Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > Choosing the Best PCB Colors for Your Projects
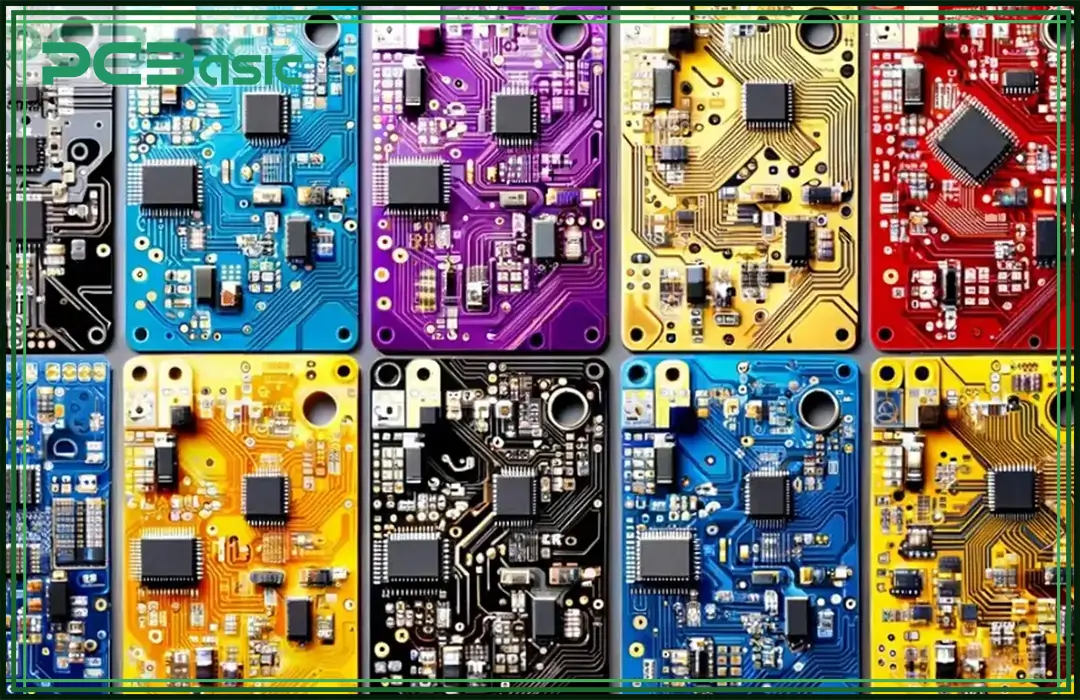
The PCB colors are set by the solder mask, a protective layer that stops oxidation and short circuits. While green PCBs are still the most common because of their high contrast along with their cost-effectiveness, modern designs now include red PCBs, blue PCBs, black PCBs, white PCBs, yellow PCBs, and purple PCBs to balance the aesthetics as well as functionality. For example, black PCB boards absorb heat well, while blue PCBs improve trace visibility in aerospace applications.
The PCB background, set by the solder mask colors, balances the aesthetics, the functionality, and the manufacturing efficiency. While the solder mask colors do not change the electrical performance, they affect trace visibility, the heat dissipation, and the brand identity.
The high-contrast solder masks (such as the green PCB and yellow PCB) make the inspections easier, helping in defect detection for the industrial along with the medical devices, though black PCB boards need special lighting for better readability.
Black PCBs absorb less radiation, making them good for the heat-sensitive designs, while red PCBs and purple PCBs focus on the aesthetically pleasing branding in the high-end electronics as well as the niche markets. White PCBs have a clean look but low contrast, needing the dark silkscreen text. The green PCBs are affordable and widely used, whereas purple PCBs cost more because of the complex production.
The design process should consider the application (such as the green PCB for industrial use), the contrast needs (such as yellow PCB for visibility), and the cost (such as purple PCB for luxury applications).
Circuit boards are mostly green because of the historical military rules, the technical benefits, and the cost-efficiency. The green solder mask was first used in the 1950s when the U.S. military made it a standard for its high contrast against copper traces, helping in defect detection in tough environments. Later, the manufacturers used green PCBs for civilian electronics due to extra materials and easy production, making it the industry standard by the 1970s.
