Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > Reflow Soldering: Challenges and Solutions
Reflow soldering is a very important part of the modern PCB assembly, used for making strong and stable electrical connections by melting the solder paste. The process is done so that the parts are fixed tightly on the PCB, along with the safety of the full connection.
But some problems are also faced in the process. Key things like the reflow oven's work and the proper control of the solder heat are carefully watched to prevent bad joints that harm the PCB's work and strength.
Common problems like cold solder joints, blowholes, less solder, as well as sticky flux can badly hurt the work of the device. In this article, the usual issues will be clearly shared, good and easy fixes will be given, and the best tips in PCB design will also be shown to stop these problems.
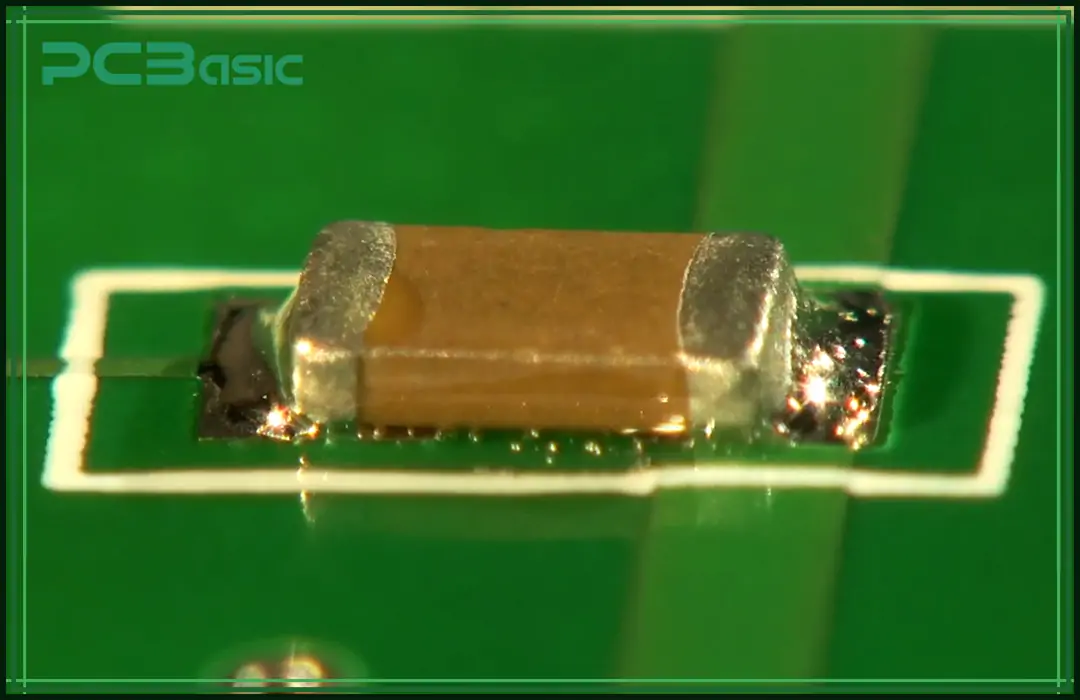
Reflow soldering is widely regarded as the most effective method in Surface Mount Technology (SMT) for PCB assembly.
The process starts with careful putting of solder paste on the PCB pads, along with the exact setting of the small parts.
The whole board is then slowly heated in the reflow oven. The solder paste is warmed to its reflow heat—usually from 180°C to 250°C, based on the solder type—and is melted, as well as joined to make a metal bond between the part legs and the PCB pads.
When cooled, the solder gets hard and makes a strong electric and solid bond.
