Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > Motherboard vs Circuit Board: A Comprehensive Guide to Their Differences
Do you want to know the difference between a circuit board and a motherboard? It is helpful for anyone who considers themselves a technology lover or technology professional. While they might be thought to be of the same type, these are as similar as two variants but entirely different for use in electronic devices.
On comparing printed circuit board with motherboard, it is important to note that the motherboard is known as the basic structure part of the computer. On the other hand, printed circuit boards (PCBs) can be used in simple and complex designs for any electronic device, depending on their usefulness. This guide will give you a detailed contrast between circuit board and motherboard (PCB vs motherboard), key functional differences, and uses of a circuit board and/or motherboards to cater to present day technological needs.

When the term PCB is used, potential electrician must understand that all motherboards are PCBs, but not all PCBs are motherboard design because there are differences in their design, levels of complication, and functionality. Therefore, the motherboard is a computer’s central communications backbone connectivity point to work smoothly by connecting hardware components in a computer or other electronic systems.
There are copper layers in the motherboard with the intention of creating proper conduction and supply of electricity. Control connections that are normally put on expansion slots include Wi-Fi, Ethernet, and USB. Okay, so motherboard is a kind of pcb motherboard that is designated for computer systems. Now by understanding both these concepts you are able to know difference between pcb and motherboard.

Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is the pcb assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB Assembly Services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB Assembly Manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB Prototype Factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
Circuit boards are mechanical bases that hold and connect the components with electricity in everyday electronic devices and components. Simply, a circuit board mechanically supports and electrically connects electronic components. This way, a complete structure of electronic devices or hardware, Batteries, lights, buzzers, motors, resistors, potentiometers, and switches operates.
An important thing is that circuit boards come in multiple types to fit into different respective devices. That is:
· Breadboard
· Strip Board
· Printed Circuit Board

A breadboard is a known circuit board type due to its prototyping nature. As they do not need to solder any components, students and DIYers can use it in experimentation. Therefore, all the elements in a breadboard circuit can be reused in other projects, making it cost-effective.
The specifications of different breadboards may vary, but the design always remains the same. The breadboard layout includes two areas: terminal strips and bus strips.
0.1-inch rectangular grid holes characterize stripboards that are generally used in the UK. There are parallel strips of copper on one side of the Stripboard. Due to which you can use it for prototyping and producing functional circuit boards. One of the common uses of Stripboards is in building small circuits. But it can adapt more holes for big or complex projects.
PCB stands for printed circuit board, which is common due to its advanced and flexible use. Its accommodating nature, design flexibility, and ease of use make it vital for electrical engineers, manufacturers, and hobbyists. There are 1000s of PCB design software that are used for schematic design. In this way engineers connect copper tracks etched on a board.
Nowadays, PCBs are the most widely used in every electronic device due to their ability to integrate complex and simpler designs. There are different types of PCBs according to assemblies PCB motherboard device requirements:
Single Layer PCBs
This PCB is called single-sided as it possesses only one layer of the base material of the substrate coated on the board. This means that all the electrical components will have solder pins that shall only be soldered on that surface. Single-sided are specifically designed for small electronics and are equally applicable for prototyping. Owing to their relatively low costs, they are among the popular circuit boards for use in student and hobby projects.
Double-Sided PCBs

A double-sided PCB is built by having two copper layers on two surfaces of one dielectric layer. There is an interconnection between two sides of a board through holes that are drilled into the board. Interconnection components on double-sided PCBs include through-hole and surface-mount interconnections. Through-hole means the component's lead is passed through a hole and solders the end to the surface. Indeed, the surface mount includes fixing the component and soldering on the board. This PCB is the most consumed and used by students and hobbyists working on their projects.
Rigid PCBs
A rigid PCB is a circuit board containing fiberglass. Thus, the incorporation of fiberglass prevents the PCB from twisting or getting distorted whenever it is applied. Full-featured PCBs are primarily applied in circuits that come in contact with ordinary use or have moving parts nearby.
Flex PCBs
Flex PCBs use flexible board or plastic substrate material can be used as connectors, full circuits assembled with components. Due to adaptation nature it is best where flexibility is required in a certain device.

