Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > How to Use a Voltmeter?
A voltmeter is a key electronic device that is found in the electronic industry. It plays an important role in the maintenance and diagnosis of electronic equipment. A voltmeter is an essential tool for electrical enthusiasts. It measures the voltage at different points of the circuit to ensure an accurate supply of voltage at each stage of the circuit. A voltmeter is an electronic device that is used for measuring the potential difference between two electrical points in an electrical circuit.
It is important to diagnose and identify the specific part of a circuit that is malfunctioning and not working as expected. That’s where it comes to the need for a voltmeter to check the voltage levels at different points and see at which specific point the voltage level is not as it should be. This article will cover an in-depth guide to how to use a voltmeter, how to read a voltmeter, and how a voltmeter works.

A voltmeter is a measuring instrument that is primarily used
for the measurement of voltage in electrical circuits. Voltmeters come in
various types, such as DC Voltmeter, AC Voltmeter, Analog Voltmeter, Digital
Voltmeter, and Multimeter. A typical voltmeter has two leads or probes i.e.
positive and negative leads. When measuring a voltage across any input/output
or a specific component, the probes are always connected in parallel to check
the voltage level across that specific component. The voltmeter probes are
connected in parallel mainly because the voltage is the same in a parallel
connection.
For example, when a 5-volt fully charged battery voltage is measured using a voltmeter across its positive and negative terminals, it shows 5V on the voltmeter.
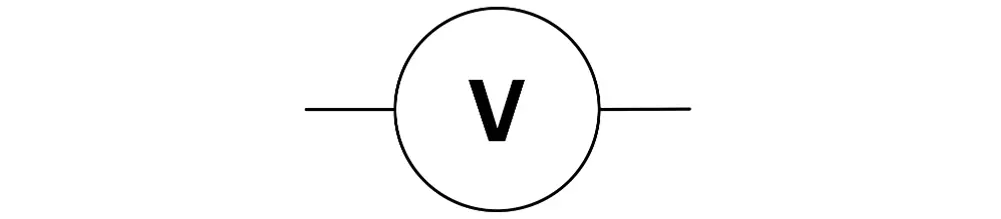
A voltmeter is represented by the letter "V" in electrical circuits, as shown in the figure. A typical voltmeter has a 0.1 volt least count. This indicates the precision of a voltmeter. In other words, a typical voltmeter can measure a minimum of 0.1 Volts.
Have you ever wondered, how a voltmeter measures the voltage in circuits? You have come to the right place. The voltmeter uses a very high resistance typically in the range of mega ohms (MΩ). When the voltmeter is connected in parallel with the circuit to measure the voltage, it draws a very tiny current due to high resistance. This prevents the voltmeter from affecting the voltage that is being measured.
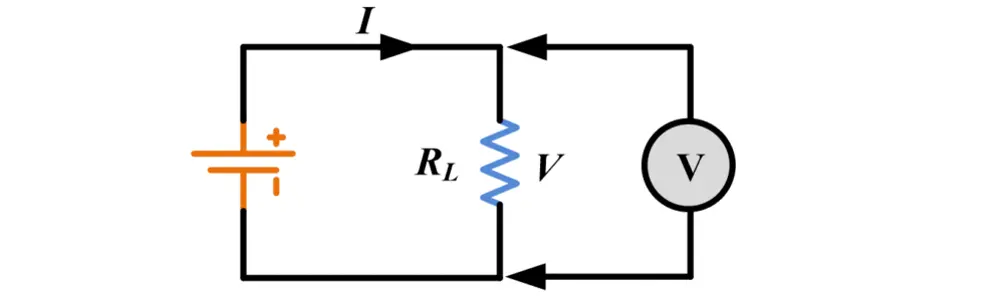
However, an analog voltmeter has a moving coil galvanometer. A series resistor is added to a galvanometer. When the current is applied, the coil of the galvanometer produces a magnetic field and forces the coil to rotate. When the coil rotates, it is proportional to the current. This current is proportional to the applied voltage that is shown on the pointer scale of the analog voltmeter.

When measuring a voltage in an electronic circuit, it is important to accurately use the voltmeter. Any mishandling can lead to incorrect readings of voltage. To have an accurate reading of voltage on a voltmeter use the following simple steps.
Step 1. Set up your device
Nowadays, mostly, a multimeter is used. Therefore, first, set your device to measure voltage. If measuring DC voltage, set the knob to (V– or VDC). If measuring the AC voltage, set the knob to (V ~, VAC).
Step 2. Set Range of Voltmeter
Most voltmeters have different voltage ranges e.g. millivolts and volts. Set your voltmeter higher than the voltage expected. You can also choose the auto setting if your voltmeter has one.
