Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > > Basic Electronic Components: The Ultimate Guide
Electronic components are the basic building blocks of every electronic device, no matter if it is a simple circuit or a complex system. From putting together, a minor kitchen appliance to creating a state-of-the-art electronic consumer device, knowing what components make a circuit is essential for the job to be done well. Resistors, capacitors, diodes and transistors are common electronic components in the core of nearly any electronic application.
This blog explains the most common electronic components with names and schematic symbols, how they are recognized, and their function in a circuit, from the very generic electrical components to particular parts for complicated circuits. In this article, we will see different electronic components, divide types of electronic components into passive and active electronic components with their electronic components list.
These are the key building parts of the electronic components which regulates the flow of current in a circuit. There are several varieties, sizes, types and styles but all serve a specific purpose in electronic devices. They are one of the most important components in any electronic circuit, and none of the devices will function without them. Such aspects of electronics are vital as they are executed in behaviors of electrical systems, all the while completing even simple tasks such as controlling the flow of current to more complex tasks such as signal amplification, or even energy storage.
Every electronic component possesses properties that determine its work. For example, resistors limit current, capacitors store energy, and diodes control current flow. The key to building real electronic devices is getting these most basic electronic components and their interactions inside of circuits straight first.
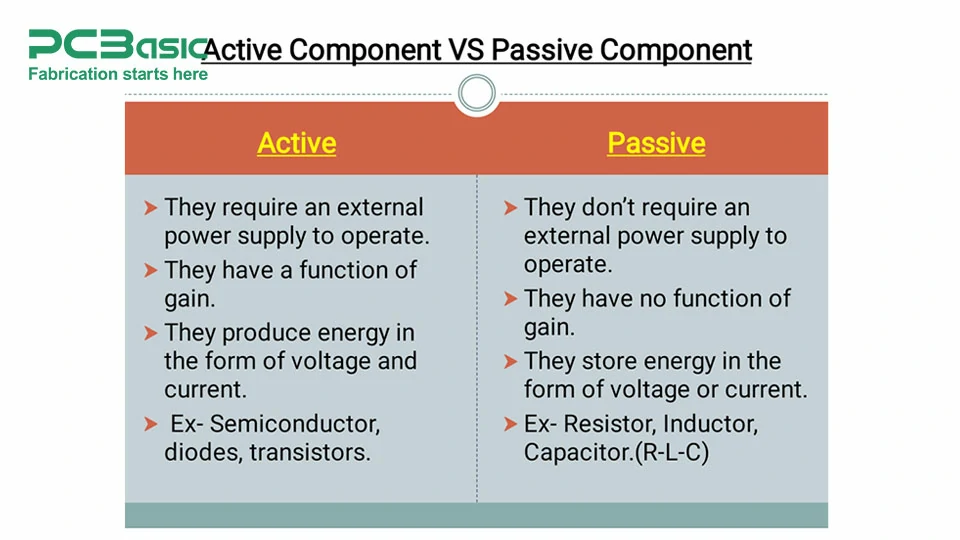
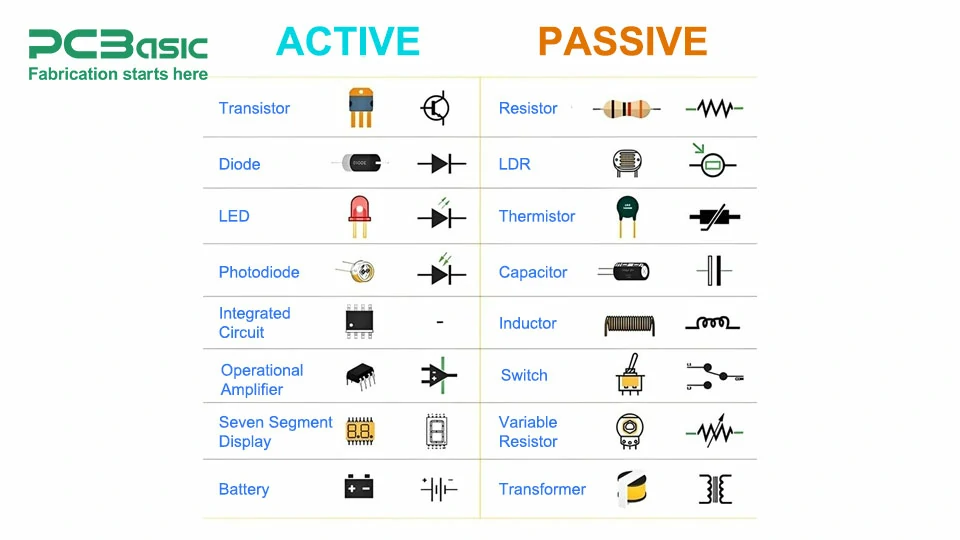
Types of electronic components are primarily classified into two parts: active components, and passive components. These types are essentially based on how these components interact with the circuit and if they require external power supply to work.
Active components are electronic components that need an external power supply to function. These elements can also direct the energy to the circuit.
Passive components do not need any external power supply for operation, so they can be termed as passive components. They're either charged with current, in other words, store energy, or they impede current but on their own, they aren't capable of amplification or signal generation.
Active and passive components play a crucial role in determining the behavior and function of electronic circuits.
Some of the most widely used common electronic components include:
• Resistor: A resistor is an electronic device that resists the current pass through it because excessive current can damage the electronic devices. Resistors are used to limit current according to Ohm's law, and they always have some value of resistance. They are typically used with colored bands indicating the resistance value of the resistor, and they are typically how the user selects the type of resistor that will be used in the circuit. It may be a constant or adjustable resistor, for instance.