The practical benefits include lower eye strain (the green color reduces visual fatigue during long inspections), better protection from oxidation and environmental damage, and cost-effectiveness (cheaper to produce than blue PCB or red PCB). Its technical advantages, such as improved signal integrity and smooth manufacturing, make it the top choice in industries like aerospace and IoT, though alternatives like purple PCBs are used for unique aesthetics.
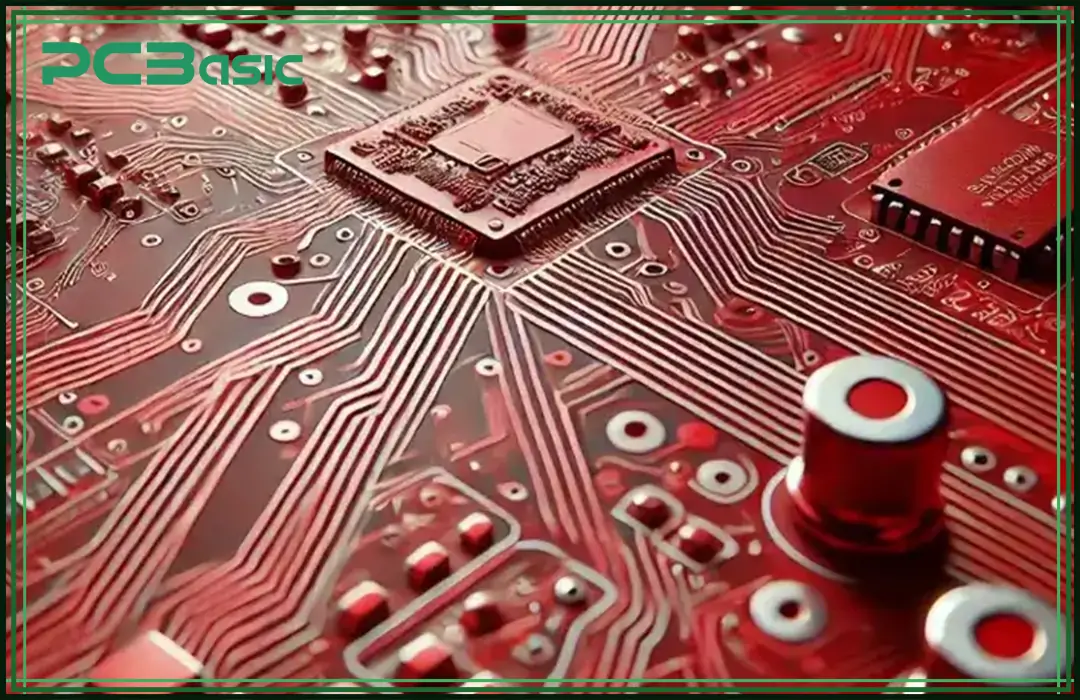
Red PCBs are popular for their bold and aesthetically pleasing look, often used in the high-end electronics along with the automotive systems. Their high contrast helps in defect detection, though the magnification may be needed for the fine traces.
Key Advantages
· Heat Management: Red PCB materials spread the heat well, improving the thermal performance.
· Durability: Made with strong materials for use in harsh environments.
· High-Frequency Use: A low dielectric loss tangent (0.002 vs. 0.02 in the standard PCBs) lowers the signal distortion in the RF or microwave circuits.
Applications
Used in the automotive (like EV charging), aerospace, and medical devices.