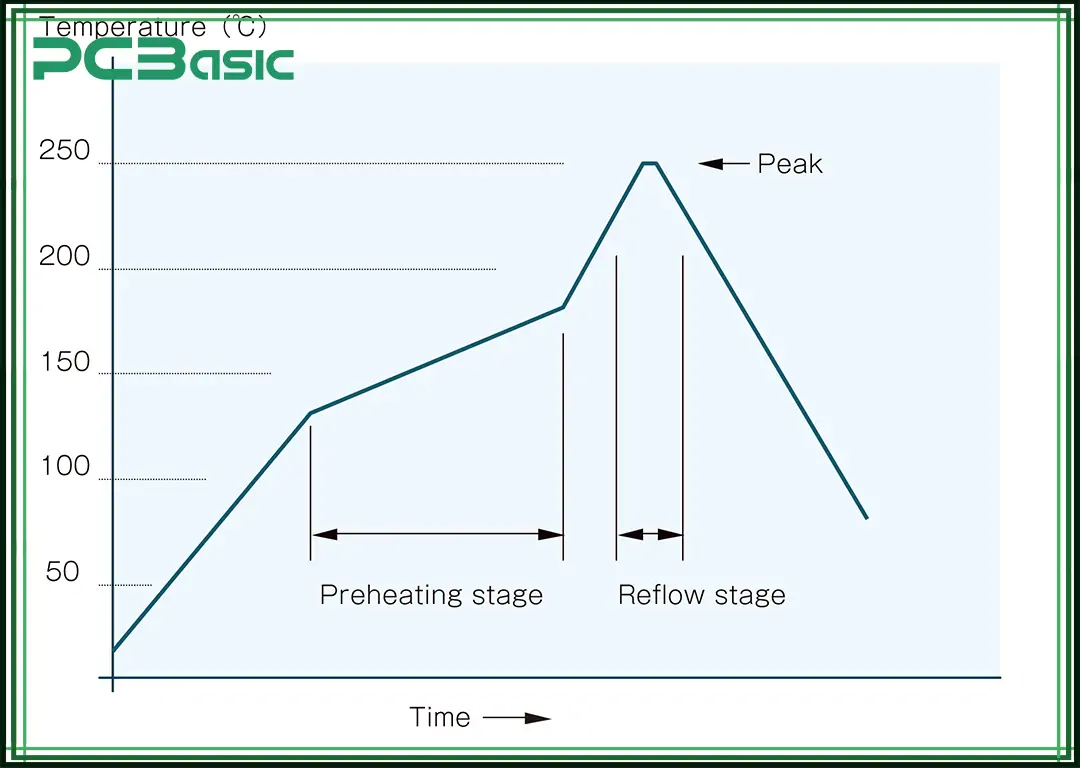
Successful reflow soldering is done in three main steps: the preheat phase, the reflow phase, as well as the cooling phase.
In the preheating step, the PCB and parts are slowly heated to stop heat shock, start the flux for better metal cleaning, along with giving even heat to all areas.
The reflow step is when the solder paste is melted, and the component leads are joined to the PCB pads, with the heat carefully controlled to stop damage and reach the right reflow level.
In the cooling step, the heat is slowly reduced so the melted solder becomes solid and makes strong and trusted joints, with gentle cooling needed to stop stress in the solder.
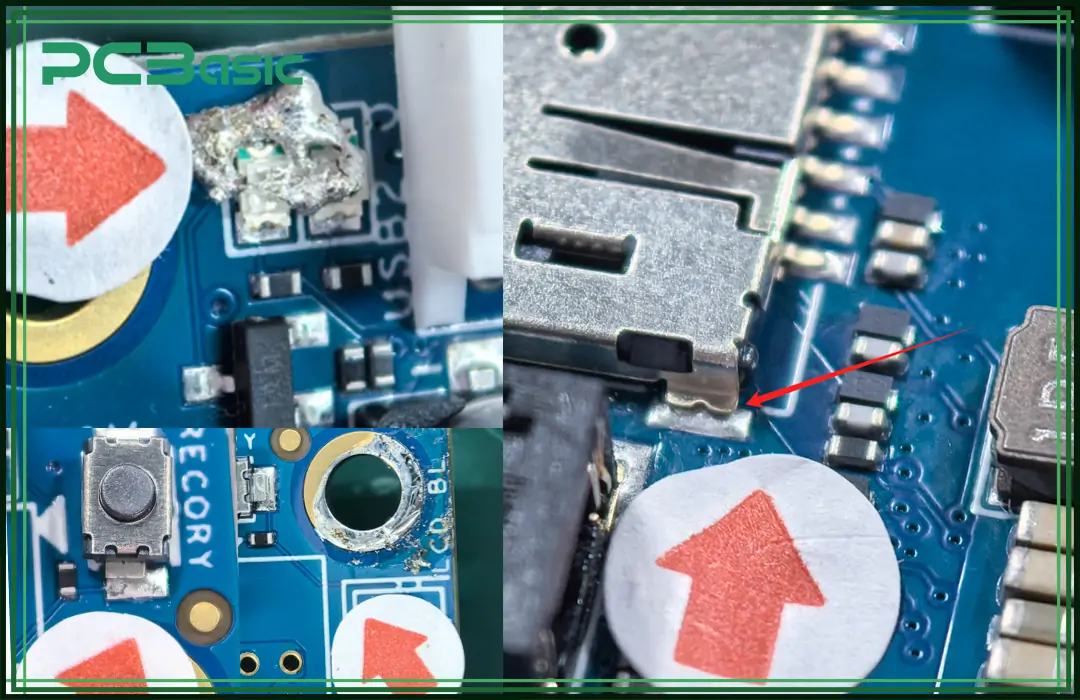
Even though reflow soldering is widely used, it is often troubled by many defects.