Step 3. Connect the voltmeter probes
Each voltmeter comes with two probes or leads i.e. positive (red lead) and negative (black lead). Insert the red lead into the hole labeled as (V) and insert the black lead into the hole labeled as (COM).
Step 4. Hold the probes and measure the voltage
Hold the voltmeter leads carefully, connect the black lead with the negative side of the circuit and connect the red lead with the positive side of the circuit. This will show the measured voltage on the screen of the voltmeter. Make sure not to touch the leads with each other when connected in a circuit.
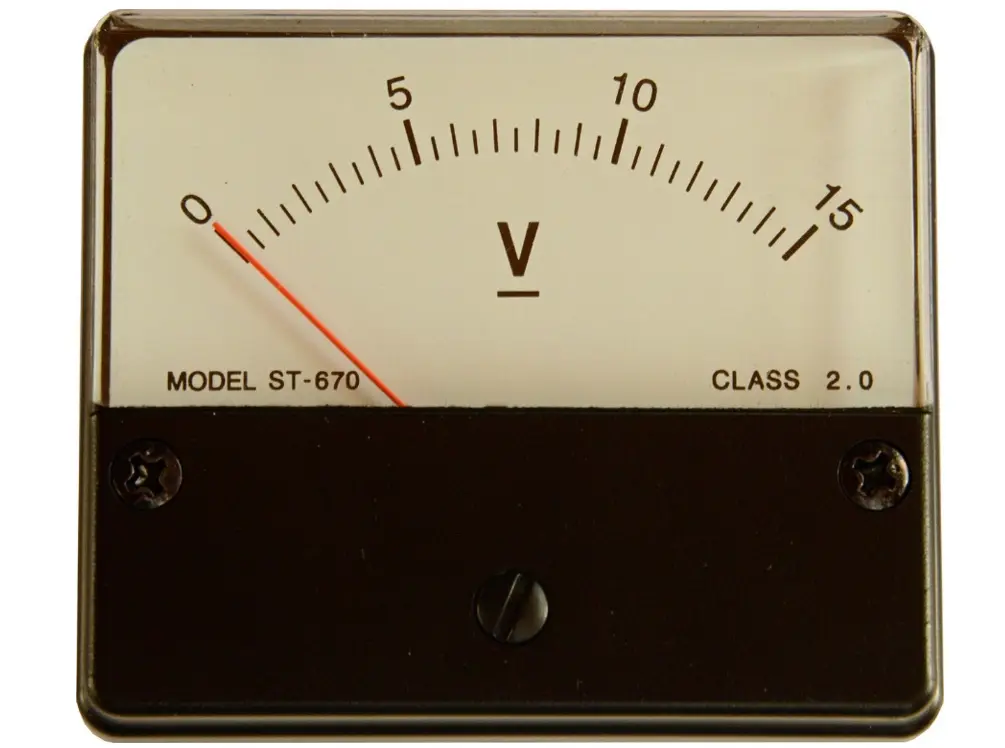
There are two types of voltmeters, i.e. analog voltmeter and digital voltmeters. Therefore, it is important to understand how to read and operate both analog and digital voltmeters.
The analog voltmeter has mainly two parts: a needle and a scale that displays voltage values. To read the voltage on an analog voltmeter, observe where the needle stopped on the scale. For example, the needle stopped at exactly halfway between 7 and 8. It means the measured voltage is 7.5 volts.
Digital voltmeters are easy to operate and display more precise values of voltages. When the digital voltmeter leads are connected across the component properly, it measures the precise voltage and displays the digital values of voltage on the voltmeter screen. To read the voltage on digital voltmeters, it is important to know its various buttons and symbols. Some of the symbols are:
|
Symbol |
Function |
|
ACV or V ~ |
Voltmeter in this mode measures the AC voltage |
|
DCV or V– |
The voltmeter in this mode measures the DC voltage. |
|
Auto-ranging |
When set in ‘auto range’ mode, the voltmeter automatically selects the appropriate range. |
|
Hold button |
When the hold button is pressed on the voltmeter, it holds the voltage reading. |
A voltmeter measures only voltage. Whereas, a multimeter can measure voltage, current, and resistance.
No. Voltmeter cannot measure current. It only measures voltage.
The voltmeter leads are connected in parallel to a circuit to measure voltage.
Voltmeter is a device to measure voltage. Whereas an ammeter is a device that measures the current. A voltmeter is connected in parallel in a circuit and an ammeter is connected in a series in a circuit.
In conclusion, voltmeters are essential parts of the electronic industry and electrical maintenance. Understanding voltmeters, how they work, and how to read voltmeter readings is essential for electrical engineers and technicians to accurately measure voltage. Voltmeters have diverse applications in the home appliances industry and large electronics industry. Understanding its use and operations is important for everyone associated with the electronic industry.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