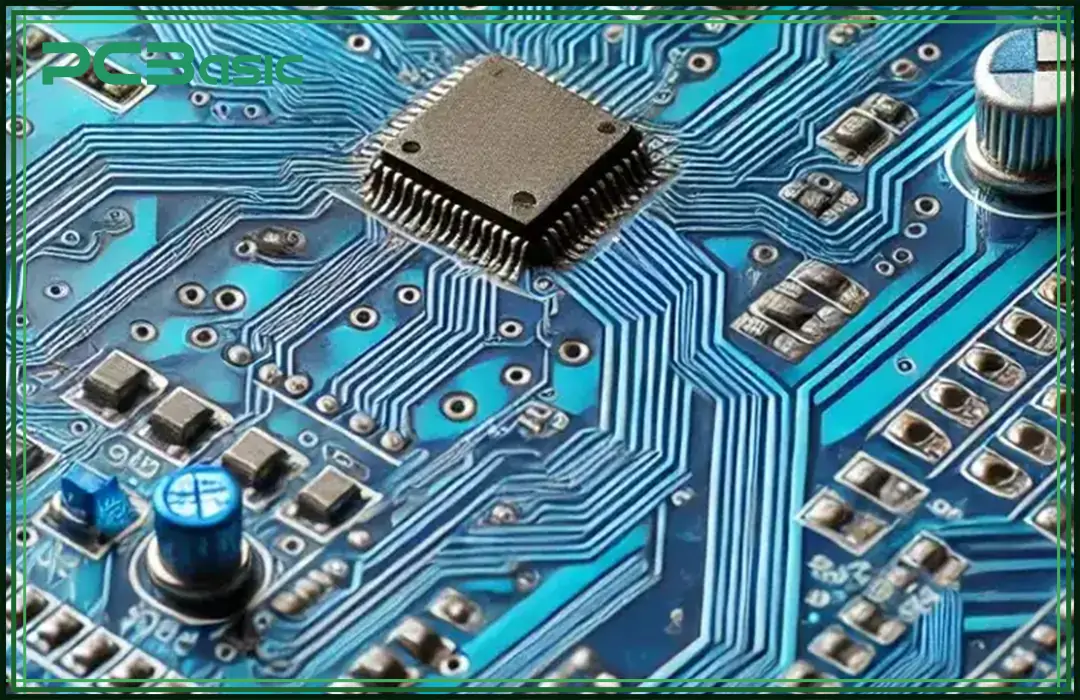
Blue PCBs are commonly used in the aerospace and the robotics for their professional look along with their clarity. They offer excellent contrast with the components, making the inspections easier.
Key Advantages
· Moisture/Chemical Resistance: Blue solder masks last longer in harsh environments than green PCBs.
· Signal Integrity: Provides better performance in high-frequency communication systems.
· Durability: Strongly resists the cracks and the peels under stress.
Applications
Used in industrial control systems, gaming consoles, and IoT devices.

Black PCB boards have a sleek design and are heat-efficient, absorbing less radiation than the lighter colors. However, their low contrast makes trace visibility harder without the special lighting.
Key Advantages
· High Current Handling: The higher copper content supports power-heavy applications like electric heaters.
· Voltage Regulation: Best for the high-frequency power supplies (SWPS) along with the rectifiers.
· Aesthetics: Resistant to fingerprints and smudges, improving the look of the consumer electronics.
Applications
Used in consumer electronics (like the cameras and the laptops), communications (like the routers), and medical devices.
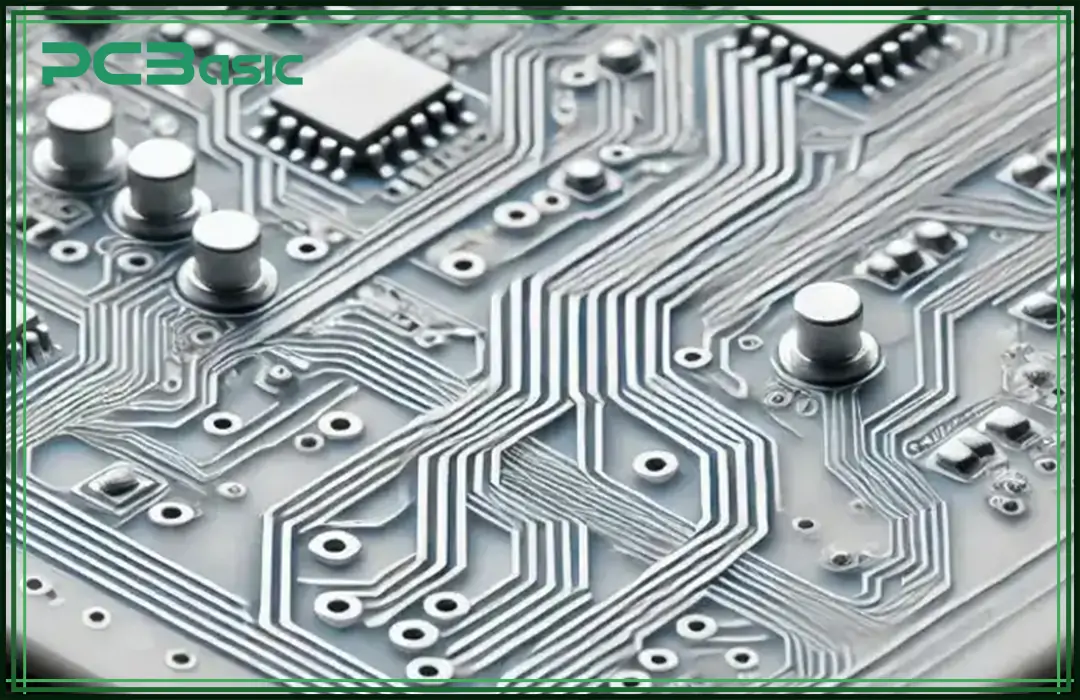
White PCBs have a clean finish but low contrast, which makes them easy to stain. They are often used in consumer electronics, like smartphones, for their polished and modern look.
