withstand large power and has high accuracy
Large volume
Metal Oxide Film Resistor
Coating a ceramic substrate with a metal oxide (e.g., tin oxide)
High heat resistance and overload resistance
Slightly less accurate than metal film resistors
Thick Film Resistor
A thick film structure is formed by printing on the substrate with a conductive paste.
Small size and good mechanical stability
Low accuracy
When choosing a 3.3K resistor, the appropriate material type can be selected according to the actual needs of the circuit.
Color code allows quick identification of resistance values and tolerances without additional marking, making it easy and fast to select the right resistor. Each color ring has a specific meaning in the color coding system.
Let’s see a table of color codes:
Color
Digit Value
Multiplier (Ω)
Tolerance
Black
0
×1
None
Brown
1
×10
±1%
Red
2
×100
±2%
Orange
3
×1,000
None
Yellow
4
×10,000
None
Green
5
×100,000
±0.5%
Blue
6
×1,000,000
±0.25%
Purple
7
×10,000,000
±0.1%
Gray
8
None
±0.05%
White
9
None
None
Gold
None
×0.1
±5%
Silver
None
×0.01
±10%
Normally, 3.3k resistors have 4 band resistor color code:
1. The first two rings (significant number) indicate the significant amount of resistance.
2. Third ring (multiple): indicates the multiple to be multiplied after the significant number.
3. Fourth ring (tolerance): Indicates the allowable deviation range of the resistance value; for example, gold indicates a tolerance of ±5%, and brown indicates a tolerance of ±1%.
As an example of the 3.3k resistor in the following figure,
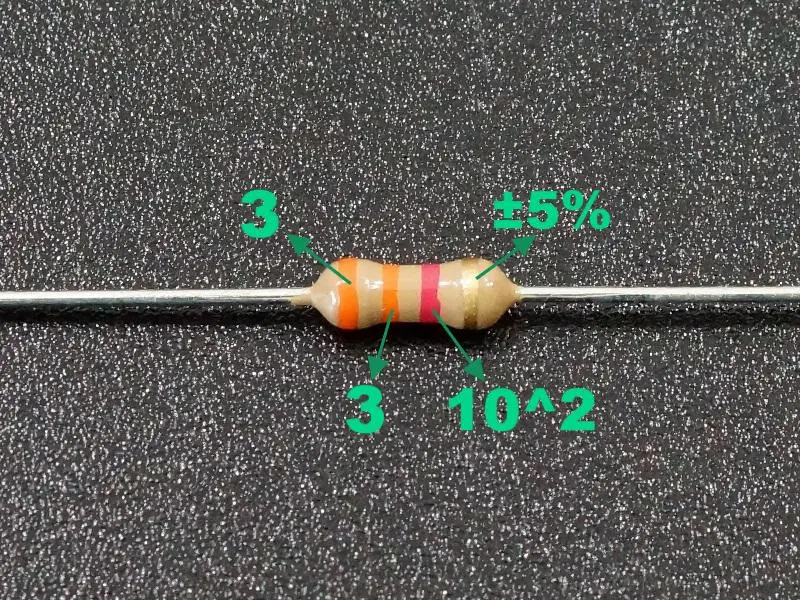
First ring: Orange - indicates the first significant number "3"
Second ring: Orange - indicates the second significant number "3"
Third ring: Red - represents a multiple of 10, i.e., "10^2" or "100."
Fourth ring: Indicates tolerance - Common tolerance ring is gold ±5%
Therefore, its resistance value is 33×100=3300Ω, and the tolerance is ±5%. If its fourth ring is brown, then its tolerance is ±1%.
1. If you want to choose a resistor that can play a stable role in a low-current circuit and the power consumption is not too high, a 3.3k resistor whose resistance value is not too high or too low is a good choice.
2. If you want a resistor that limits the current flow through the circuit, can adjust and divide the voltage signal, and can stabilize the transistors in the bias circuit, you can also choose a 3.3k resistor.
3. The 3.3KΩ resistor is one of the standard value resistors, and its price is relatively low and easy to obtain, which is easy to purchase and apply in large quantities.
A 3.3k resistor has certain limits of power consumption and precision, so it is not suitable for circuits with high power consumption and high precision requirements. In addition, the resistance value of the 3.3k resistor will change with the temperature, and electrical noise will be generated. Its temperature fluctuations and the electrical noise vary according to its material.
In a word, 3.3k resistor has its advantages and disadvantages, which is not suitable for all application scenarios, so you should select the resistors according to the specific situation.
|
|
3.3K Resistor
|
2.2K Resistor
|
|
Function |
Commonly used in voltage regulation, filtering, and voltage divider circuits |
Generally used in low-power circuits |
|
Tolerance |
±1%, ±5% |
±1%, ±5% |
|
Common Applications |
Consumer electronics, automotive, industrial applications |
Sensors, signal processing circuits |
|
Availability |
Widely available |
Easy to find |

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
