Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > FCCL, FCCL PCB | Do you Know?
Flexible copper-clad laminate is considered the major material input in the manufacturing of printed circuit boards and, in particular, flexible printed circuit board development. FCCL is basically a thin copper layer laminated onto a flexible polymer, usually polyimide; thus, it is very suitable for applications that require light and capable electronic components. It is especially the laminate structure that allows the designer to provide for bending, folding, and even twisting without damage, thus making high demands possible and always increasing on compact and wearable devices, including smartphones, wearables, and automotive systems.

The advantages of FCCL can be seen with both PCB designers and its manufacturers; its flexibility can, in turn, provide for compact circuit designs in more compact devices without affecting the durability factor. The FCCL material also offers reliability in terms of high-stress situations where temperature and extreme conditions could not deter the functioning of this material. What the market demand says to itself speaks volumes about its value for FCCL. It would experience significant growth due to the ever-growing demands of portables and flexible electronics in the global arena.
For PCB manufacturers, the relevance of understanding the requirements of FCCL continues to grow every passing day for them to catch up with this landscape demanding flexibility, high efficiency, and high ruggedness.
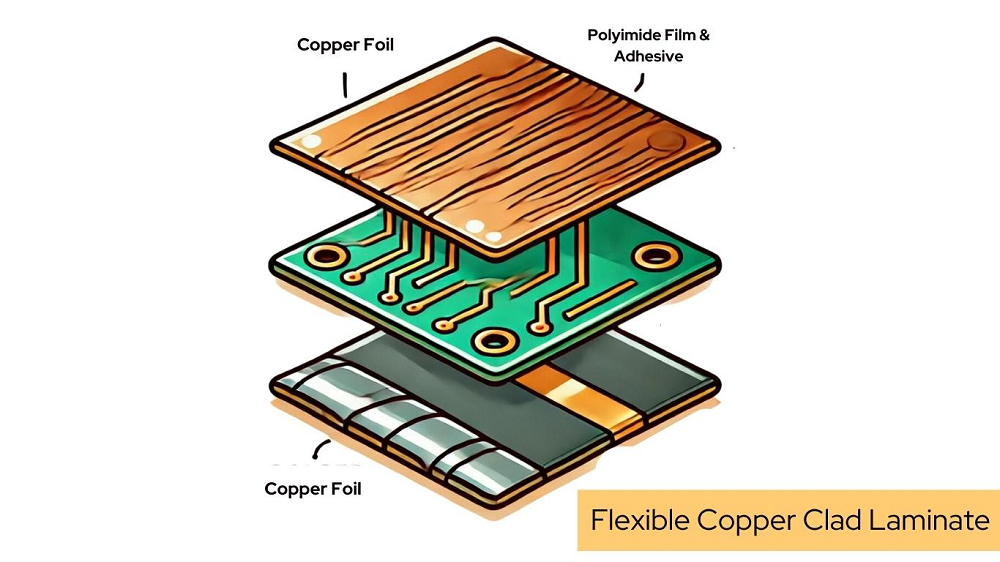
Flexible Copper Clad board Laminate is a special laminate that integrates a thin copper layer bonded to a flexible polymeric substrate, usually polyimide or polyester. The resultant combination of materials is exceptionally strong and flexible, and it is an electrical conductor that can conduct with flexibility. FCCL is one of the most important constituents in flexible printed circuitry. Unlike the rigid laminates of old, FCCL is flexible and resilient enough to support a bending circuit in various shapes for such demanding applications in flexible, high-performance electronics.
In those devices that go through the processes of repetitive bending or compacting into small spaces, FCCL's flexibility and strength become an important aspect where functionality cannot be sacrificed. FCCL is, thus, indispensable in an advanced application where reliability and toughness are the highest priorities. FCCL plays an important part in the most ordinary aspects of modern technology, especially wearable technology such as smartphones, tablets, and wearables, all of which benefit from FCCL's ability to conform to limited spaces without any loss of conductivity. Other key applications include medical devices, automotive electronics, and industrial equipment. All these need materials that can enable dynamic movement under extreme conditions to ensure their long-term reliability.