• Capacitor: The capacitor is the component that stores and releases electrical energy. It operates by holding a charge in an electric field. Capacitors are widely used in power circuits, filtering circuits, where they are used to smooth a current fluctuation or provide instantaneous power. And in many cases, in timing circuits as well as isolators to separate high-frequency circuits. Capacitors can be divided into ceramic, electrolytic and tantalum.
• Diode: A diode is a type of device that only lets current flow in one direction. One of the main jobs it does is rectification, which is the conversion of AC to DC. In one direction (the forward direction) it has a small resistance and in the other (the reverse direction) it has a large resistance, so it stops the reverse current from flowing. They are used in a variety of applications like power rectification, signal processing, etc.

• Zener Diode: A diode used to stabilize voltage. While other diodes simply pass current through them to produce a voltage drop across them, the Zener diode will produce a constant output voltage (even in reverse bias). These are mostly used to get a constant supply voltage in voltage regulation circuits, over-voltage protection circuits.

• Inductor: Inductor is a component in which electrical energy gets stored in the form of magnetic energy. Inductors are typically coils made from copper wires with positive changes in current flow. They are found in inductive loads (like motors), transformers, and also in filters including high-frequency noise reduction, filtering, and energy storage, if you will paper-induced reference.

• Varactor Diode: A varactor diode is a special type of diode whose capacitance can vary depending on the external bias voltage. It is commonly used in tuning circuits, such as those in FM radios, televisions, and wireless communication devices. The ability to vary capacitance allows it to adjust frequency response and tune circuits to the desired operating frequency.

• Transistor: A transistor is an electronic device with three terminals that is used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power. In transistors, the input current ( or voltage) will control the output current. Typically, they are employed in both analog circuits (e.g. sound amplifiers) and digital circuits (e.g. logic circuits and memory). Transistors are further classified into Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) and Field Effect Transistors (FET).

• Field-Effect Transistor (FET): A field-effect transistor (FET) is a transistor in which the current is carried by an electric field. Complementary to BJTs, FETs offer high input impedance low power consumption and are very significant for every modern electronics in applications like signal amplification in electronic devices, switching circuits and integrated circuits. FETs have higher input impedance than BJTs, which allows for better control of current flow and use in high-frequency applications. Different types of FET are available, like MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor FET).
• Sensor: Sensor — a device that converts one or more physical variables such as temperature, light, pressure, motion etc. into electrical signals. It allows machines to engage with their environment and respond. Sensors are used in many applications ranging from temperature control systems to autonomous vehicles to smart home devices to medical equipment. They supply feedback and monitor data in real-time.