Rigid-Flex PCBs
Rigid-flex PCB from a systematic point of view may not have the flex part laminated permanently; it could be soldered or connected with it through a connector like the 3 different types of rigid-flex PCB image below shows. Therefore, A rigid-flex PCB is one where a rigid board is connected to a flexible board to provide the full circuit.
A motherboard is the main board used in smart devices such as computers, servers, and mobiles. The key role of the motherboard is to provide a base structure for the device. The computer's largest t PCB connects and allows communication between key components like the CPU (Central Processing Unit), RAM (Random Access Memory), storage drives, and various peripheral devices.
Motherboards have external slots, sockets, and ports to connect with external devices such as graphics cards, memory modules, and processors. The earliest computer designed by IBM had a very simple motherboard compatible with every type of CPU and memory. Compaq replaced IBM's design with Intel, which dominated the market in the 1990s for personal computer motherboards.
The most common and main types of motherboards are
1. ATX (Advanced Technology eXtended): The ATX is, undoubtedly, the most popular form factor and is used in standard desktop personal computers. They afford large areas for components, usually several expansion slots, and are very good for general and gaming use.
2. Micro-ATX: For users with low budget and fewer expansion slots requirements, Micro-ATX motherboards are designed. This system is a smaller, more compact version of ATX concerning space.
3. Mini-ITX: For small size and portable devices Mini-ITX motherboards with ultra-compact size are suitable. It has limited expansion options that are ideal for lightweight setups.
4. E-ATX (Extended ATX): Heavy setup requires systems such as E-ATX motherboards specially designed for gaming and other heavy tools. It offers wide features for additional PCIe slots and support for multiple GPUs.
5. Proprietary Motherboards: For more custom designs and requirements, there is a proprietary motherboard. They provide custom facilities for laptops and other server devices to meet unique hardware requirements and space constraints.
Below is a detailed comparison of the motherboard vs circuit board based on key factors:
|
Feature |
Motherboard |
Circuit Board |
|
Functions |
A central hub for connecting major hardware components. |
Provides electrical connections for various electronic devices. |
|
Complexity |
It is highly complex, with integrated chipsets and slots. |
It can range from simple single-layer boards to complex multi-layers. |
|
Purpose |
Designed to connect CPUs, GPUs, and other peripherals. |
Acts as a general support for any circuit-based application. |
|
Integration |
Includes sockets, ports, and embedded systems. |
Typically lacks the high level of integration seen in motherboards. |
|
Components |
Includes processors, memory slots, and chipsets. |
Houses resistors, capacitors, and simple ICs. |
|
Size |
Larger and tailored for specific hardware requirements. |
Varies based on device and application needs. |
|
Costs |
It is more expensive due to its advanced features. |
Lower cost for basic PCB designs. |
|
Manufacturing |
Requires precision and advanced manufacturing techniques. |
It can be manufactured using simpler methods for basic boards. |
|
Applications |
Computers, servers, and gaming consoles. |
Broad applications in electronics like TVs, phones, and toys. |
|
Design |
Focused on communication and hardware compatibility. |
Focused on electrical connection efficiency. |
|
Durability |
Built to last with heat management systems. |
Durability depends on materials and usage conditions. |
|
Heat Management |
It uses heat sinks and fans to prevent overheating. |
Limited heat management features. |
|
Scalability |
Supports upgrades like additional RAM or GPUs. |
Rarely designed for scalability. |
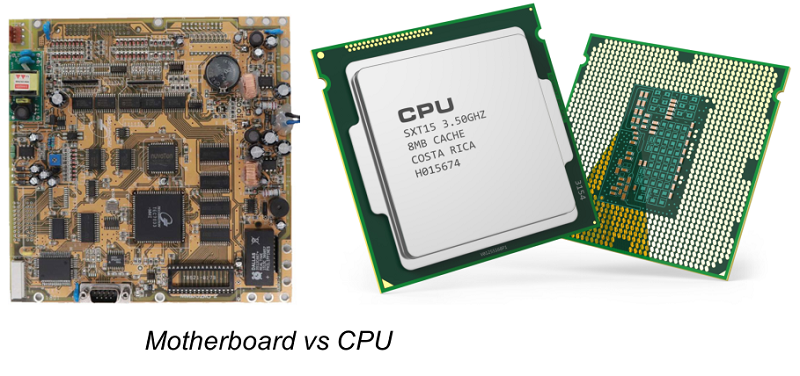
Both motherboard and CPU (Central Processing Unit) are two distinct components that work together but differently. The motherboard is a central part of the computer that connects all parts of the parts the systems, such as CPU, RAM, storage, and peripherals, to work collectively. At the same time, the CPU works as a "brain" of the computer to perform all calculations, logic processing, and task execution. So motherboard provides infrastructure and slots to connect these components while the CPU processes data for the system's operation.
The terms "processor" and CPU are used interchangeably. The processor is the motherboard, an independent chip that slots into the motherboard to perform tasks and data processing; on the other hand motherboard provides a structural base to a computer or system.
Understanding the circuit board vs motherboard/PCB vs motherboard is essential for grasping the electronics' foundation and working concepts. For those looking to answer whether a motherboard is a PCB? This guide provides a clear answer to printed circuit board vs motherboard.
In short, a circuit board is a broader term that is more generalized, while a motherboard is a specialized type of PCB that serves as the central hub of computing systems.
By understanding this key difference between circuit board vs motherboard/PCB vs motherboard now, you can better understand the complexity of electronic systems.
A PCB (Printed Circuit Board) on a motherboard is a design of electrical pathways. Each device offers different purposes and has distinct roles in the functioning of electronic systems.
The term "motherboard" reflects its role as the central board that manages connectivity and mutual functionality of all components in a system. It is a central component of electronics such as computers that can be extended by plugging other circuit boards into it.
A motherboard PCB is a basic component of a computer that connects the processor, memory, storage, and other peripherals. It also ensures seamless communication between all internal and external parts.
As we discussed, the motherboard is the backbone of a computer and other electronic devices. So, if it is damaged, the device's functionality fully stops, and the system cannot perform any operation.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