Yellow PCBs work well in the high-visibility applications, such as the medical devices, where their bright color helps in safety as well as the component identification.
Purple PCBs are rare and expensive but are used in the niche markets needing custom designs. Their bright color helps in the brand differentiation.
Key Advantages
· UV Resistance: Purple solder masks prevent fading under the sunlight.
· Heat Dissipation: Said to improve thermal management, though more testing is needed.
· Eye Strain Reduction: The high contrast makes long inspections easier for the technicians.
Applications
Used in smartphones, wearables, automotive electronics, and IoT devices
Choosing the best PCB color depends on the application, the aesthetics, the cost, and the manufacturing efficiency.
· For heat-sensitive designs, black PCBs or blue PCBs absorb heat well, making them ideal for high-power electronics.
· The green PCB or yellow PCB offers high contrast, helping in defect detection for industrial and medical devices.
· White PCB improves LED efficiency by reflecting light.
· Black PCB or red PCB gives a premium look to consumer electronics.
· Purple PCBs or blue PCBs are used in niche markets.
· The green PCB is cost-effective due to standardized manufacturing, while the purple PCB or red PCB is more expensive.
Make sure the silkscreen contrast is clear (such as dark text on white PCBs) and that the color works well with automated inspection tools (such as the green PCB for AOI systems).
|
Use Case |
Recommended PCB Color |
Why? |
|
General electronics |
Green PCB |
Cost-effective, high contrast. |
|
High-end consumer goods |
Black PCB |
Premium aesthetics, heat management. |
|
LED lighting |
White PCB |
Reflects light and enhances efficiency. |
|
Medical/industrial tools |
Yellow PCB |
High visibility and safety. |
|
Custom branding |
Purple PCB or Red PCB |
Unique appeal, niche markets. |
When adding PCB colors to the design process, focus on silkscreen contrast, manufacturing tolerances, and application-specific needs.
· Use dark text on white PCBs or light text on black PCBs for better readability.
· Black PCB boards need reflective silkscreen inks to improve low contrast.
· Automated inspection systems (AOI) prefer green PCBs because of their standard contrast, making defect detection easier.
· Thermal management matters: black PCBs absorb heat but need cooling, while white PCBs reflect light, helping LED efficiency.
· Aesthetically pleasing choices like red PCB or purple PCB improve branding but may raise costs and production complexity.
Balancing these factors ensures PCB colors match functionality, cost, and visual goals.
PCB colors combine functionality, aesthetics, and cost-efficiency, guided by solder mask choices. While the green PCBs remain standard for their high contrast, cost-effectiveness, and automated inspections, modern designs now use red PCB, blue PCB, black PCB, white PCB, yellow PCB, and purple PCB to meet specialized needs.
· Black PCBs perform well in heat-sensitive applications.
· White PCBs improve LED efficiency by reflecting light.
· Purple PCBs support custom branding in niche markets.
The design process must balance thermal management, inspection ease, and brand identity to ensure the best PCB aligns with performance, cost, and visual goals. By considering these factors, engineers and manufacturers can optimize PCB colors to drive innovation while maintaining practicality and aesthetics.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