• Transformer: A transformer is a type of electrical device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction and is used mainly for AC (alternating current) signals. The transformer is based on electromagnetic induction and can step up (increase) or step down (decrease) the voltage per the need. Transformers are essential in power transmission and distribution, power adapters, and audio circuits. There are various types of transformers available based on the operation frequency like power transformers, signal transformers, high-frequency transformers etc.

These common electrical components are essential in both simple and complex circuits, which can enable everything from power conversion to signal processing.
Once you work with electronic components, you should be able to identify them quickly and in an accurate manner. This guarantees the components are used correctly and also helps to prevent damage during assembly or a repair from occurring due to identification issues.
Identifying the right components in an electronic component list is of paramount importance. Though there are many components that take a similar form like field effect transistors and varicap diodes, but play an entirely different role in the circuit. Identifying their features and patterns is vital for ensuring proper identification and assembly of the circuitry.
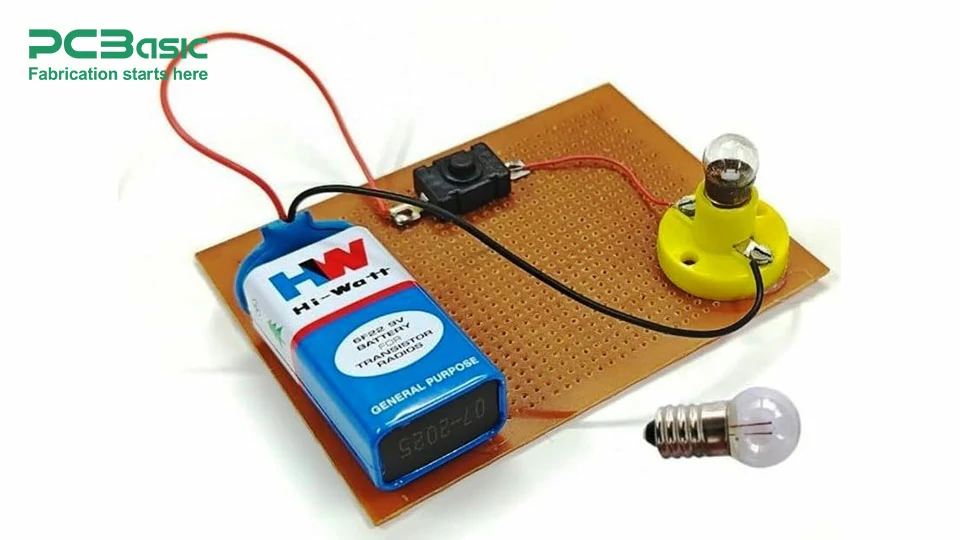
A circuit is a collection of electronic components that create a path for current to flow. These pieces need to be connected in a specific way to allow energy to flow continuously and properly so that every part of the system does the job it is supposed to do. So, what components make a circuit?
• Power Source: The first component of any circuit is a power source like a battery or a power supply which will provide the voltage required by the circuit to function.
• Resistors: Resistors are probably the most common electrical components. They restrict the current flowing through the circuit and protect sensitive components from too much current.
• Capacitors: Capacitors act to store electrical energy and release it as necessary. They smooth out fluctuations in voltage and typically can be found in power supply circuits.
• Diodes: It is a device that permits current to pass through in one direction only, thus it is useful for converting alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC).
• Transistors: Transistors are used to amplify electrical signals or switch them off or on. These are an essential part of signal processing and amplifying the signal.
• Inductors: Inductors store energy in a magnetic field and are most used in power supplies, filters, and RF circuits.
These basic electronic components are fundamental and combined with other components to form a complete circuit. Depending on the common electronic components that are used in the design process, you will either come up with a lighting circuit or even some more complex ones such as a power control system.

What are electronic components? They are the building blocks that compound every circuit no matter how simple or convoluted. Whether electronic components are as common as resistors and capacitors, specialized as diodes and transistors, knowing your fundamental components and how to identify them is your key to succeeding in electronics.
Once you learn about the electronic component list and identification of electronic components, you will be equipped to tackle any project and make sense of how the parts of electronics control the world around us.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