Regarding structural composition and flexibility, these represent FCCL materials that serve appropriate applications within the electronics manufacturing industry.
● Single layer FCCL: Here, one copper layer is bonded to a flexible substrate. The single-layer FCCL is used in very simple and lower-cost circuits. These circuits will have just one conductive layer, such as LED lighting and static display modules.
● Double-layer FCCL: It has two layers of copper separated by an insulating layer. This configuration enables the possibility of complex wiring, increased functionality, and connectivity, characteristics often observed in more complex applications like automotive electronics.
● Multi-layer FCCL: Multi-layer FCCL develops one or more layers of copper and insulating films and encourages complex designs that are suitable for high-performance electronic systems. They are applied in applications requiring high performance and multiple points of connection, such as in high-speed communication devices.
● Flexible FCCL: FPC FCCL is developed to bend and flex repeatedly for applications such as wearable devices and flexible displays in the expectation of durable functioning with constant movement.
● Semi-rigid FCCL: This provides some flexibility but is stiffer than fully flexible FCCL, thus suitable for applications wherein slight movement occurs but extreme flexibility is unnecessary, such as in automotive circuit assemblies.
● Stiff FCCL: Though technically FCCL, these copper laminates are very stiff and provide very low flexibility. Rigid FCCL is used in applications based on mechanical stability, such as industrial machinery, control systems, etc.
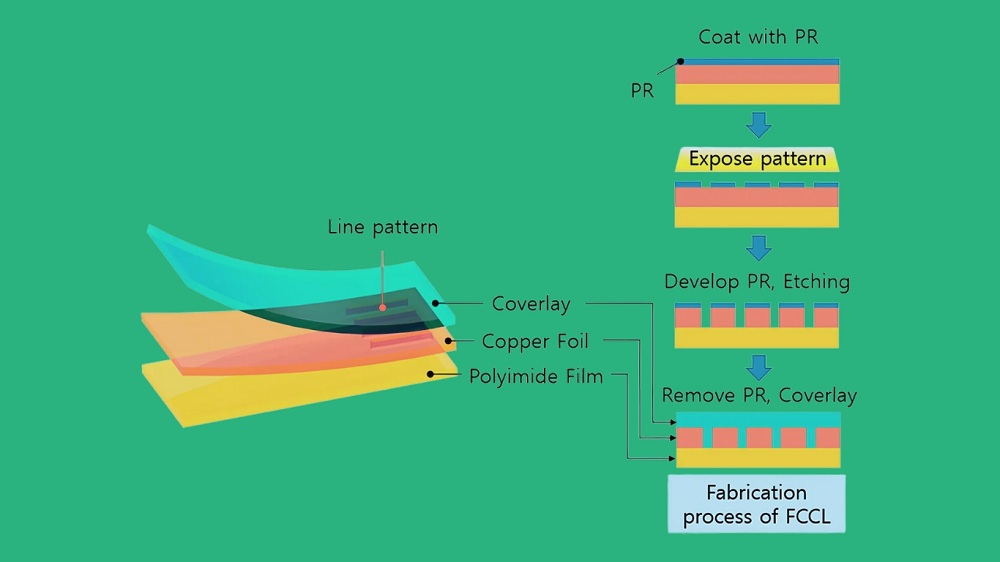
There are many layers that form the structure of the FCCL. Every layer is different and specific, thus comprising flexibility, durability, and overall electrical performance.
● Copper Foil: This is the outermost layer and carries electricity via traces of the circuit. It may vary for different purposes but provides the necessary conductive traces.
● Adhesive Layer: It is the bonding agent, and the adhesive layer bonds the copper foil firmly to the flexible base layer. The layer also supports mechanical stress absorption so that the product can bend without breaking the electrical circuit.
● Polyester Film: It applies as the base flexible film in FCCL at elevated temperatures and mechanical stability films. High flexibility enables lamina to undergo bending without cracking and thereby makes these films suitable for applications on high-performance laminates.