Cold solder joints are made when the solder is not fully melted, causing weak and loose links.
Blowholes or empty spots are gas bubbles that make the joints weak, often caused by low flux or uneven heat.
Less solder is seen when not enough paste is used or when the solder does not flow well while heating.
Sticky flux, if not cleaned, can cause rust and part failures.
Solder bridges, which are wrong links between pads, are caused by too much solder paste or badly placed parts.
Fixes include keeping steady oven heat, using the right paste, putting it properly, along with changing the reflow heat steps.
Many reflow soldering problems can be prevented by proper PCB design. This means using the right pad sizes, placing parts carefully, adding heat control features like thermal vias, along with choosing surface-mount parts instead of through-hole ones to make the reflow steps easier.
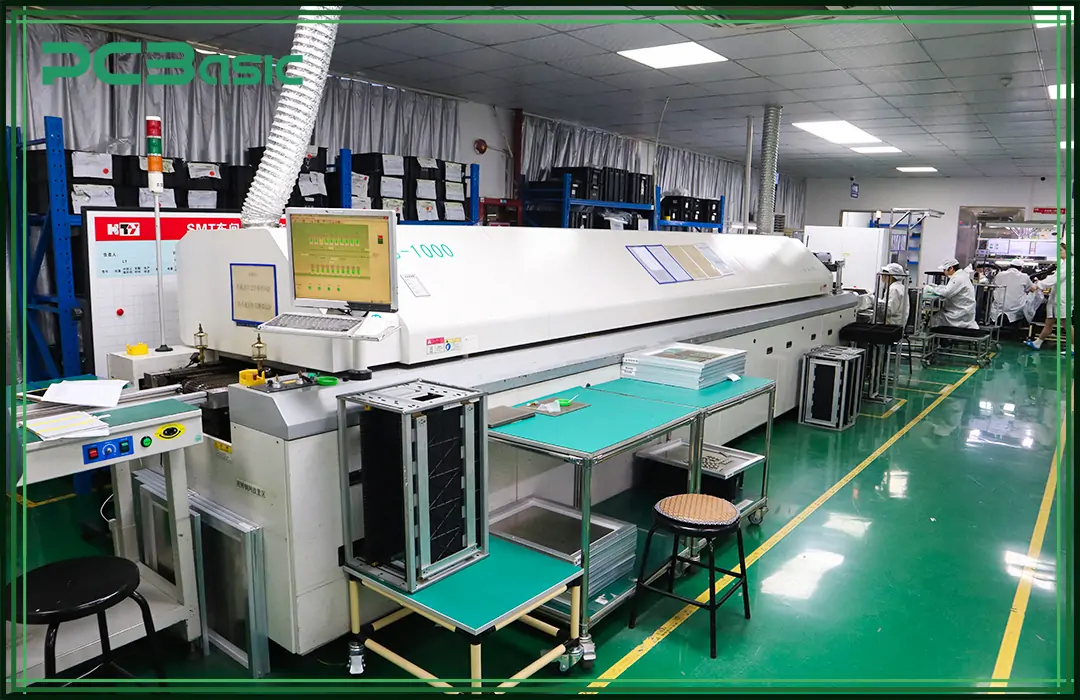

Keeping and setting your reflow oven is needed for steady work. Regular checks and changes to the heat steps and belt speeds must be done to stop problems, as well as give even heating and avoid heat changes that may cause cold solder joints.
The right solder paste and its correct use are important to stop common soldering issues. Things to check are the alloy type, the particle size, the flux strength, as well as the paste’s shelf life. Good use methods like stencil printing or paste dropping help stop problems like less solder and solder bridges.
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) and X-Ray checks are used for finding problems like cold solder joints and blowholes. Manual checking is also done along with these tools to make sure no clear problems are missed.
Finding the main causes of defects and changing the reflow steps and cleaning methods are key steps in fixing reflow soldering problems, along with helping to make the PCBs better and more trusted.
At the end of this article, reflow soldering is seen as a very important method in the PCB assembly domain that needs a careful focus on small details to lower defects and make the product more trusted by users.
Even with its hard parts, full control of the reflow soldering steps gives big rewards, making sure strong and high-quality PCBs are made that can work well in tough electronic uses. By fully knowing each step of the process—preheat, reflow, along with cooling—and by using strict checks and rules, the makers can greatly cut down common issues like cold solder joints, blowholes, as well as sticky flux.
Also, smart PCB design and best use of materials, including the careful picking and placing of solder paste, are very important for doing well in the reflow soldering process.
Regular care and setting of the reflow ovens, along with strong checking methods, help keep high-quality levels. In the end, by always improving and following the best steps, the makers can keep the PCB's strength and full working and meet the fast-growing needs of modern electronic tools.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