The manufacturing process requires several stages to produce high-quality output in FCCL.
Copper foils are prepared, treated, and cleaned in order to produce a smooth conducting surface.
1. Lamination: It laminates the polyimide film together with the copper foil, typically with an adhesive between the two surfaces, using controlled heat and pressure.
2. Etching: The lamination material is etched so as to make special designs of the circuit.
3. Quality Control: Every sheet's electrical and physical strength is tested to meet very high standards.
Flexible PCBs based on FCCL integrate the material into the circuit for its flexibility and folding capability within the tolerance of movement.
● Polyimide: This is an elastic polymer whose base material has good thermal stability and good mechanical strength.
● Adhesive: The adhesive provides flexibility and gives the foil with copper a flexible quality that keeps it attached to the polyimide film.
● Copper Foil: Copper layer forms the circuit path, with conductivity and strength.
● Manufacturing Processes: Common FCCL manufacturing processes include etching in defining circuit patterns and lamination in combining materials strongly, followed by testing to check reliability and performance.
● FCCL's stack-up provides flexibility, allowing it to bend without breaking, which is ideal for wearables and flexible screens.
● It provides toughness, resistance toward mechanical stress, and repeated movement of dynamic applications.
● Another advantage is thermal resistance because polyimide can withstand high-temperature levels, so FCCL PCBs are suited for highly stressed thermal environments and automotive or industrial electronics applications.
PCBs from FCCL are the basis for the development of long-lasting flexible electronics with continuous motion and mechanical stress resistance. For example, the polyimide film of FCCL forms a flexible backbone that maintains its structure even when the circuit is bent or twisted. Applications include wearable devices and foldable screens. Reliability improves with flexibility since FCCL-based circuits survive environmental stressors such as thermal variations without cracking or degrading.
FCCL ensures that they deliver the best electrical performance in their materials. The copper layer in FCCL is highly conductive, meaning efficient signal transfer with minimal resistance. This means that signal loss through the circuit is less likely, which is what applications with stable, high-speed data transfer require. Also, the PCB of FCCL dissipates heat better since copper is conductive, reducing the chance of overheating in closely packed electronic devices.
Thicker laminates of FCCL have more mechanical strength but less flexibility, while laminates of lesser thickness allow much greater flexibility and bendability in compact devices. Such layers find their applications in those areas requiring stability, such as automotive electronics. The designer must care for the selection of thickness according to the requirement of the device, achieving a balance between strength and flexibility.
Copper fill in FCCL PCBs impacts electrical as well as physical characteristics:
● Solid Copper Pours: The power is maximized, and solid pours offer good thermal performance. They are highly recommended for circuits that need handling higher currents or create huge heat as they show stability without losing any degree of electrical conductivity.
● Hatched Copper Pours: Hatching pours can actually reduce the total weight of a PCB but increase flexibility. The design is very useful for applications that need lighter, bendable circuits, like portable devices.
● Cross-hatched copper pours: It provides a fine balance, that is, the maximum bendability together with satisfactory strength. It is often used wherever folding or bending is performed numerous times because the layer of copper will not break off under it.
The proper design of the FCCL PCB increases its bending capacity. Thus, a bigger bend radius, no sharp corners, and uniform thickness would preserve its integrity when bent. With flexible adhesives or materials, repeating bending for wearable or foldable electronics does not delaminate or structurally fail, thus making the circuit even more durable.
A high-performance, flexible material that can be used for manufacturing PCBs, FCCL allows flexibility, reliability, and enhanced electrical performance required by today's sophisticated electronic applications. Whether a smartphone or an industrial device, there is a need for next-generation technology, where a PCB needs to be strong and flexible. With this use, designers and manufacturers of PCBs can design and manufacture high-performance flexible PCBs using FCCL.
For those interested in development based on the benefits of FCCL, it may also be considered for high-performance flexible designs. In addition to the unique properties of PCB manufacturing, full potential is a key to competitiveness in the electronics industry.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
